A) Release factors bind to sites on the hairpin turn, causing release of the RNA transcript.
B) The turns are formed from complementary base pairing and cause separation of the RNA transcript and RNA polymerase.
C) The hairpin turn prevents more nucleoside triphosphates from entering the active site of the enzymes, effectively shutting off the process of polymerization.
D) A three- base repeat signals a stop sequence, and the RNA transcript is released.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the function of the 3' end of the tRNA?
A) It is the active site of this ribozyme.
B) It stabilizes the tRNA- amino acid complex.
C) It base pairs with the codon of mRNA.
D) It attaches to the amino acid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The segments of DNA where transcription begins have a binding site for RNA polymerase. These segments are known as
A) initiation factors.
B) promoters.
C) the holoenzyme.
D) sigma.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A part of an mRNA molecule with the following sequence is being read by a ribosome: 5' CCG- ACG 3'mRNA) . The following charged transfer RNA molecules with their anticodons shown in the 3' to 5' direction) are available. Two of them can correctly match the mRNA so that a dipeptide can form. Table 17.1 What is the anticodon loop of the first tRNA that will complement this mRNA?
A) 3' UGC 5'
B) 3' GGC 5'
C) 5' GGC 3'
D) 5' UGC 3'
E) 5' ACG 3'
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an experimental situation, a student researcher inserts an mRNA molecule into a eukaryotic cell after she has removed the mRNA's 5' cap and poly- A tail. Which of the following would you expect her to find?
A) The molecule is digested by enzymes because it is not protected at the 5' end.
B) The mRNA attaches to a ribosome and is translated, but more slowly.
C) The mRNA would not be translated.
D) The mRNA is quickly converted into a ribosomal subunit.
E) The cell adds a new poly- A tail to the mRNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As scientists were unraveling the mysteries associated with transcription and translation, they discovered there was not a one- to- one correspondence between nucleotide sequence of a gene and base sequence of the mRNA it codes for. They proposed the genes- in- pieces hypothesis. How can the genes- in- pieces hypothesis be explained?
A) Introns are noncoding segments of DNA that are present in the initial transcript, but are removed by splicing.
B) Several related genes are found in the genomes of humans and other animals.
C) Introns are noncoding segments of DNA that are not read or transcribed by RNA polymerase II.
D) Exons are noncoding segments of DNA that are not read or transcribed by RNA polymerase II.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are 61 codons that each specify the addition of a specific amino acid, and three stop codons for which there is no corresponding amino acid. However, there are only about 40 tRNA molecules, representing 40 anticodons. How is that possible?
A) An anticodon forms hydrogen bonds with the codon; it must match the first two bases of the codon, but is less specific with respect to the third base.
B) Only about 40 of the recognized 61 codons are present in mRNA.
C) There are tRNAs that can bind one of two related amino acids.
D) Only 20 of the codons are active-one for each amino acid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ribosomes can attach to prokaryotic messenger RNA
A) once replication is complete.
B) once post- transcriptional modification is complete.
C) once the primary transcript has been released from RNA polymerase.
D) before transcription is complete.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes is central to the initiation of transcription?
A) formation of a DNA primer
B) binding of DNA polymerase to the promoter region
C) formation of a phosphodiester bond in the elongating RNA strand
D) binding of sigma to the promoter region
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ribosome- binding site of prokaryotes is also known as
A) the promoter.
B) the Pribnow box.
C) the Shine- Dalgarno sequence.
D) the TATA box.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Put the following events of elongation in prokaryotic translation in chronological order. 1) Binding of mRNA with small ribosomal subunit. 2) Recognition of initiation codon 3) Complementary base pairing between initiator codon and anticodon of initiator tRNA 4) Base pairing of the mRNA codon following the initiator codon with its complementary tRNA 5) Attachment of the large subunit
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 2, 1, 4, 3, 5
C) 1, 2, 3, 5, 4
D) 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until which of the following occurs?
A) The two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter.
B) The DNA introns are removed from the template.
C) DNA nucleases have isolated the transcription unit.
D) Several transcription factors have bound to the promoter.
E) The 5' caps are removed from the mRNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does termination of translation take place?
A) The ribosome reaches the end of the mRNA molecule.
B) Stop codons with no corresponding tRNAs are read.
C) Energy depletion causes termination.
D) Hairpin turns of mRNA force the ribosome off the molecule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Once a peptide has been formed between the amino acid attached to the tRNA in the P site and the amino acid associated with the tRNA in the A site, which process on the list occurs next?
A) initiation
B) translocation
C) reading of the next codon of mRNA
D) the codon- anticodon hydrogen bonds holding the tRNA in the A site are broken
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Transcription would not occur at the appropriate initiation sites in E. coli if RNA polymerase is missing which of the following?
A) mRNA
B) amino acids
C) the core enzyme
D) sigma
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A transfer RNA #1) attached to the amino acid lysine enters the ribosome. The lysine binds to the growing poly on the other tRNA #2) in the ribosome already. Where does tRNA #2 move to after this bonding of lysine to the polypeptide?
A) A site
B) directly to the cytosol
C) E site
D) exit tunnel
E) P site
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
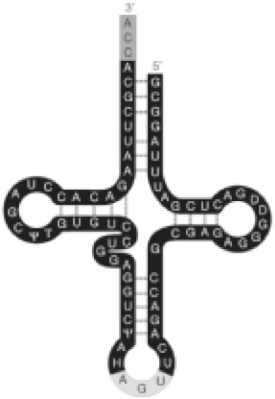 Figure 17.3
-Refer to Figure 17.3. What is the function of the AGU on the loop of the tRNA?
Figure 17.3
-Refer to Figure 17.3. What is the function of the AGU on the loop of the tRNA?
A) It is the active site of this ribozyme.
B) It base pairs with the codon of mRNA.
C) It stabilizes the tRNA- amino acid complex.
D) It attaches to the amino acid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 37 of 37
Related Exams