A) Year 2
B) Year 3
C) Year 4
D) Year 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The crowding-out effect may be dampened if the investment-demand curve is shifting to the right.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The time which elapses between the beginning of a recession or an inflationary episode and the identification of the macroeconomic problem is referred to as a(n) :
A) budget lag.
B) recognition lag.
C) operational lag.
D) administrative lag.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an economy, the government wants to increase aggregate demand by $50 billion at each price level to increase real GDP and reduce unemployment.If the MPS is .4, then it could increase government spending by:
A) $10 billion.
B) $20 billion.
C) $31.25 billion.
D) $40.50 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a deficit is financed by issuing new money, the:
A) government is using its accumulated surplus to issue the new money.
B) government will be competing with private borrowers for funds.
C) increased demand for funds will drive up the interest rate.
D) crowding-out of investment can probably be avoided.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is more meaningful to measure the growth of the public debt relative to the GDP than to measure it in absolute terms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The operational lag of fiscal policy refers to the time which elapses between the beginning of a recession or inflation and the certain awareness that it is actually happening.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fiscal policy refers to the:
A) manipulation of government spending and taxes to stabilize domestic output, employment, and the price level.
B) manipulation of government spending and taxes to achieve greater equality in the distribution of income.
C) altering of the interest rate to change aggregate demand.
D) fact that equal increases in government spending and taxation will be contractionary.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The greatest expansionary impact of a budget deficit will occur when the:
A) government finances the deficit by obtaining newly printed money.
B) government borrows the money from the general public.
C) economy is operating in the intermediate range of its aggregate supply curve.
D) marginal propensity to save for the economy is high.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Built-in stability is synonymous with discretionary fiscal policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cyclically adjusted deficits are:
A) generally smaller than actual deficits.
B) generally larger than actual deficits.
C) identical to actual deficits.
D) opposite to actual deficits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that aggregate demand in the economy is excessive, causing an inflationary gap.Which of the following would be most in accord with appropriate government fiscal policy?
A) an increase in federal income tax rates
B) an increase in the size of income tax exemptions for each dependent
C) passage of legislation providing for the construction of 8,000 new post office buildings
D) an increase in soil conservation subsidies to farmers
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The additional taxes needed to pay the interest on the public debt reduce incentives to work, save, invest, and bear risks.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in the cyclical deficits will automatically increase the full-employment budget deficit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Currently, the general agreement about a proposed fiscal policy is that:
A) it should be evaluated for its potential positive and negative impacts on long-run productivity growth.
B) only the short -run impact of it on the economy should be evaluated.
C) the politicians should not be worried about either the short-run nor long-run effects of a fiscal policy.
D) it should only be used when the economy is experiencing an inflationary and not a recessionary gap.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which cause-and-effect chain would best explain the reason for a decline in net exports? An expansionary fiscal policy:
A) increases domestic interest rates and leads to an appreciation of the dollar that reduces net exports.
B) decreases interest rates and leads to a depreciation of the dollar that reduces net exports.
C) increases domestic interest rates and leads to a depreciation of the dollar that reduces net exports.
D) decreases interest rates and leads to an appreciation of the dollar that reduces net exports.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When government tax revenues change automatically and in a countercyclical direction over the course of the business cycle, this is an example of:
A) impounding.
B) built-in stability.
C) money creation.
D) the full-employment budget.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the diagram below.If the full employment level of GDP for this economy is at H, the: 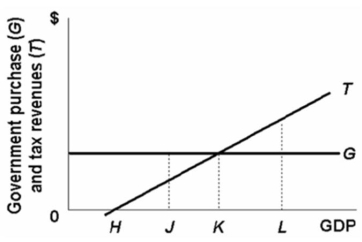
A) cyclically adjusted budget will produce a surplus.
B) cyclically adjusted budget will produce a deficit.
C) actual budget will produce a deficit.
D) actual budget will produce a surplus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
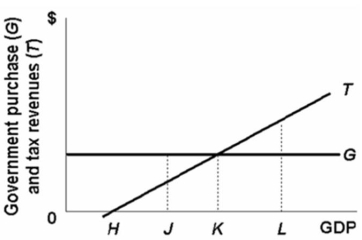 If the full-employment GDP for the above economy is at L, the:
If the full-employment GDP for the above economy is at L, the:
A) actual budget will entail a deficit.
B) cyclically adjusted budget will entail a deficit.
C) actual budget will entail a surplus.
D) cyclically adjusted budget will entail a surplus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Crowding-out is the notion that:
A) since tax revenues vary directly with GDP, a rise in the level of GDP will increase the budget surplus and limit expansion.
B) deficit financing will increase the demand for money, increase the interest rate, and reduce the level of investment spending in the economy.
C) the full-employment budget is the best indicator of whether a budget deficit crowds out investment.
D) the actual budget is the best indicator of whether a budget deficit crowds out saving.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 234
Related Exams