A) Elastic portion of its demand curve because it can increase total revenue and reduce total costs by lowering the price.
B) Inelastic portion of its demand curve because it can increase total revenue and reduce total costs by increasing the price.
C) Inelastic portion of its demand curve because it can increase total revenue by more than it increases total cost by reducing the price.
D) Segment of its demand curve where the price elasticity of demand is greater than 1.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The essence of market power is the ability to alter the price of a product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following prohibits exclusive dealing?
A) The Sherman Act.
B) The Clayton Act.
C) The Federal Trade Commission Act.
D) Case decisions, such as those for AT&T and IBM.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
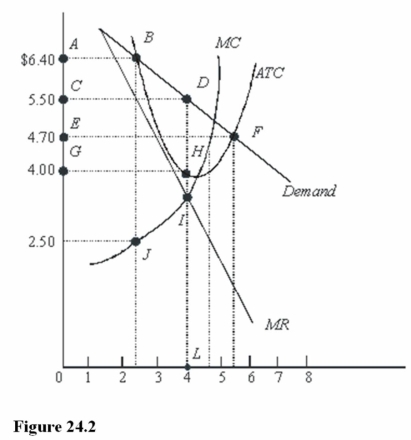 In Figure 24.2, the profit-maximizing level of output is
In Figure 24.2, the profit-maximizing level of output is
A) Between 2 and 3 units.
B) Between 4 and 5 units.
C) 4 units.
D) Between 5 and 6 units.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The World View article titled "Foxy Soviets Pelt the West: Sable Monopoly Traps Hard Currency, Coats Capitalists" provides evidence that the Soviets experienced
A) Market power.
B) Economies of scale.
C) Barriers to entry.
D) Price discrimination.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm can change market prices by altering its output, then it
A) Has market power.
B) Faces a flat demand curve.
C) Is a price taker.
D) Engages in marginal cost pricing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Economies of scale involve a reduction in minimum average costs as a result of an increase in the size of plants and equipment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There is an inherent tendency of a monopoly industry to
A) Lower prices and increase output.
B) Inhibit productivity advances.
C) Increase innovation.
D) Use minimum average cost pricing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
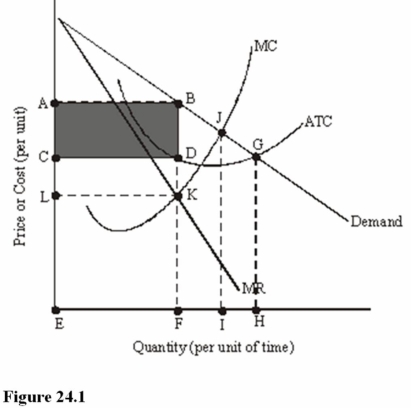 In Figure 24.1, total revenue is represented by the area
In Figure 24.1, total revenue is represented by the area
A) ABFE.
B) CDFE.
C) ABGHE.
D) ABDC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
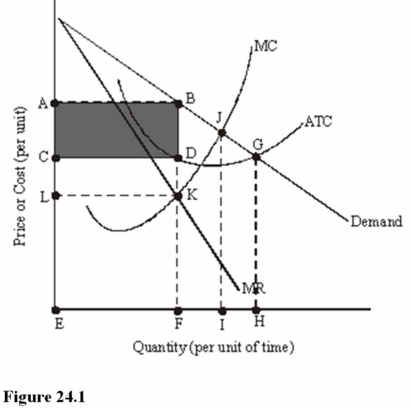 The shaded area in Figure 24.1 represents
The shaded area in Figure 24.1 represents
A) Total revenue.
B) Total cost.
C) Total profit.
D) Total loss.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A multi-plant monopolist produces more than if each of its plants were a separate firm in a competitive market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an accurate argument in support of market power?
A) It restricts output and raises prices, contributing to more efficient use of resources.
B) It contributes to efficient production when there are diseconomies of scale.
C) It provides the economic profit necessary for survival and efficient production in a market.
D) It provides greater ability to fund research and development.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If tourists are charged a much higher price than the natives of a country for exactly the same item, what kind of pricing is involved?
A) Monopoly pricing.
B) Price discrimination.
C) Competitive pricing.
D) MC = MR pricing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal revenue of a monopolist
A) Is equal to price at all output levels.
B) Is above a downward-sloping demand curve.
C) Is positive up to the rate of output that maximizes total revenue.
D) Is negative up to the rate of output that maximizes total revenue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Monopolists have an advantage over competitive markets in receiving the full benefit of research and development efforts.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
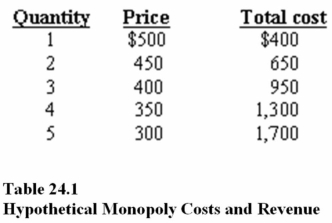 In Table 24.1, according to the profit maximization rule, at the profit-maximizing level of output marginal, cost is
In Table 24.1, according to the profit maximization rule, at the profit-maximizing level of output marginal, cost is
A) $200.
B) $250.
C) $300.
D) $350.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Price discrimination allows a producer to
A) Reap the highest possible average price for the quantity supplied.
B) Increase the elasticity of consumer demand.
C) Minimize marginal costs.
D) Decrease total costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When markets are contestable, a monopoly firm must behave as if it had competitors, even though the market structure is monopolistic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following prohibits price discrimination, certain types of mergers, and interlocking boards of directors among competing companies?
A) The Sherman Act.
B) The Clayton Act.
C) The Federal Trade Commission Act.
D) The Full Employment and Balanced Growth Act.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
For a monopolist, profit is maximized at the level of output where MR = MC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 151
Related Exams