A) a positive demand shock due to an increase in investment.
B) a positive supply shock caused by improved productivity.
C) a negative demand shock caused by fall in consumption.
D) a negative supply shock caused by higher input prices.
E) an increase in the price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A measure that has been developed to analyze the amount of output that must be given up in order to reduce the inflation rate by one percentage point is called the
A) misery index.
B) Phillips measure.
C) credibility index.
D) output gap.
E) sacrifice ratio.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Inflationary pressures that result from a rightward shift in the AD curve
A) cause Y to fall below Y*.
B) will worsen any existing unemployment problem.
C) will initiate a wage-price spiral.
D) will eventually subside unless accompanied by continual increases in the money supply.
E) will permanently increase output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider an economy that is in the process of a disinflation. Suppose that over a 2 -year period, the rate of inflation is reduced from 6% to 1%. Over this same time, the cumulative loss in real GDP is $30 billion. Potential GDP is $600 billion. What is the sacrifice ratio?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the AD/AS model below with a constant rate of inflation. No exogenous AD or AS shocks are occurring.
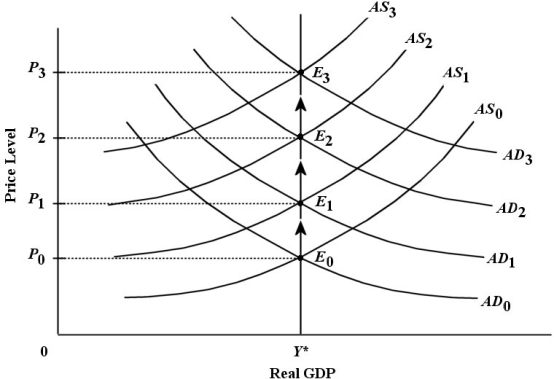 FIGURE 29-1
-Refer to Figure 29-1. Assume there are no demand or supply shocks present in this analysis. What explains the movement of the AS curve from AS0 to AS1 to AS2 and so on?
FIGURE 29-1
-Refer to Figure 29-1. Assume there are no demand or supply shocks present in this analysis. What explains the movement of the AS curve from AS0 to AS1 to AS2 and so on?
A) unit costs are rising due to excess demand for labour
B) expectations of inflation are causing wage costs to rise continually
C) unit costs are rising because real wages are rising faster than nominal wages
D) expectations of inflation are causing a perpetual inflationary output gap
E) the AS curve shifts up as potential GDP Y*) is continuously rising
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The acceleration hypothesis states that
A) when the central bank holds an inflationary gap constant, inflation will tend to accelerate.
B) if an economy is growing, inflation will grow at an ever-increasing rate.
C) capital investment is the primary cause of inflation.
D) monetary validation causes inflation.
E) if a recessionary gap is not closed, unemployment will tend to accelerate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the NAIRU is 8% and the actual unemployment rate is 5%,
A) there is no pressure on the AS curve to shift.
B) there is a recessionary gap.
C) demand forces put upward pressure on wages.
D) the AS curve will shift downward.
E) it will get stuck there permanently.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The three figures below show the phases of a disinflation. In part i) , the economy is experiencing a sustained inflation at E 1.
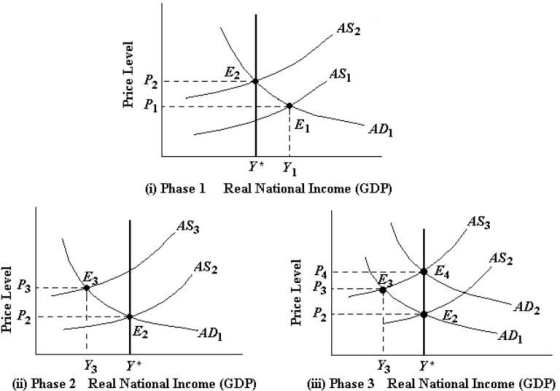 FIGURE 29-4
-Refer to Figure 29-4, part ii) , Phase 2 of the disinflation process. The upward drift of the AS curve will generally continue longer, with rising unemployment and falling output, when
FIGURE 29-4
-Refer to Figure 29-4, part ii) , Phase 2 of the disinflation process. The upward drift of the AS curve will generally continue longer, with rising unemployment and falling output, when
A) real wages and other factor prices are falling.
B) the price level is falling as a result of the disinflation.
C) firms and consumers regard the central bankʹs disinflation policy as highly credible.
