A) underallocation of resources.
B) overallocation of resources.
C) a scarcity of goods and services in society.
D) a surplus of goods and services in society.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Productive efficiency means that the society is producing the combination of the output most desirable by consumers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal benefit to society of reducing pollution declines with increases in pollution moderation because of the law of:
A) increasing costs.
B) diminishing returns.
C) diminishing marginal utility.
D) conservation of matter and energy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For which one of the following would we need to sum individual demand curves vertically to obtain the total demand curve?
A) frozen yogurt
B) bubble gum
C) microwave popcorn
D) courts of law
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graphs below refer to two separate product markets.Assume that society's optimal level of output in each market is Q0 and that government purposely shifts the market supply curve from S to S1 in diagram (a) and from S to S2 in diagram (b) .The shift of the supply curve from S to S2 in diagram (b) might be caused by a per unit: 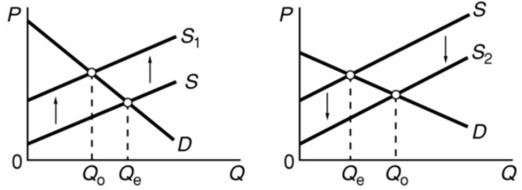
A) subsidy paid to the producers of this product.
B) tax on the producers of this product.
C) subsidy paid to the buyers of this product.
D) tax on the buyers of this product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Quasi-public goods are:
A) government produced goods that can be produced so that exclusion is possible.
B) government produced goods that can be produced so that exclusion is not possible.
C) privately produced goods that can be produced so that exclusion is possible.
D) privately produced goods that can be produced so that exclusion is not possible.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these is an example of an external cost?
A) an increase in the value of land you own when a nearby development is completed.
B) the costs paid by a company to build an automated factory.
C) decreased property values in a neighbourhood where several houses are burglarized.
D) the higher price you pay when you buy a heavily advertised product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Market failures
A) fall only on the demand-side.
B) fall only on the supply-side.
C) can fall on either the demand-side or the supply-side.
D) fall on non-competitive markets only.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
There is a positive relationship between equilibrium price and the amount of producer surplus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question based on the following information.Way-Below Normal University has found it necessary to institute a crime-control program on its campus to deal with the high costs of theft and vandalism.The university is now considering several alternative levels of crime control.This table shows the expected annual costs and benefits of these alternatives.The marginal benefits of crime control for Level Two are: 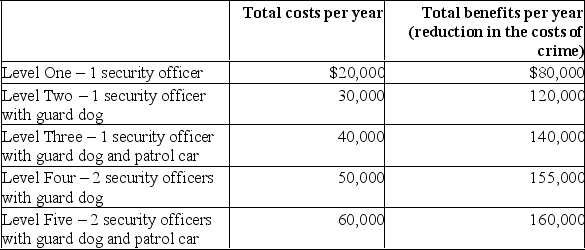
A) $20000
B) $40000
C) $60000
D) $140000
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the full cost of producing a good or service is not reflected in the resultant curve this is referred to as what type of failure?
A) Supply side
B) Demand side
C) Market side
D) Demand-supply side
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which method for correcting externalities is common to both negative and positive externalities?
A) Private bargaining
B) Lawsuits
C) Government provision
D) Direct controls
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Efficiency loss refers to:
A) the situation where the maximum willingness to pay for a product is less than minimum acceptable price.
B) the situation where the maximum willingness to pay for a product is equal to the minimum acceptable price.
C) the difference between consumer and producer surplus.
D) the sum of consumer and producer surplus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following ways does the government of a nation estimate the true demand for a public good?
A) Surveys
B) Government elections
C) Voting in parliament
D) Legislation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It has been proposed that a government agency be charged with the responsibility for determining the amount of pollution which the atmosphere or a body of water can safely recycle, and sell these limited rights to polluters.What would be the advantage of such a market for pollution rights?
A) Government agencies can make a great deal of money.
B) Pollution would be eliminated because nobody would want to pay for such a right.
C) The quality of water or air can be maintained at some acceptable standard through economic incentives.
D) The social consciousness of people would be raised as they obtain more appreciation for the importance of conservation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If some activity creates external benefits as well as private benefits, then economic theory suggests that the activity ought to be:
A) taxed.
B) prohibited.
C) subsidized.
D) left alone.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graphs below refer to two separate product markets.Assume that society's optimal level of output in each market is Q0 and that government purposely shifts the market supply curve from S to S1 in diagram (a) and from S to S2 in diagram (b) .The shift of the supply curve from S to S1 in diagram (a) might be caused by a per unit: 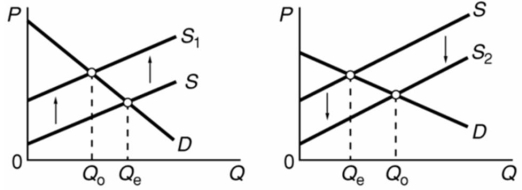
A) subsidy paid to the producers of this product.
B) tax on the producers of this product.
C) subsidy paid to the buyers of this product.
D) tax on the buyers of this product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A demand-side market failure occurs when demand curves do not reflect consumers' full willingness to pay for a good or service.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The major difficulty in asking people to pay voluntarily what a government program is worth to them is:
A) the free-rider problem.
B) people have poor judgment.
C) the fact that people don't know what programs they want.
D) we would increase government expenditures too much.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the diagram in which S is the market supply curve and S1 is a supply curve comprising all costs of production, including external costs.Assume that the number of people affected by these external costs is large.If the government wishes to establish an optimal allocation of resources in this market, it should: 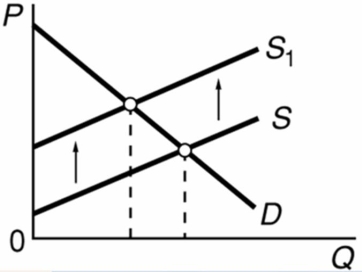
A) not intervene because the market outcome is optimal.
B) subsidize consumers so that the market demand curve shifts leftward.
C) subsidize producers so that the market supply curve shifts leftward (upward) .
D) tax producers so that the market supply curve shifts leftward (upward) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 133
Related Exams