A) increase and potential output to increase.
B) decrease and potential output to decrease.
C) increase and potential output to remain stable.
D) decrease and potential output to remain stable.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-6 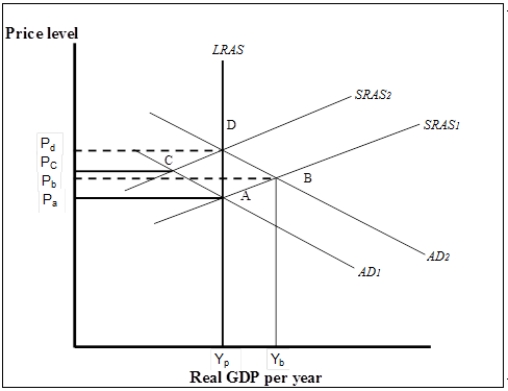 -Refer to Figure 7-6. Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at B. If policy-makers decide to intervene to close the gap, which of the following can it do?
-Refer to Figure 7-6. Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at B. If policy-makers decide to intervene to close the gap, which of the following can it do?
A) Decrease personal income taxes.
B) Increase government welfare spending.
C) Decrease the level of government purchases of goods and services.
D) Institute investment tax credits to encourage business investment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true of the economy in the long run? In the long run, I. real GDP eventually moves to potential output because all wages and prices are assumed to be flexible. II. the economy can achieve its natural level of employment and potential output at any price level. III. there is no cyclical unemployment.
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-6  -Refer to Figure 7-6. Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at B. Policy makers could either pursue a stabilization policy or allow the economy to adjust on its own. What is the difference between the two policy choices, if any?
-Refer to Figure 7-6. Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at B. Policy makers could either pursue a stabilization policy or allow the economy to adjust on its own. What is the difference between the two policy choices, if any?
A) A stabilization policy would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pa while a nonintervention policy would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pd.
B) A stabilization policy would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pd while a nonintervention policy would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pa.
C) Both policies would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pa.
D) Both policies would return real GDP to its potential at a price level of Pd.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All other things unchanged, a higher exchange rate
A) reduces net exports and aggregate demand.
B) reduces net exports and increases aggregate demand.
C) increases net exports and aggregate demand.
D) increases net exports and reduces aggregate demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical at the level of real output that corresponds to the natural rate of employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following occurs if an economy experiences an inflationary gap? I. Actual real GDP is less than potential output. II. Actual real GDP is greater than potential output. III. Unemployment is less than the natural rate. IV. Unemployment is greater than the natural rate.
A) I and III
B) I and IV
C) II and III
D) II and IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-1 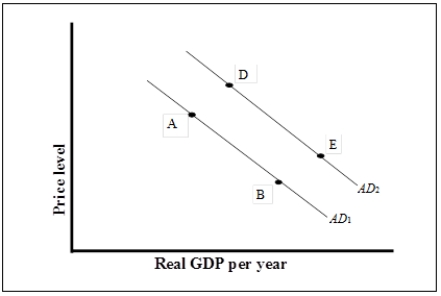 -Refer to Figure 7-1. What could have caused the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right from AD1 to AD2?
-Refer to Figure 7-1. What could have caused the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right from AD1 to AD2?
A) An increase in exports
B) An increase in imports
C) A decrease in defense spending
D) An increase in the domestic price level
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Inflationary and recessionary gaps are always eliminated automatically through changes in aggregate demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All other things unchanged, an increase in government spending will
A) shift the aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.
C) make the aggregate demand curve flatter.
D) make the aggregate demand curve steeper.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-3 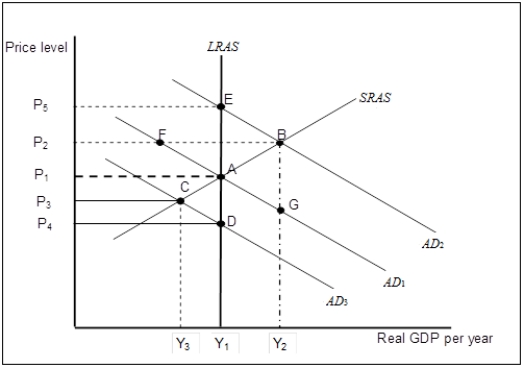 -Refer to Figure 7-3. Suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A. Now suppose net exports increase. What happens in the long-run, all other things unchanged?
