A) 3.7 ×10-5
B) 1.4 ×10-4
C) 5.9 × 10-4
D) 9.6 × 10-2
E) 1.8 × 103
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2.5 L flask is filled with 0.25 mol SO3,0.20 mol SO2,and 0.40 mol O2,and allowed to reach equilibrium.Assume the temperature of the mixture is chosen so that Kc = 0.12.Predict the effect on the concentration of SO3 as equilibrium is achieved by using Q,the reaction quotient. 2 SO3(g) ![A 2.5 L flask is filled with 0.25 mol SO<sub>3</sub>,0.20 mol SO<sub>2</sub>,and 0.40 mol O<sub>2</sub>,and allowed to reach equilibrium.Assume the temperature of the mixture is chosen so that K<sub>c</sub> = 0.12.Predict the effect on the concentration of SO<sub>3</sub> as equilibrium is achieved by using Q,the reaction quotient. 2 SO<sub>3</sub>(g) 2 SO<sub>2</sub>(g) + O<sub>2</sub>(g) A) [SO<sub>3</sub>] will decrease because Q > K. B) [SO<sub>3</sub>] will decrease because Q < K. C) [SO<sub>3</sub>] will increase because Q < K. D) [SO<sub>3</sub>] will increase because Q > K. E) [SO<sub>3</sub>] will remain the same because Q = K.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7480/11eac9a9_4bb4_135a_acc3_479b56c0d2da_TB7480_11.jpg) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g)
2 SO2(g) + O2(g)
A) [SO3] will decrease because Q > K.
B) [SO3] will decrease because Q < K.
C) [SO3] will increase because Q < K.
D) [SO3] will increase because Q > K.
E) [SO3] will remain the same because Q = K.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the equilibrium constants for the following reactions: 4Cu(s) + O2(g)  2Cu2O(s) ,K1
4CuO(s)
2Cu2O(s) ,K1
4CuO(s)  2Cu2O(s) + O2(g) ,K2
What is K for the system
2Cu(s) + O2(g)
2Cu2O(s) + O2(g) ,K2
What is K for the system
2Cu(s) + O2(g)  2CuO(s)
Equivalent to?
2CuO(s)
Equivalent to?
A) ![]()
![]()
B) ![]()
C) (K1) (K2)
D) ![]()
![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the reaction quotient,Q,is equal to K in a gas phase reaction,then
A) the chemical system has reached equilibrium.
B) the temperature must be increased for the reaction to proceed in the forward direction.
C) the reaction will proceed in the forward direction until equilibrium is established.
D) the reaction will proceed in the backward direction until equilibrium is established.
E) the reaction will proceed in the direction that increases the number of gas phase particles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Write a balanced chemical equation which corresponds to the following equilibrium constant expression. 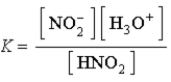
A) HNO2(aq) + H2O( ![]() )
) ![]() NO2-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
NO2-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
B) NO2-(aq) + H3O+(aq) ![]() HNO2(aq) + H2O(
HNO2(aq) + H2O( ![]() )
)
C) NO2-(aq) + H3O+(aq) ![]() HNO2(aq)
HNO2(aq)
D) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) ![]() H2O(
H2O( ![]() )
)
E) HNO2(aq) ![]() NO2-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
NO2-(aq) + H3O+(aq)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following expressions for K is correct for the reaction given below? Al3+(aq) + 4 OH-(aq)  Al(OH) 4-(aq)
Al(OH) 4-(aq)
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
When 1.0 mole of acetic acid is diluted with water to a volume of 1.0 L at 25 °C,0.42% of the acetic acid ionizes to form acetate ion and hydronium ion.
CH3CO2H(aq)+ H2O(  )
)  CH3CO2-(aq)+ H3O+(aq)
What percentage of the acid ionizes when 0.75 mole of acetic acid is diluted with water to 1.0 L at 25 °C?
CH3CO2-(aq)+ H3O+(aq)
What percentage of the acid ionizes when 0.75 mole of acetic acid is diluted with water to 1.0 L at 25 °C?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The equilibrium constant (Kc) for the decomposition of ammonium hydrogen sulfide,NH4HS(s) 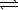 NH3(g) + H2S(g) ,is 1.8 × 10-4 at 25 °C.If excess NH4HS(s) is allowed to equilibrate at 25 °C,what is the equilibrium concentration of NH3?
NH3(g) + H2S(g) ,is 1.8 × 10-4 at 25 °C.If excess NH4HS(s) is allowed to equilibrate at 25 °C,what is the equilibrium concentration of NH3?
A) 3.2 × 10-8 M
B) 9.0 × 10-5 M
C) 1.8 × 10-4 M
D) 6.7 × 10-3 M
E) 1.3 × 10-2 M
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is always true for a reaction where Kc is 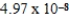 at 25°C?
at 25°C?
A) The reaction mixture contains mostly reactants at equilibrium.
B) The reaction mixture contains mostly products at equilibrium.
C) The rate of reaction is very slow.
D) There are approximately equal moles of reactants and products at equilibrium.
