A) DNA polymerase I and DNA polymerase III have different functions.
B) The sliding clamp molecule is a ribozyme.
C) DNA polymerase I and DNA polymerase III are the same enzyme found in different organisms.
D) Topoisomerase is involved in proofreading activity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
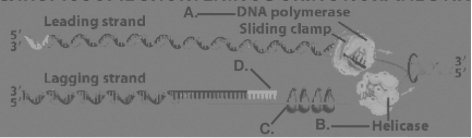 Figure 15.3
-Refer to Figure 15.3. Which of the structures in the figure breaks hydrogen bonds between complementary bases?
Figure 15.3
-Refer to Figure 15.3. Which of the structures in the figure breaks hydrogen bonds between complementary bases?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the mismatch repair process, enzyme complexes replace bases that were incorrectly inserted into the newly synthesized DNA strand. To function, they must be able to distinguish between the parent DNA strand and the new strand. How is this accomplished?
A) The new strand contains ribose sugars.
B) The parent strand is methylated.
C) The new strand contains the diphosphate bases.
D) The parent strand is usually radiolabeled.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The epsilon s) subunit of DNA polymerase III of E. coli has exonuclease activity. How does it function in the proofreading process?
A) The epsilon subunit excises a segment of DNA around the mismatched base.
B) The epsilon subunit can remove a mismatched nucleotide.
C) The epsilon subunit can recognize which strand is the template or parent strand, and which is the new strand of DNA.
D) It adds nucleotide triphosphates to the 3' end of the growing DNA strand.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
\text {Single strand as a template plus 3 ^ { \prime } end to }
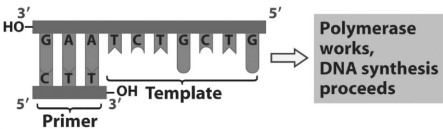 Figure 15.1
-Refer to Figure 15.1. What bases will be added to the primer as DNA replication proceeds? The bases should appear in the order that they will be added.
Figure 15.1
-Refer to Figure 15.1. What bases will be added to the primer as DNA replication proceeds? The bases should appear in the order that they will be added.
A) A, G, A, C, G, A, C
B) T, C, T, G, C, T, G
C) C, A, G, C, A, G, A
D) U, G, U, C, G, U, C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If during the process of DNA replication, the enzyme topoisomerase was not functioning i.e. it was mutated) what do you expect will happen to the replication process?
A) The double helix would unwind completely but no primers would be added to the template strand.
B) The double helix would unwind completely but no new strand would be created due to the formation of secondary structures.
C) The double helix would begin to unwind but this unwinding would stop prematurely due to over- twisting of the DNA.
D) The double helix would not begin to unwind at all.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fact that within a double- stranded DNA molecule, adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with thymine and cytosine forms three hydrogen bonds with guanine is known as
A) a double helix.
B) complementary base pairing.
C) semi- conservative replication.
D) secondary structure of a DNA molecule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following agents can cause mutations in DNA?
A) ultraviolet radiation from sunlight
B) aflatoxins that are found in moldy grains
C) free radicals that are formed as by- products of aerobic respiration
D) All of the above are mutagenic agents.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The transduction experiments done by Hershey and Chase, and the transformation experiments done by Griffith, supported the same conclusion, which was that
A) genetic recombination in living organisms is rare.
B) organisms must be sacrificed for science to progress.
C) pathogenic molecules affect the health of all living organisms.
D) DNA is the molecular substance of genetic inheritance.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What appears to be a dark side to telomerase activity with regard to human health?
A) Telomerase is active in most cancer cells.
B) Telomerase activity is only seen in somatic cells; therefore, chromosome shortening is likely in gametic chromosomes.
C) Telomerase is inhibited by p53.
D) There are more chromosomal ends than can be repaired by telomerase.
E) p53 inhibits telomerase.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Telomere shortening is a problem in which types of cells?
A) prokaryotes
B) eukaryotes
C) both prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Who performed the classic experiments that proved DNA was copied by semiconservative replication?
A) Meselson and Stahl
B) Hershey and Chase
C) Watson and Crick
D) Franklin and Wilkins
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the simple primary and secondary structure of DNA hold the information needed to code for the many features of multicellular organisms?
A) The hydrogen bonding among backbone constituents carries coded information.
B) The base sequence of DNA carries all the information needed to code for proteins.
C) The amino acids that make up the DNA molecule contain the information needed to make cellular proteins.
D) The covalent bonding among backbone constituents contains the information that is passed from generation to generation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Put the following steps of DNA replication in chronological order. 1) Single- stranded binding proteins attach to DNA strands. 2) Hydrogen bonds between base pairs of antiparallel strands are broken. 3) Primase binds to the site of origin. 4) DNA polymerase binds to the template strand. 5) An RNA primer is created.
A) 3, 2, 1, 5, 4
B) 1, 2, 3, 4, 4
C) 2, 1, 3, 5, 4
D) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNA replication is highly accurate. It results in about one mistake per billion nucleotides. For the human genome, how often would errors occur?
A) on average, once every 6 cell divisions
B) on average, once or twice in the lifetime of an individual
C) on average, 6 times each time the entire genome of a cell is replicated
D) on average, once a lifetime in 10% of the population
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC) is an inherited disorder. The genetic defect identified is an error in the mismatch repair mechanism. Which of the following would be an expected result of this mutation?
A) increased rate of repair of pyrimidine dimers
B) increased rate of errors by wild- type DNA polymerase
C) decreased ability to repair certain DNA mutations
D) increased rate of formation of pyrimidine dimers
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Semiconservative replication involves a template. What is the template?
A) an RNA molecule
B) one strand of the DNA molecule
C) DNA polymerase contains the template needed
D) single- stranded binding proteins
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would you expect of a eukaryote lacking telomerase?
A) a high probability of somatic cells becoming cancerous
B) high sensitivity to sunlight
C) a reduction in chromosome length in gametes
D) an inability to produce Okazaki fragments
E) an inability to repair thymine dimers
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is least likely to cause mutations in DNA?
A) ultraviolet radiation from sunlight
B) aflatoxins that are found in mouldy grains
C) hydroxyl radicals formed as by- products of aerobic respiration
D) medical X- rays to detect broken bones
E) light from an incandescent bulb
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are thymine dimers?
A) pyrimidines C and T) that have gained an extra nitrogen- containing ring structure
B) thymines on antiparallel DNA strands that form complementary base pairs
C) thymines formed by demethylation of purines
D) adjacent thymines on the same DNA strand that join by covalent bonding
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 39
Related Exams