A) A project's NPV increases as the cost of capital declines.
B) A project's MIRR is unaffected by changes in the cost of capital.
C) A project's regular payback increases as the cost of capital declines.
D) A project's discounted payback increases as the cost of capital declines.
E) A project's IRR increases as the cost of capital declines.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Assuming that their NPVs based on the firm's cost of capital are equal, the NPV of a project whose cash flows accrue relatively rapidly will be more sensitive to changes in the discount rate than the NPV of a project whose cash flows come in later in its life.
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If you were evaluating two mutually exclusive projects for a firm with a zero cost of capital, the payback method and NPV method would always lead to the same decision on which project to undertake.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in the firm's cost of capital will decrease projects' NPVs, which could change the accept/reject decision for any potential project.However, such a change would have no impact on projects' IRRs.Therefore, the accept/reject decision under the IRR method is independent of the cost of capital.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are on the staff of O'Hara Inc.The CFO believes project acceptance should be based on the NPV, but Andrew O'Hara, the president, insists that no project should be accepted unless its IRR exceeds the project's risk-adjusted cost of capital.Now you must make a recommendation on a project that has a cost of $15,000 and two cash flows: $110,000 at the end of Year 1 and −$100,000 at the end of Year 2.The president and the CFO both agree that the appropriate cost of capital for this project is 10%.At 10%, the NPV is $2,355.37, but you find two IRRs, one at 6.33% and one at 527%, and a MIRR of 11.32%.Which of the following statements best describes your optimal recommendation, i.e., the analysis and recommendation that is best for the company and least likely to get you in trouble with either the CFO or the president?
A) You should recommend that the project be rejected because, although its NPV is positive, it has an IRR that is less than the cost of capital.
B) You should recommend that the project be accepted because (1) its NPV is positive and (2) although it has two IRRs, in this case it would be better to focus on the MIRR, which exceeds the cost of capital.You should explain this to the president and tell him that the firm's value will increase if the project is accepted.
C) You should recommend that the project be rejected.Although its NPV is positive it has two IRRs, one of which is less than the cost of capital, which indicates that the firm's value will decline if the project is accepted.
D) You should recommend that the project be rejected because, although its NPV is positive, its MIRR is less than the cost of capital, and that indicates that the firm's value will decline if it is accepted.
E) You should recommend that the project be rejected because its NPV is negative and its IRR is less than the cost of capital.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Clifford Company is choosing between two projects.The larger project has an initial cost of $100,000, annual cash flows of $30,000 for 5 years, and an IRR of 15.24%.The smaller project has an initial cost of $50,000, annual cash flows of $16,000 for 5 years, and an IRR of 16.63%.The projects are equally risky.Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Since the smaller project has the higher IRR, the two projects' NPV profiles will cross, and the larger project will look better based on the NPV at all positive values of the cost of capital.
B) If the company uses the NPV method, it will tend to favor smaller, shorter-term projects over larger, longer-term projects, regardless of how high or low the cost of capital is.
C) Since the smaller project has the higher IRR but the larger project has the higher NPV at a zero discount rate, the two projects' NPV profiles will cross, and the larger project will have the higher NPV if the cost of capital is less than the crossover rate.
D) Since the smaller project has the higher IRR and the larger NPV at a zero discount rate, the two projects' NPV profiles will cross, and the smaller project will look better if the cost of capital is less than the crossover rate.
E) Since the smaller project has the higher IRR, the two projects' NPV profiles cannot cross, and the smaller project's NPV will be higher at all positive values of the cost of capital.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT? Assume that the project being considered has normal cash flows, with one outflow followed by a series of inflows.
A) A project's regular IRR is found by discounting the cash inflows at the cost of capital to find the present value (PV) , then compounding this PV to find the IRR.
B) If a project's IRR is greater than the WACC, then its NPV must be negative.
C) To find a project's IRR, we must solve for the discount rate that causes the PV of the inflows to equal the PV of the project's costs.
D) To find a project's IRR, we must find a discount rate that is equal to the cost of capital.
E) A project's regular IRR is found by compounding the cash inflows at the cost of capital to find the terminal value (TV) , then discounting this TV at the cost of capital.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The NPV method's assumption that cash inflows are reinvested at the cost of capital is generally more reasonable than the IRR's assumption that cash flows are reinvested at the IRR.This is an important reason why the NPV method is generally preferred over the IRR method.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If the cost of capital declines, this lowers a project's NPV.
B) The NPV method is regarded by most academics as being the best indicator of a project's profitability; hence, most academics recommend that firms use only this one method.
C) A project's NPV depends on the total amount of cash flows the project produces, but because the cash flows are discounted at the cost of capital, it does not matter if the cash flows occur early or late in the project's life.
