A) contract its muscular walls to expel urine from the cortex.
B) determine the final volume and concentration of urine.
C) drain blood from the kidney and deliver it to the renal vein.
D) transport resorbed water back into the cardiovascular system.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the following, the only epithelial type that does not line the urethra is
A) simple squamous.
B) pseudostratified columnar.
C) stratified squamous.
D) stratified columnar.
E) transitional.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
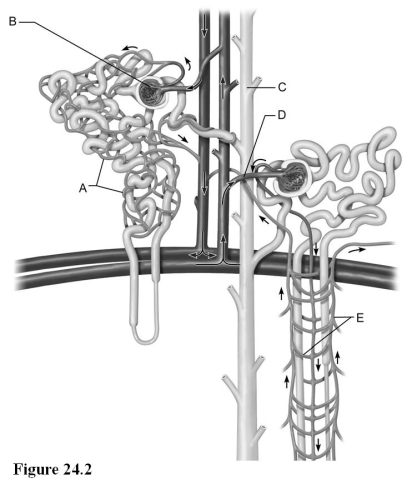 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
-Identify the letter that indicates the region of the nephron with receptors sensitive to antidiuretic hormone (ADH) .
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
-Identify the letter that indicates the region of the nephron with receptors sensitive to antidiuretic hormone (ADH) .
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arteries that branch to form the afferent arterioles to the glomeruli are
A) segmental arteries.
B) arcuate arteries.
C) cortical radiate arteries.
D) interlobar arteries.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes does not participate in the production of urine in the kidney?
A) filtration
B) secretion
C) evaporation
D) resorption
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which segment of the nephron has a simple squamous epithelium?
A) collecting duct
B) descending limb of the nephron loop
C) distal convoluted tubule
D) proximal convoluted tubule
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How much of the fluid filtered by the kidney actually becomes urine?
A) 1%
B) 10%
C) 50%
D) 99%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The external urethral sphincter is located
A) at the external urethral orifice.
B) at the junction of the bladder wall and urethra.
C) at the ureteral orifice.
D) at the urogenital diaphragm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
85% of nephrons are described by this term that relates to their location in the kidney.
A) sinusoidal
B) trabecular
C) medullary
D) cortical
E) extrinsic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the urinary bladder is false?
A) In females, the bladder lies posterior to the uterus but anterior to the rectum.
B) The ureters attach to the bladder through oblique posterolateral orifices.
C) Two ureteral openings and the internal urethral orifice bound the trigone of the bladder.
D) When empty, the bladder lies inferior to the abdominal cavity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Venous structures of the kidney mirror those of the arterial circuit, except for the absence of segmental veins.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The ________ urethral sphincter is composed of skeletal muscle and under voluntary control.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
-Identify the letter that indicates the afferent arteriole.
Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
-Identify the letter that indicates the afferent arteriole.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mucosal folds in the bladder (rugae)
A) act to increase the surface area for absorption.
B) thicken the bladder wall so that it does not burst.
C) are not present in life, only in cadavers.
D) have the same basic function as transitional epithelium-accommodating stretch as the bladder fills.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The location and length of the urethra are two factors that contribute to the high incidence of urinary tract infections in women.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which vessels lie within the renal columns?
A) arcuate arteries
B) cortical radiate arteries
C) interlobar arteries
D) segmental arteries
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The ________ layer of the ureters propel urine to the bladder by peristalsis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Most water and solutes are resorbed from the convoluted renal tubules into the ________.
Correct Answer

verified
peritubula...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Knot of capillaries that directs blood into the efferent arteriole.
A) arcuate arteries
B) cortical radiate arteries
C) glomerulus
D) afferent arterioles
E) peritubular capillaries
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Adjacent collecting ducts join to form larger ________ that drain into the minor calyx.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 112
Related Exams