-Refer to Figure 7-3. Suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A. Now suppose net exports increase. What happens in the long-run, all other things unchanged?
A) The economy will return to its initial equilibrium at point A.
B) Equilibrium will be re-established at point B with a higher potential output.
C) Equilibrium will be re-established at point E at a higher price level.
D) The aggregate demand curve will shift back to AD1.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Taking no action and allowing an economy to adjust by itself is called a nonintervention policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-1  -Refer to Figure 7-1. What could have caused a movement from point D to point A?
-Refer to Figure 7-1. What could have caused a movement from point D to point A?
A) An increase in the economy's general price level
B) A decrease in investment demand due to lower expected sales
C) A decrease in capital gains taxes
D) An increase in money supply that lowers interest rate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-2 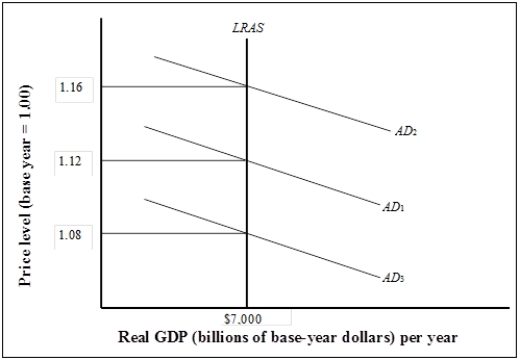 -Refer to Figure 7-2. If the real GDP is $7,000 billion and the implicit price deflator is 1.12, what is the value of nominal GDP?
-Refer to Figure 7-2. If the real GDP is $7,000 billion and the implicit price deflator is 1.12, what is the value of nominal GDP?
A) $6,250 billion
B) $7,840 billion
C) $9,000 billion
D) cannot be determined from the information given
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-5 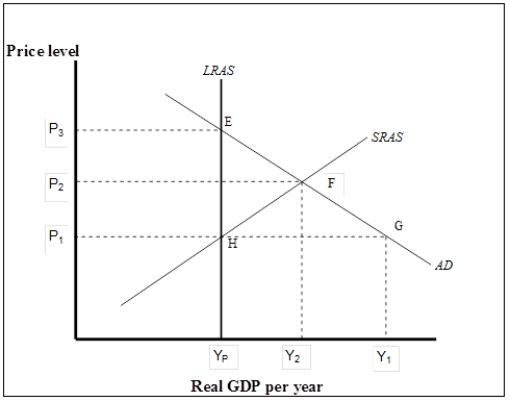 -Refer to Figure 7-5. What are the prevailing price level and the output level in the economy?
-Refer to Figure 7-5. What are the prevailing price level and the output level in the economy?
A) Price level = P1; real GDP = Yp
B) Price level = P1; real GDP = Y1
C) Price level = P2; real GDP = Y2
D) Price level = P3; real GDP = Yp
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Public policy to eliminate inflationary or recessionary gaps is called stabilization policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in aggregate demand, all other things unchanged, in the long run will generate
A) an increase in potential output and no change in the price level.
B) a decrease in potential output and no change in the price level.
C) no change in potential output and an increase in the price level.
D) no change in potential output and a decrease in the price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An economy adjusts on its own to close an inflationary gap because there is
A) pressure on nominal wages to fall and this shifts the SRAS curve rightward.
B) pressure on nominal wages to rise and this shifts the SRAS curve rightward.
C) pressure on nominal wages to fall and this shifts the SRAS curve leftward.
D) pressure on nominal wages to rise and this shifts the SRAS curve leftward.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose net exports decreases by $100 million due to a slump in foreign economies. If the the value of the multiplier is 2, what happens to the domestic aggregate demand curve?
A) Since less will be produced, the aggregate demand does not shift. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the left by $100 million at each price level.
B) It shifts to the left by $50 million at each price level.
C) It shifts to the left by $100 million at each price level.
D) It shifts to the left by $200 million at each price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an explanation for price stickiness? I. There are adjustment costs associated with changing prices such as the cost of printing new price lists. II. Worker unions may forbid firms from raising prices for fear that workers may be laid off if demand for output falls. III. Firms may have explicit long-term contracts to sell their products to other firms at specified prices.
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 166
Related Exams