A) change in aggregate demand.
B) change in the aggregate quantity of good and services demanded.
C) determinant of aggregate demand.
D) revealed expenditure on aggregate demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions .
Exhibit: Using the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1 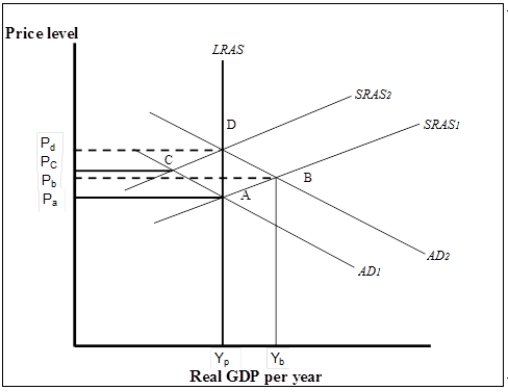 -(Exhibit: Using the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1) Suppose the economy is initially at point A. Now suppose an increase in government purchases shifts the aggregate demand curve to AD2. Which of the following statements best explains how the economy responds to restore long-run macroeconomic equilibrium?
-(Exhibit: Using the Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model 1) Suppose the economy is initially at point A. Now suppose an increase in government purchases shifts the aggregate demand curve to AD2. Which of the following statements best explains how the economy responds to restore long-run macroeconomic equilibrium?
A) The increase in the price level to Pb reduces real GDP demanded, shifting the aggregate demand curve back to AD1, returning the economy to its potential output at A.
B) Firms produce more in anticipation of future higher prices, thus shifting the SRAS curve upward until the gap is eliminated at D.
C) Firms and workers will negotiate higher nominal wages to restore lost purchasing power. This shifts the SRAS curve to the left until the gap is eliminated at D.
D) The increase in the price level to Pb decreases consumption which in turn leads firms to cut production shifting the SRAS curve to the left until the gap is eliminated at D.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the short-run, an output gap occurs because
A) there is insufficient demand for goods and services.
B) there is insufficient supply of goods and services.
C) wages and prices are fully flexible.
D) wages and some prices have not adjusted sufficiently to maintain output at its potential level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wage and price stickiness
A) gives rise to a vertical long-run aggregate supply curve.
B) gives rise to a vertical short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) creates a surplus or a shortage of real GDP.
D) prevents the economy from producing its potential level of real GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest rate effect suggests that the negative slope of the aggregate demand curve results because changes in the price level affect
A) domestic purchases of foreign goods.
B) the demand for money by households and firms.
C) the real purchasing power of household wealth.
D) the level of income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a source of wage stickiness? I. fixed wage contracts II. minimum wage laws III. workers and firms want to avoid complexity of negotiating contracts frequently
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 166 of 166
Related Exams