A) increase interest rates and increase exchange rates.
B) increase interest rates and decrease exchange rates.
C) decrease interest rates and increase exchange rates.
D) decrease interest rates and decrease exchange rates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the Fed sells bonds in the open market, we can expect
A) investment and net exports to rise.
B) investment to rise and net exports to fall.
C) investment to fall and net exports to rise.
D) investment and net exports to fall.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The congressional act passed in 1946 that contained the first official statement of goals for economic performance in the United States was the
A) Federal Reserve Act.
B) Gramm-Rudman Act.
C) Employment Act.
D) Humphrey-Hawkins Act.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 11-4 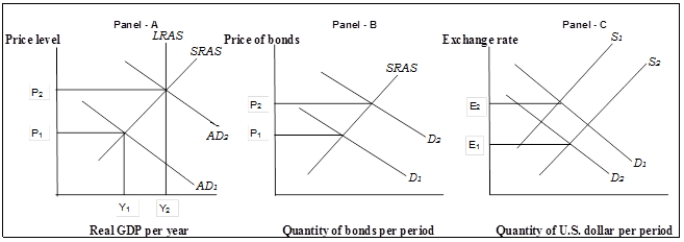 -Refer to Figure 11-4. If the Fed acts to close the output gap in Panel (a) , it would
-Refer to Figure 11-4. If the Fed acts to close the output gap in Panel (a) , it would
A) sell government bonds which will lead to the shift in demand for bonds in Panel (b) . This action will raise the price of bonds and lower the interest rate.
B) buy government bonds which will lead to the shift in demand for bonds in Panel (b) . This action will raise the price of bonds and increase the interest rate.
C) buy government bonds which will lead to the shift in demand for bonds in Panel (b) . This action will raise the price of bonds and lower the interest rate.
D) sell government bonds which will lead to the shift in demand for bonds in Panel (b) . This action will raise the price of bonds and increase the interest rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The equation of exchange always holds because
A) the quantity of money is determined by the amount of spending on goods and services.
B) the quantity of money dictates the size of nominal GDP, since money is a social usage.
C) the number of times money is spent to obtain goods and services measures total spending on GDP.
D) MV measures total spending on GDP and PY also measures of total spending on GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 11-6 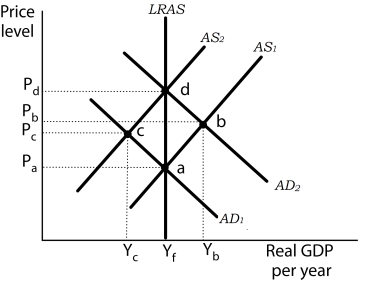 -Refer to Figure 11-6. If rational expectations exist and the economy is initially operating at
Point d. If the Fed undertakes contractionary monetary policy the economy will
-Refer to Figure 11-6. If rational expectations exist and the economy is initially operating at
Point d. If the Fed undertakes contractionary monetary policy the economy will
A) spend some time at c with a recessionary gap.
B) spend no time at c and move directly to b.
C) bypass c and move to a, because the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left.
D) bypass c and move to a, because the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts immediately to the right and the economy moves down the long-run aggregate supply curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the velocity of money is constant, then a 2% increase in the money supply
A) must be the result of a 2% increase in the price level.
B) would change nominal GDP by a smaller percentage.
C) would change nominal GDP by an equal percentage.
D) would change nominal GDP by a larger percentage.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If velocity is constant, which of the following results flow from the quantity equation?
A) Nominal GDP could change only if there were a change in the money supply.
B) In the short run, nominal GDP could change only if there were a change in the money supply and in the long run, nominal GDP could change only if there were a change in the money supply.
C) In the short run, nominal GDP could change only if there were a change in the money supply but in the long run, nominal GDP is affected by changes in any component of GDP.
