Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For enzyme-catalyzed reactions, what happens as the concentration of the substrate is increased?
A) The rate continues to increase as substrate concentration increases.
B) The rate increases until it reaches a maximum, constant value.
C) The rate increases until it reaches a maximum, then the rate decreases.
D) The rate decreases with increasing concentration of the substrate.
E) The rate decreases until it reaches a minimum, constant value.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
About half of the 223 amino acids in the enzyme trypsin are hydrophobic. Where in the tertiary structure of this globular protein are these amino acids most likely to be found?
A) at the N-terminal end of the protein chain
B) at the C-terminal end of the protein chain
C) on the exterior surface of the folded protein
D) in the interior of the folded protein
E) in the active site of the enzyme
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The penicillin class of antibiotics is inhibitors of an enzyme responsible for the formation of bacterial cell walls.The penicillin covalently binds to a serine residue in the active site of the enzyme, as depicted below.What type of bond is formed between the penicillin and the active site? 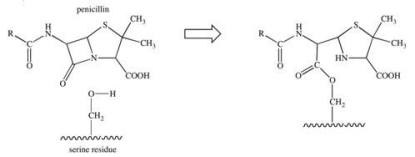
A) hydrogen bond
B) ionic bond
C) glycosidic linkage
D) ester bond
E) acetal bond
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Proteolytic digestive enzymes are often produced in an inactive form.What is the name that refers to the inactive form of an enzyme?
A) isozyme
B) zwitterion
C) proenzyme
D) inhibitor
E) allele
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pancreatic enzymes trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase all hydrolyze peptide bonds on the carbonyl side of several different amino acids in a protein.What term best describes their enzyme specificity?
A) stereospecific
B) peptide
C) absolute
D) linkage
E) group
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shows how the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction depends on the variable x.Which of the following quantities could x most likely represent? 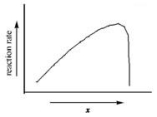
A) enzyme concentration
B) energy
C) temperature
D) substrate concentration
E) progress of reaction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Isomerases rearrange the functional groups within a molecule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the water-soluble vitamin from which NAD+ is made?
A) riboflavin (B2)
B) niacin (B3)
C) pyridoxine (B6)
D) cyanocobalamine (B12)
E) riboflavin (B2) and niacin (B3) are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The presence of an enzyme will alter the relative ratio of product to reactant for a biochemical reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The protease enzyme chymotrypsin cleaves peptide bonds on the carbonyl side of aromatic amino acids.Which labeled bond in the peptide below would be cleaved by chymotrypsin? 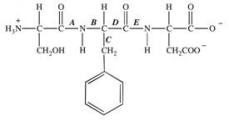
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement concerning an enzyme is true?
A) An enzyme increases the size of the equilibrium constant of the reaction it catalyzes.
B) An enzyme decreases the size of the equilibrium constant of the reaction it catalyzes.
C) An enzyme shifts the equilibrium so that more product is formed when equilibrium is reached.
D) An enzyme increases the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the activation energy.
E) An enzyme slows down reactions that occur too rapidly to be effective in the body.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the first step in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
A) catalysis of enzyme
B) dimerizing the substrate
C) ionization of enzyme
D) decrease of pH
E) formation of an enzyme-substrate complex
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A proenzyme is an inactive form of an enzyme.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of specificity is displayed by an enzyme that is able to catalyze a reaction of D-glucose, but not L-glucose?
A) absolute specificity
B) stereospecificity
C) group specificity
D) optical specificity
E) sugar specificity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Proteases, or proteolytic enzymes, are responsible for which of the following functions?
A) formation of the zwitterion form of a protein
B) hydrolysis of the ester bonds in dietary triglycerides
C) hydrolysis of the peptide bonds between amino acids in proteins
D) formation of the glycosidic linkages in disaccharides and polysaccharides
E) formation of bacterial cell walls
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enzyme hexokinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of glucose according to the reaction shown below.Glucosamine is a competitive inhibitor of hexokinase.Which of the following best describes the inhibition by glucosamine? 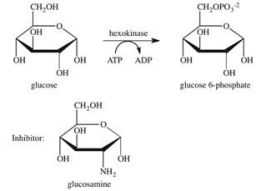
A) Glucosamine stabilizes the active site of the enzyme, preventing glucose-6-phosphate from being released.
B) Glucosamine reacts with glucose, preventing it from binding to the active site of the enzyme.
C) Glucosamine binds to the active site of the enzyme, preventing glucose from binding.
D) Glucosamine binds to the surface of the enzyme, causing a change in the shape of both the enzyme and the active site, preventing glucose from binding.
E) Glucosamine reacts with glucose-6-phosphate, preventing it from being released from the active site.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Elastase is a protease enzyme that cleaves peptide bonds on the carbonyl side of the amino acids glycine and alanine.What products result from treatment of a peptide with the primary structure shown below with elastase? Pro-Gly-Phe-Ala
A) the individual amino acids proline, glycine, phenylalanine, and alanine
B) Pro-Gly, phenylalanine, and alanine
C) proline, Gly-Phe, and alanine
D) Pro-Gly, and Phe-Ala
E) proline, glycine, and Phe-Ala
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A holoenzyme is a functional enzyme composed of what two parts?
A) apoenzyme and cofactor
B) amino acid and NAD+
C) substrate and catalyst
D) transferase and ligase
E) substrate and inhibitor
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph shows how the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction depends on the variable x.Which of the following quantities could x most likely represent? 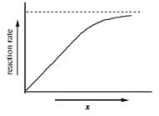
A) temperature
B) pH
C) energy
D) substrate concentration
E) progress of reaction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 72
Related Exams