E) Both A and C.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the Kc equilibrium-constant expression for the following equilibrium? NiO(s) + H2(g) 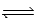 Ni(s) + H2O(g)
Ni(s) + H2O(g)
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the expression for Kc for the following equilibrium? CaSO3(s) 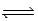 CaO(s) + SO2(g)
CaO(s) + SO2(g)
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At a given temperature,K = 0.024 for the equilibrium: PCl5(g)  PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
What is K for:
Cl2(g) + PCl3(g)
PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
What is K for:
Cl2(g) + PCl3(g)  PCl5(g) ?
PCl5(g) ?
A) 1700
B) 24
C) 0.00058
D) 42
E) 0.024
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction quotient,Q,for a system is 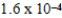 .If the equilibrium constant for the system at some temperature is
.If the equilibrium constant for the system at some temperature is 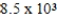 ,what will happen as the reaction mixture returns to equilibrium?
,what will happen as the reaction mixture returns to equilibrium?
A) The equilibrium constant will increase until it equals the reaction quotient.
B) There will be a net loss in both product(s) and reactant(s) .
C) There will be a net loss in product(s) .
D) There will be a net loss in reactant(s) .
E) The equilibrium constant will increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the correct balanced equation for the equilibrium expression given below? 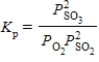
A) 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) ![]() 2 SO3(g)
2 SO3(g)
B) 2 SO3(g) ![]() 2 SO2(g) + O2(g)
2 SO2(g) + O2(g)
C) 2 SO3(aq) ![]() 2 SO2(aq) + O2(aq)
2 SO2(aq) + O2(aq)
D) 2 SO2(aq) + O2(aq) ![]() 2 SO3(aq)
2 SO3(aq)
E) SO2(g) + ![]() O2(g)
O2(g) ![]() SO3(g)
SO3(g)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the reaction given below,2.00 moles of A and 3.00 moles of B are placed in a 6.00-L container. A(g) + 2B(g)  C(g)
At equilibrium,the concentration of A is 0.230 mol/L.What is the value of Kc?
C(g)
At equilibrium,the concentration of A is 0.230 mol/L.What is the value of Kc?
A) 1.20
B) 1.53
C) 5.22
D) 0.230
E) 0.449
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the reaction quotient,Q,for the equilibrium CuCl(s) 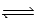 Cu+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
When 0.3746 L of
Cu+(aq) + Cl−(aq)
When 0.3746 L of 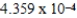 M Cu+ is combined with 0.4326 L of
M Cu+ is combined with 0.4326 L of 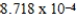 M Cl− in the presence of an excess of CuCl(s) ?
M Cl− in the presence of an excess of CuCl(s) ?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
In 1913,the Haber-Bosch process was patented.The product of the Haber-Bosch process is ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following reactions does a decrease in the volume of the reaction vessel at constant temperature favor the formation of the products?
A) 2 H2(g) + O2(g) ![]() 2 H2O(g)
2 H2O(g)
B) NO2(g) + CO(g) ![]() NO(g) + CO2(g)
NO(g) + CO2(g)
C) H2(g) + I2(g) ![]() 2 HI(g)
2 HI(g)
D) 2 O3(g) ![]() 3 O2(g)
3 O2(g)
E) MgCO3(s) ![]() MgO(s) + CO2(g)
MgO(s) + CO2(g)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the reaction A(aq) ![Consider the reaction A(aq) 2 B(aq) where K<sub>c</sub> = 4.1 at 25 °C.If 0.50 M A(aq) and 1.5 M B(aq) are initially present in a 1.0 L flask at 25 °C,what change in concentrations (if any) will occur in time? A) [A] will decrease and [B] will decrease. B) [A] will decrease and [B] will increase. C) [A] will increase and [B] will decrease. D) [A] will increase and [B] will increase. E) [A] and [B] remain unchanged.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7480/11eac9a9_4bb4_617c_acc3_356f223a2abc_TB7480_11.jpg) 2 B(aq) where Kc = 4.1 at 25 °C.If 0.50 M A(aq) and 1.5 M B(aq) are initially present in a 1.0 L flask at 25 °C,what change in concentrations (if any) will occur in time?
2 B(aq) where Kc = 4.1 at 25 °C.If 0.50 M A(aq) and 1.5 M B(aq) are initially present in a 1.0 L flask at 25 °C,what change in concentrations (if any) will occur in time?
A) [A] will decrease and [B] will decrease.
B) [A] will decrease and [B] will increase.
C) [A] will increase and [B] will decrease.
D) [A] will increase and [B] will increase.
E) [A] and [B] remain unchanged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the equilibrium PCl5(g) 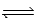 PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ,Kc = 4.0 at 228°C.If pure PCl5 is placed in a 1.00-L container and allowed to come to equilibrium,and the equilibrium concentration of PCl5(g) is 0.19 M,what is the equilibrium concentration of PCl3?
PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ,Kc = 4.0 at 228°C.If pure PCl5 is placed in a 1.00-L container and allowed to come to equilibrium,and the equilibrium concentration of PCl5(g) is 0.19 M,what is the equilibrium concentration of PCl3?
A) 0.095 M
B) 0.4 M
C) 0.19 M
D) 0.87 M
E) 0.009 M
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 77
Related Exams