A) 6.5 *10-5 rad
B) 1.3*10-4 rad
C) 9.2 *10-5 rad
D) 3.0 *10-9 rad
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Light of wavelength 500 nm shines on a soap bubble film (n = 1.46) . For what soap film thickness, other than the minimum thickness, will constructive interference occur?
A) 63 nm
B) 102 nm
C) 308 nm
D) 257 nm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At what angle will the second order (m = 2) maximum occur for a wavelength of 450 nm using a diffraction grating with 10,000 lines per cm?
A) 64°
B) 27°
C) 53°
D) No second order maximum will occur in this case.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At what angle will the highest order (m value) maximum appear for a wavelength 400 nm using a grating with 600 lines per mm?
A) 54°
B) 90°
C) 74°
D) 36°
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two flat glass plates are in contact along one end and are separated by a sheet of paper 3.0 *10 - 6 m thick at the other end. The top plate is illuminated by a monochromatic light source of wavelength 490 nm. How many dark parallel bands will be evident across the top plate? (1 nm = 10 - 9 m) Note that a dark band occurs where the plates contact.
A) 13
B) 7
C) 9
D) 17
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A multiple slit diffraction grating has a slit separation of 2.00 * 10 - 6 m. Find the wavelength of the monochromatic light that will have its second order (m = 2) bright fringe diffracted through an angle of 43.4°. (1 nm = 10 - 9 m)
A) 616 nm
B) 500 nm
C) 687 nm
D) 120 nm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A single-slit diffraction pattern is produced from a light source of wavelength 580 nm. The light goes through a single slit and onto a screen 1.0 m away. The first dark fringe is 5.8 mm from the central bright fringe. What is the slit width? (1 nm = 10 - 9 m)
A) 0.12 mm
B) 0.24 mm
C) 0.081 mm
D) 0.10 mm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A Young's double-slit experiment is performed in air and then the apparatus is submerged in water. What happens to the fringe separation, and what can be used to explain the change, if any?
A) The separation decreases because the frequency of the light decreases in the water.
B) The separation decreases because the wavelength of the light decreases in the water.
C) The separation stays the same as it is the same experiment independent of the medium.
D) The separation increases because the wavelength of the light increases in the water.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Interference effects observed in the early 1800s were instrumental in supporting a concept of the existence of which property of light?
A) electromagnetic character
B) particle nature
C) wave nature
D) polarization
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A silicon monoxide (n = 1.45) film of 330 nm thickness is used to coat a glass camera lens (n = 1.56) . What wavelength of light in the visible region (390 to 710 nm) will be most efficiently transmitted by this system? (1 nm = 10 - 9 m)
A) 522 nm
B) 492 nm
C) 638 nm
D) 409 nm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When light passes from a material with a low index of refraction into material with a high index of refraction:
A) some light is reflected with a 180° change of phase.
B) none of the light is reflected.
C) some light is reflected without a change of phase.
D) the light that is not reflected has a 180° change of phase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A light source simultaneously emits light of two wavelengths, 480 nm and 560 nm, respectively. The source is used in a double-slit interference experiment where the slit spacing is a 0.040 mm, and the distance between double slits and the screen is 1.6 m. What is the separation between the m = 3 bright fringes of the two wavelengths as they appear on the screen? (1 nm = 10 - 9 m)
A) 0.96 cm
B) 0.48 cm
C) 0.64 cm
D) 0.16 cm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Waves from a radio station with a wavelength of 900 m arrive at a home receiver a distance 50 km away from the transmitter by two paths. One arrives via a direct-line path and the second by reflection from a mountain directly behind the receiver. What is the minimum distance between the mountain and receiver such that destructive interference occurs at the location of the listener? Assume no phase change on reflection.
A) 675 m
B) 900 m
C) 450 m
D) 225 m
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A Young's double-slit apparatus is set up where a screen is positioned 0.80 m from the double slits. If the distance between alternating bright fringes is 0.83 cm, and the light source has a wavelength of 580 nm, what is the separation of the double slits? (1 nm = 10 - 9 m)
A) 6.0 *10 - 5 m
B) 2.8 *10 - 5 m
C) 4.9 *10 - 5 m
D) 5.6 *10 - 5 m
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What wavelength monochromatic source in the visible region (390 to 710 nm) can be used to constructively reflect off a soap film (n = 1.46) in air if the film is 70.0 nm thick?
A) 558 nm
B) 430 nm
C) 450 nm
D) 409 nm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following primarily determines the resolution of a telescope?
A) the diameter of the eyepiece
B) the diameter of the objective
C) the focal length of the objective
D) the barrel length
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A telescope is used to view two small lights separated by 2.0 cm at a distance of 500 m. What minimum objective lens diameter is needed to just resolve these objects if their wavelength is 656 nm?
A) 2.0 cm
B) 1.0 cm
C) 1.2 cm
D) 2.4 cm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A thin film ( 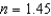 ) of thickness 77.6 nm, applied to a camera lens (
) of thickness 77.6 nm, applied to a camera lens ( 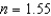 ) , is the minimum thickness that results in destructive interference for reflected light of wavelength 450 nm. which of the following is the next greater thickness that will also give destructive interference for this wavelength?
) , is the minimum thickness that results in destructive interference for reflected light of wavelength 450 nm. which of the following is the next greater thickness that will also give destructive interference for this wavelength?
A) 120 nm
B) 155 nm
C) 116 nm
D) 233 nm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fringe shift occurs for every ______ wavelength movement of the adjustable mirror in a Michelson interferometer. A fringe shift occurs when the intensity goes from bright to dark or when it goes from dark to bright.
A) half
B) eighth
C) quarter
D) whole
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A silicon monoxide (n = 1.45) film of 108 nm thickness is used to coat a glass camera lens (n = 1.56) . What wavelength of light in the visible region (390 to 710 nm) will be most efficiently transmitted by this system? (1 nm = 10 - 9 m)
A) 580 nm
B) 400 nm
C) 492 nm
D) 626 nm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 83
Related Exams