D) the central bank pursues a contractionary monetary policy even more severe than they had announced.
E) firms and consumers do not regard the central bankʹs disinflation policy as credible.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rightward shift of the AD curve accompanied by a rightward shift of the AS curve will
A) increase GDP but have an uncertain effect on the price level.
B) reduce GDP but have an uncertain effect on the price level.
C) increase the price level but have an uncertain effect on GDP.
D) reduce the price level but have an uncertain effect on GDP.
E) reduce both the price level and GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the AD/AS model with a constant rate of inflation. In this situation, the money supply is rising, which tends to reduce interest rates. However, interest rates are actually likely to remain stable. Why?
A) Because the money transmission mechanism does not apply in a situation of sustained inflation.
B) Because the rising price level is decreasing the demand for money which is pushing interest rates up.
C) Because the declining interest rates cause the investment demand curve to shift to the right, which causes interest rates to rise.
D) Because the rising price level is increasing the demand for money which tends to push interest rates up.
E) Because the declining interest rates cause the investment demand curve to shift to the left, which causes interest rates to rise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Bank of Canada validates a positive AD shock,
A) it will have eliminated the possibility of a continued inflation.
B) there is the risk of continued inflation.
C) wages will fall to reduce the resulting unemployment.
D) output will fall more rapidly than if the shock had not been validated.
E) the AD curve will shift to the left and inflation will stop.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An inflation that begins as a result of any demand or supply shock will eventually come to a halt
A) if there is no monetary validation.
B) in the long run.
C) in the short run.
D) independent of the economyʹs adjustment process.
E) if expected inflation is positive but constant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the AS curve is continuously shifting upward due to expectations of future inflation. If there is repeated monetary validation of this supply shock,
A) unemployment will continue to rise.
B) the supply shocks will reverse themselves.
C) workers will have higher real wages.
D) there will be ongoing inflation.
E) there will be a once-and-for-all rise in the price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sacrifice ratio is calculated by
A) dividing the number unemployed by the labour force.
B) dividing the number employed by the labour force.
C) dividing the cumulative loss of real GDP as a percentage of potential GDP) due to disinflation by the number of percentage points by which inflation fell.
D) dividing the cumulative loss of potential GDP as a percentage of actual GDP) due to disinflation by the number of percentage points by which inflation fell.
E) adding the cumulative loss of real GDP as a percentage of potential GDP) due to disinflation to the number of percentage points by which unemployment exceeds the NAIRU.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the ʺacceleration hypothesis,ʺ the inflation rate will accelerate when actual output is held
A) at the NAIRU.
B) at the level where unemployment is at the natural rate.
C) below potential output.
D) at potential output.
E) above potential output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the Canadian economy is facing an inflationary output gap Y > Y*) . In our macro model, such an output gap can explain changes in which of the following variables?
A) the average level of wages
B) the level of wages in the forestry sector relative to the mining sector
C) the level of wages in a high-growth region of the country relative to a slow-growth region
D) the level of wages for skilled workers relative to unskilled workers
E) the level of wages for female workers relative to male workers
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the current inflation rate is 4% and the Bank of Canada wants to reduce it to 2%, knowing that the sacrifice ratio is 2. Apparently, the Bank of Canada is prepared to accept a decline of real GDP of as the cost of disinflation.
A) 1% of potential output
B) 0.5% of potential output
C) 2% of potential output
D) 4% of potential output
E) 8% of potential output
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the central bank responds to repeated negative supply shocks with monetary validations, the economy will be faced with
A) a one-time increase in prices.
B) a one-time decrease in prices.
C) alternating periods of inflation and deflation.
D) steady reductions in real output.
E) continuous inflation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the economy is in a long-run equilibrium. The AS curve now shifts upward due to a one-time increase in the price of raw materials. If the central bank validates this supply shock,
A) an inflationary gap will be created with further inflation.
B) an inflationary gap will be created, which will cause the AS curve to shift upward again.
C) the aggregate demand curve will shift up and result in a higher price level.
D) a recessionary gap will be created, which eventually causes the AS curve to shift downward.
E) a recessionary gap will be created and will cause a permanent reduction of employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A leftward shift in the AD curve accompanied by a leftward shift of the AS curve will
A) increase the price level but have an uncertain effect on GDP.
B) reduce the price level but have an uncertain effect on GDP.
C) increase GDP but have an uncertain effect on the price level.
D) reduce GDP but have an uncertain effect on the price level.
E) increase both GDP and the price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 123
Related Exams