D) In the short run, nominal GDP is affected by changes in any component of GDP but in the long run, nominal GDP could change only if there were a change in the money supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The major tools of monetary policy available to the Federal Reserve System are
A) reserve requirements, margin regulations, and moral suasion.
B) reserve requirements, open-market operations, and the discount rate.
C) open-market operations, margin regulations, and moral suasion.
D) the discount rate, margin regulations, and moral suasion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the economy experiences a recessionary gap. Expansionary monetary policy will
A) increase real GDP and increase the price level.
B) increase real GDP and decrease the price level.
C) decrease real GDP and increase the price level.
D) decrease real GDP and decrease the price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 11-1 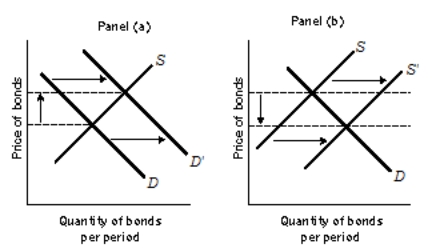 -Refer to Figure 11-1. Suppose the Fed takes action that shifts the demand curve from D to D′, as illustrated in Panel (a) . As a result, the interest rate
-Refer to Figure 11-1. Suppose the Fed takes action that shifts the demand curve from D to D′, as illustrated in Panel (a) . As a result, the interest rate
A) increases and investment increases.
B) increases and investment decreases.
C) decreases and investment increases.
D) decreases and investment decreases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 11-4  -Refer to Figure 11-4. The shift in the demand for bonds from D1 to D2, in Panel (b) will result in a
-Refer to Figure 11-4. The shift in the demand for bonds from D1 to D2, in Panel (b) will result in a
A) lower interest rate and no change in investment.
B) higher interest rate and lower investment.
C) lower interest rate and higher investment.
D) higher interest rate and higher investment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If inflation is a threat, then the Fed will be expected to engage in
A) expansionary monetary policy.
B) contractionary monetary policy.
C) policies to increase the money supply.
D) policies to lower the rate of interest.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All other things unchanged, we expect that an increase in interest rates will tend to
A) increase the quantity of money demanded and increase velocity.
B) increase the quantity of money demanded and reduce velocity.
C) reduce the quantity of money demanded and increase velocity.
D) reduce the quantity of money demanded and reduce velocity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 11-4  -Refer to Figure 11-4. If a nonintervention policy were adopted in Panel (a) ,
-Refer to Figure 11-4. If a nonintervention policy were adopted in Panel (a) ,
A) the aggregate demand curve would have eventually shifted as shown.
B) the short-run aggregate supply curve would have eventually shifted to the left and restored full employment.
C) the short-run aggregate supply curve would have eventually shifted to the right and restored full employment.
D) both the aggregate demand curve and the short-run aggregate supply curve would have eventually shifted to the left.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In December 2008, the Federal Reserve announced that it would take extraordinary measures to address the financial crisis in the economy. These measures include all of the following except
A) buying mortgage-backed securities.
B) buying long-term Treasury bills.
C) creating other new credit facilities to make credit more easily available to households and small businesses.
D) lowering the reserve requirement to encourage banks to create loans.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All other things unchanged, we expect that a reduction in interest rates will tend to
A) increase the quantity of money demanded and increase velocity.
B) increase the quantity of money demanded and reduce velocity.
C) reduce the quantity of money demanded and increase velocity.
D) reduce the quantity of money demanded and reduce velocity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the equation of exchange, the variable whose value must be computed from the other variables is the
A) price level.
B) quantity of output.
C) quantity of money.
D) velocity of money.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Changing the required reserve ratio is an often-used monetary tool to influence the federal funds rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Adjusting monetary growth based on previous changes in nominal GDP
A) is relatively easy for the Fed to undertake because the implementation lag is quitelong.
B) could be destabilizing because of the uncertainty of the length of impact lags.
C) is an effective policy because it allows the Fed to influence future macroeconomic performance.
D) raises the price level proportionately.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 176
Related Exams