D) The NPV and IRR methods may give different recommendations regarding which of two mutually exclusive projects should be accepted, but they always give the same recommendation regarding the acceptability of a normal, independent project.
E) The NPV method was once the favorite of academics and business executives, but today most authorities regard the MIRR as being the best indicator of a project's profitability.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The internal rate of return is that discount rate that equates the present value of the cash outflows (or costs) with the present value of the cash inflows.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Projects S and L are equally risky, mutually exclusive, and have normal cash flows.Project S has an IRR of 15%, while Project L's IRR is 12%.The two projects have the same NPV when the cost of capital is 7%.Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If the cost of capital is 6%, Project S will have the higher NPV.
B) If the cost of capital is 13%, Project S will have the lower NPV.
C) If the cost of capital is 10%, both projects will have a negative NPV.
D) Project S's NPV is more sensitive to changes in cost of capital than Project L's.
E) If the cost of capital is 10%, both projects will have positive NPVs.
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If a project has "normal" cash flows, then its MIRR must be positive.
B) If a project has "normal" cash flows, then it will have exactly two real IRRs.
C) The definition of "normal" cash flows is that the cash flow stream has one or more negative cash flows followed by a stream of positive cash flows and then one negative cash flow at the end of the project's life.
D) If a project has "normal" cash flows, then it can have only one real IRR, whereas a project with "nonnormal" cash flows might have more than one real IRR.
E) If a project has "normal" cash flows, then its IRR must be positive.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) One advantage of the NPV over the IRR is that NPV assumes that cash flows will be reinvested at the cost of capital, whereas IRR assumes that cash flows are reinvested at the IRR.The NPV assumption is generally more appropriate.
B) One advantage of the NPV over the MIRR method is that NPV takes account of cash flows over a project's full life whereas MIRR does not.
C) One advantage of the NPV over the MIRR method is that NPV discounts cash flows whereas the MIRR is based on undiscounted cash flows.
D) Since cash flows under the IRR and MIRR are both discounted at the same rate (the cost of capital) , these two methods always rank mutually exclusive projects in the same order.
E) One advantage of the NPV over the IRR is that NPV takes account of cash flows over a project's full life whereas IRR does not.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Projects A and B have identical expected lives and identical initial cash outflows (costs) .However, most of one project's cash flows come in the early years, while most of the other project's cash flows occur in the later years.The two NPV profiles are given below: 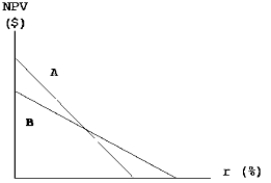 Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) More of Project B's cash flows occur in the later years.
B) We must have information on the cost of capital in order to determine which project has the larger early cash flows.
C) The NPV profile graph is inconsistent with the statement made in the problem.
D) The crossover rate, i.e., the rate at which Projects A and B have the same NPV, is greater than either project's IRR.
E) More of Project A's cash flows occur in the later years.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If two projects are mutually exclusive, then they are likely to have multiple IRRs.
B) If a project is independent, then it cannot have multiple IRRs.
C) Multiple IRRs can occur only if the signs of the cash flows change more than once.
D) If a project has two IRRs, then the smaller one is the one that is most relevant, and it should be accepted and relied upon.
E) For a project to have more than one IRR, then both IRRs must be greater than the cost of capital.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Under certain conditions, a project may have more than one IRR.One such condition is when, in addition to the initial investment at time = 0, a negative cash flow (or cost) occurs at the end of the project's life.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If Project A's IRR exceeds Project B's, then A must have the higher NPV.
B) A project's MIRR can never exceed its IRR.
C) If a project with normal cash flows has an IRR less than the cost of capital, the project must have a positive NPV.
D) If the NPV is negative, the IRR must also be negative.
E) If a project with normal cash flows has an IRR greater than the cost of capital, the project must also have a positive NPV.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Conflicts between two mutually exclusive projects occasionally occur, where the NPV method ranks one project higher but the IRR method ranks the other one first.In theory, such conflicts should be resolved in favor of the project with the higher positive IRR.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) The NPV method assumes that cash flows will be reinvested at the risk-free rate, while the IRR method assumes reinvestment at the IRR.
B) The NPV method assumes that cash flows will be reinvested at the cost of capital, while the IRR method assumes reinvestment at the risk-free rate.
C) The NPV method does not consider all relevant cash flows, particularly cash flows beyond the payback period.
D) The IRR method does not consider all relevant cash flows, particularly cash flows beyond the payback period.
E) The NPV method assumes that cash flows will be reinvested at the cost of capital, while the IRR method assumes reinvestment at the IRR.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A firm should never accept a project if its acceptance would lead to an increase in the firm's cost of capital (its WACC).
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 52
Related Exams