A) defeat this project and resources will be underallocated to it.
B) defeat this project and resources will be efficiently allocated.
C) pass this project and resources will be underallocated to it.
D) pass this project and resources will be overallocated to it.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Because of the force of law and bureaucratic structure, government accountability is less of a problem than in the private sector.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The political technique called logrolling:
A) always increases economic efficiency.
B) always decreases economic efficiency.
C) involves trading votes to secure favorable outcomes that otherwise could be rejected.
D) is an example of the paradox of voting.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that in a series of paired-choice votes a new park is preferred to a new recreation center and a new recreation center is preferred to street widening.Also suppose that street widening is preferred to a new park.This set of votes is an example of the:
A) principal-agent problem.
B) benefits-received principle.
C) median-voter model.
D) paradox of voting.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Public choice theorists point out that the political process:
A) differs from the marketplace in that voters and congressional representatives often face limited and bundled choices.
B) is less prone to failure than is the marketplace.
C) is a much fairer way to allocate society's scarce resources than is the impersonal marketplace, which is dominated by high-income consumers.
D) involves logrolling, which is always inefficient.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under what circumstances would government loan guarantees be socially beneficial?
A) When the guarantees socialize losses and privatize gains.
B) When the guarantees stimulate production of goods generating significant spillover costs.
C) When the guarantees promote production of goods otherwise underproduced by the private sector.
D) When the guarantees increase company profits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some people argue that the three main television networks all have similar programming.If true, this observation might best be explained by the:
A) paradox of voting.
B) median-voter model.
C) law of diminishing marginal utility.
D) ability-to-pay principle.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An economic analysis of the relationship between proposed legislation affecting major employers in each state and the voting patterns of senators and representatives in Congress on that legislation would fit within the subcategory of economics called:
A) the economics of fiscal policy.
B) public choice theory.
C) behavioral economics.
D) monetarism.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Information problems create inefficient outcomes in:
A) the private sector but not the public sector.
B) the public sector but not the private sector.
C) neither the private nor the public sector.
D) both the private and the public sectors.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The government's ability to coerce can enhance economic efficiency by:
A) eliminating income inequality.
B) correcting market failures.
C) preventing resources from going to their most valued uses.
D) restraining self-interest.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Bank of Canada, U.S.Federal Reserve, the Bank of Japan, the Bank of England, and the European Central Bank are all in charge of what for the countries they represent?
A) Debt management.
B) Unfunded liabilities.
C) Monetary policy.
D) Fiscal policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
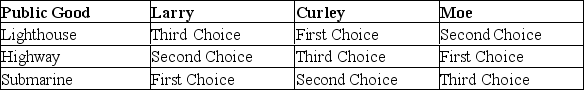 Refer to the table.In a choice between education and public safety:
Refer to the table.In a choice between education and public safety:
A) a majority of voters would favor education.
B) no voter decision is possible.
C) a majority of voters would favor public safety.
D) the outcome would depend on which item was listed first on the ballot.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As it relates to corporations, the principal-agent problem is that:
A) the goals of the corporate managers (the principals) may not match the goals of the corporate owners (the agents) .
B) the goals of the corporate managers (the agents) may not match the goals of the corporate owners (the principals) .
C) the federal government (the agent) taxes both corporate profits and the dividends paid to stockholders (the principals) .
D) it is costly for the corporate owners (the principals) to obtain a corporate charter from government (the agent) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following will tend to socialize losses and privatize gains?
A) Lowering interest rates to encourage private borrowing and investment.
B) Government regulation to promote human safety and environmental protection.
C) Government creating projects rather than supporting private efforts.
D) Government guarantees to private investors that they will get their money back even if the company fails.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The political tendency to favor spending priorities with immediate benefits but deferred costs results in:
A) chronic budget deficits.
B) misdirection of stabilization policy.
C) unfunded liabilities.
D) all of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following topics would be of the most interest to a public choice economist?
A) The theory of comparative advantage.
B) The law of increasing opportunity cost.
C) Inflation and unemployment.
D) Rent-seeking behavior.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question on the basis of the following table that shows the total costs and total benefits facing a city of five different potential baseball stadiums of increasing size.All figures are in millions of dollars. 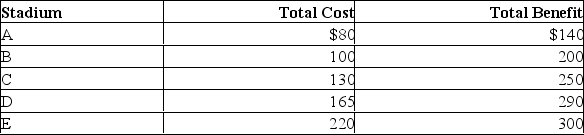 Refer to the table.The marginal cost and marginal benefit of stadium B (relative to A) are:
Refer to the table.The marginal cost and marginal benefit of stadium B (relative to A) are:
A) $20 million and $50 million, respectively.
B) $100 million and $200 million, respectively.
C) $30 million and $50 million, respectively.
D) $20 million and $60 million, respectively.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Government fiscal policy involves changing which of the following?
A) Interest rates.
B) Taxes and government spending.
C) Regulations on business.
D) The amount of money in circulation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The many layers of the federal government in Canada:
A) lead to economic inefficiencies because of difficulty aggregating and conveying information.
B) enhance government's ability make effective decisions quickly.
C) better allow the invisible hand to direct government resources to their best uses.
D) improve accountability of government officials, thus leading to more efficient policies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Because majority voting fails to incorporate the strength of the preferences of individual voters, it:
A) creates negative externalities.
B) under some circumstances produces economically inefficient outcomes.
C) leads to market failure.
D) leads to politics dominated by special interest groups.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 121
Related Exams