A) increase the supply of loanable funds and reduce interest rates.
B) be offset by a decrease in savings by businesses.
C) cause long-run fluctuations in the rate of consumption.
D) result in a decline in aggregate demand, output, and employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When government spending flows to areas where resources are already fully employed,
A) the additional spending will stimulate strong growth in those areas.
B) aggregate demand will place downward pressure on the general level of prices.
C) the coordination problem accompanying the composition of aggregate demand is likely to improve.
D) the coordination problem accompanying the composition of aggregate demand is likely to worsen.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is part of the synthesis view of fiscal policy?
A) During a severe recession, the best policy is a "balanced budget policy."
B) During a recession, higher real interest rates and lower net exports will help direct the economy back to full employment.
C) Since changes in discretionary policy are easy to time, fiscal policy should be altered in response to each minor disturbance.
D) Automatic stabilizers help reduce the fluctuations in aggregate demand and output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Both the crowding-out effect and new classical model indicate that
A) expansionary fiscal policy is a highly effective weapon with which to fight an economic downturn.
B) restrictive fiscal policy is a highly effective weapon with which to control inflation caused by excess demand.
C) there are side effects of budget deficits that will substantially, if not entirely, offset their expansionary impact on aggregate demand.
D) fiscal policy can be used effectively to restrain inflation but it is largely ineffective as a weapon against recession.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best explains why high marginal tax rates retard output?
A) High marginal tax rates reduce the incentive to earn, invest, and use resources efficiently.
B) High marginal tax rates will encourage foreign investment.
C) High marginal tax rates will reduce budget deficits and lower interest rates.
D) High marginal tax rates encourage people to substitute more-desired nondeductible goods for less-desired tax-deductible goods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a reduction in government borrowing leads to lower real interest rates in the United States,
A) U.S.investors will decrease their investments abroad.
B) U.S.exports will decrease relative to imports.
C) the inflow of loanable funds from abroad will moderate the fall in the real rate of interest.
D) the dollar will depreciate in the foreign exchange market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Historically, Keynesian economists have argued that government spending will stimulate aggregate demand more than tax cuts because
A) government spending will stimulate aggregate demand more quickly than a tax cut.
B) there are fewer adverse side effects to an increase in government spending.
C) all of the spending will add to aggregate demand, but a portion of the tax cut will be saved.
D) an increase in government spending can quickly be reversed once the economy has recovered.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Measured as a share of GDP, federal spending during 2001-2010
A) increased more rapidly than during the 1990s.
B) increased less rapidly than during the 1990s.
C) declined after increasing rapidly during the 1990s.
D) was virtually unchanged during the decade.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the critics of Keynesian economics, the rapid increase in government spending and large budget deficits in response to the recession of 2008-2009 would
A) slow the recovery process and result in weak long-term growth of real GDP.
B) speed the recovery process and provide the foundation for strong long-term growth of real GDP.
C) stimulate a more rapid recovery, but cause the economy to fall back into a recession in the near future.
D) slow the recovery process, but provide a foundation for rapid long-term growth of real GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following question(s) .
Figure 12-3 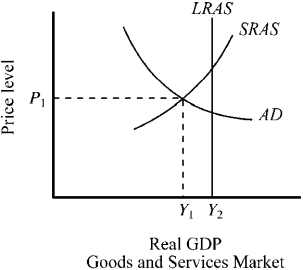 -Refer to Figure 12-3. If an economy is currently operating at Y1, which of the following would a new classical economist be most likely to favor?
-Refer to Figure 12-3. If an economy is currently operating at Y1, which of the following would a new classical economist be most likely to favor?
A) higher taxes and reductions in expenditures in order to shift the budget toward a surplus
B) lower taxes and increase in expenditures in order to shift the budget toward a deficit
C) a balanced budget
D) no government action and reliance on the self-corrective mechanism
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Kimani sells life insurance and is considering buying a $50,000 Cadillac for business purposes (thus, the expense reduces her taxable income) . If Kimani is in the 40 percent marginal tax bracket, how much after-tax income will she have to give up in order to enjoy the Cadillac?
A) $20,000
B) $30,000
C) $25,000
D) $70,000
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fiscal policy moved toward expansion during the 1980s but toward restriction during the 1990s. How did these differences affect the economy?
A) The expansionary fiscal policy of the 1980s led to strong growth while the restrictive policy of the 1990s led to stagnation.
B) The expansionary fiscal policy of the 1980s led to weaker growth than the restrictive policy of the 1990s.
C) The expansionary fiscal policy of the 1980s generated more rapid growth than the restrictive policy of the 1990s.
D) There is little evidence that the differences in fiscal policy between the two decades exerted much impact on either aggregate demand or real output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The crowding-out effect refers to the possibility that an
A) increase in the money supply will result in a decline in taxes.
B) increase in consumption spending will crowd out government spending.
C) increase in private savings will crowd out the taxable income of households.
D) increase in government borrowing will result in higher interest rates, which will crowd out private investment and consumption.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most important for long-run growth and a healthy economy?
A) a low rate of household savings and a high rate of consumption
B) a high rate of both savings and consumption
C) a high rate of government expenditures financed by borrowing
D) high tax rates and budget surpluses
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a fiscal policy change is going to exert a stabilizing impact on the economy, it must
A) add demand stimulus during a slowdown but restraint during an economic boom.
B) exert an expansionary impact during all phases of the business cycle.
C) restrain aggregate demand during all phases of the business cycle.
D) keep the government's budget in balance.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Advocates of the crowding-out effect maintain that the large budget deficits during the recession of 2008-2009
A) stimulated output and employment, leading to a quicker recovery.
B) will lead to a slower recovery than would have been the case if government borrowing had been more restrained.
C) led to lower interest rates, stimulating private investment and consumption.
D) will lead to lower future taxes and more private spending as the economy recovers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since the mid-1980s, the debt-to-income ratio of American households
A) has remained about the same as the previous 25 years.
B) has been slowly declining.
C) has fluctuated between about 55 and 70 percent of after-tax income.
D) has rapidly increased.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the new classical model, a $100 billion increase in government purchases financed by borrowing will
A) increase the real interest rate, which will crowd out private spending.
B) lead to a $100 billion increase in real GDP.
C) lead to a $400 billion increase in real GDP if the marginal propensity to consume is three-fourths.
D) leave the interest rate, aggregate demand, and real output unchanged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fiscal stimulus is most likely to direct resources into productive projects when spending decisions are left in the hands of
A) government agencies.
B) consumers.
C) Congress.
D) lobbyists and special-interest groups.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The crowding-out effect indicates that budget deficits
A) will stimulate aggregate demand and, therefore, exert a strong impact on output and employment.
B) will lead to additional borrowing and higher interest rates that will reduce the level of private spending.
C) are highly appropriate when the threat of inflation is present.
D) are highly appropriate when the threat of recession is present.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 146
Related Exams