A) "citrate synthase"
B) "fumarase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Compare the two ways the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction is controlled by the cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is regulated by a...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Which enzyme in the citrate cycle produces NADH?
A) aconitase
B) citrate synthase
C) isocitrate dehydrogenase
D) fumarase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which reaction in the citrate cycle produces CO2? 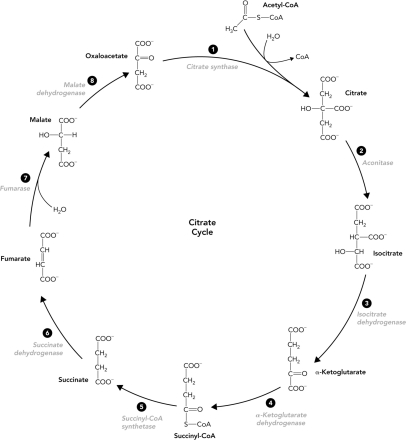
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An in vitro study shows that citrate synthase is inhibited in the citrate cycle. What is a possible explanation for this inhibition?
A) high levels of ADP
B) low levels of succinyl-CoA
C) high levels of NADH
D) high levels of AMP
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which enzyme regulates the flux of acetyl-CoA through the citrate cycle?
A) "pyruvate dehydrogenase"
B) "citrate synthase"
C) "isocitrate dehydrogenase"
D) " -ketoglutarate dehydrogenase"
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Classify the reaction that occurs at step 1 in the reaction schematic of the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction below. 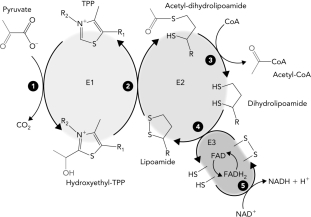
A) isomerization
B) addition
C) oxidation reduction
D) decarboxylation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If acetyl-CoA is not metabolized by the citrate cycle, the molecule in the cell
A) undergoes fatty acid metabolism.
B) is transported across the cell membrane.
C) is used to synthesize amino acids.
D) is used during glycolysis.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Using the table below, calculate G ' and determine if the conversion from malate to oxaloacetate is favorable under standard biochemical conditions.
Malate + NAD+ Oxaloacetate + H+ + NADH

Correct Answer

verified
Calculate the E for the coupled redox rea...
E for the coupled redox rea...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Pantothenic acid is essential for life because it is the vitamin precursor to the molecule that
A) provides a reactive disulfide that can participate in redox reactions within the enzyme active site of pyruvate dehydrogenase.
B) can accept one or two electrons in redox reactions in the cell.
C) is involved in at least 200 redox reactions in the cell.
D) is a cofactor in the biosynthetic pathways that produce fatty acids, acetylcholine, heme, and cholesterol.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the strongest reductant in the table below. 
A) O2
B) oxaloacetate
C) pyruvate
D) ferredoxin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the E ' of a coupled redox reaction with O2 and ferredoxin (Fe2+) using the table below. 
A) "-1.25"
B) "-0.39"
C) "0.39"
D) "1.25"
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A high NADH to NAD+ ratio would inhibit which enzyme in the citrate cycle?
A) succinate dehydrogenase
B) succinyl-CoA synthetase
C) aconitase
D) isocitrate dehydrogenase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the purpose of the first 3 steps in the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction?
A) regenerate the oxidized form of lipoamide
B) form NADH
C) transfer electrons
D) form acetyl-CoA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary function of the citrate cycle is to oxidize
A) glucose.
B) pyruvate.
C) acetyl-CoA.
D) citrate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Use the overall net reaction of the citrate cycle to explain why excess NADH inhibits the pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
NADH is a product in the balanced citrat...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
An in vitro study shows that isocitrate dehydrogenase is activated in the citrate cycle. What is a possible explanation for the activation?
A) high levels of ATP
B) low levels of ATP
C) high levels of NADH
D) low levels of AMP
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which vitamin is the precursor to the coenzyme that functions as a reductant in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in the final step of the reaction?
A) thiamine
B) pantothenic acid
C) riboflavin
D) niacin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The citrate cycle is considered to be a(n) pathway.
A) anabolic
B) catabolic
C) anaplerotic
D) amphibolic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
What two features of the citrate cycle make it unique compared with linear metabolic pathways?
Correct Answer

verified
Oxaloacetate is both the substrate for t...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Showing 1 - 20 of 100
Related Exams