A) wages and other costs of production respond immediately to changes in prices.
B) profit is lower when prices increase, so output decreases.
C) workers are willing to work for lower wages rather than be laid off.
D) higher prices lead to higher profit and higher output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the U.S. government doubles its spending on health care. The _____ curve shifts _____, output _____, and prices _____.
A) short-run aggregate supply; right; increases; decrease
B) short-run aggregate supply; left; decreases; increase
C) aggregate demand; left; decreases; decrease
D) aggregate demand; right; increases; increase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Demand shocks do NOT include a(n) :
A) reduction in money supply.
B) tax increase.
C) increase in government expenditure.
D) increase in commodity prices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The negative relationship between the aggregate price level and aggregate output demanded gives the aggregate demand curve a _____ slope.
A) positive
B) vertical
C) horizontal
D) negative
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The short-run aggregate supply curve slopes upward because a _____ aggregate price level leads to _____.
A) higher; lower output as costs of production increase
B) higher; higher output, since most production costs are fixed in the short run
C) lower; higher output, since production costs tend to fall in the short run
D) lower; higher profit and higher productivity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: The Multiplier 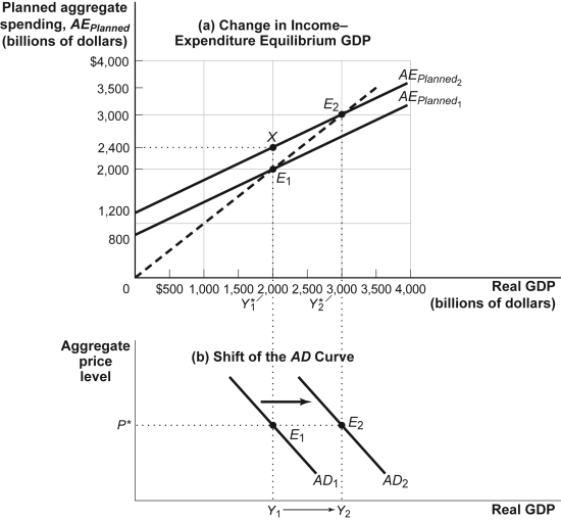 -(Figure: The Multiplier) Refer to Figure: The Multiplier. If this economy is at Y1 and the price level decreases:
-(Figure: The Multiplier) Refer to Figure: The Multiplier. If this economy is at Y1 and the price level decreases:
A) AD1 will shift to the left, reflecting a multiplied decrease in real GDP at every price level.
B) AD1 will shift to the right, reflecting a multiplied increase in real GDP at every price level.
C) an upward movement along the AD1 will take place, reflecting an increase in the price level.
D) a downward movement along the AD1 will take place, reflecting a decrease in the price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the stock market crashes, which causes a large decrease in the value of many households' financial assets. The most likely outcome is a _____ the aggregate demand curve.
A) rightward shift of
B) leftward shift of
C) movement up
D) movement down
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rise in labor productivity will MOST likely result in a(n) :
A) increase in aggregate demand.
B) decrease in aggregate demand.
C) decrease in aggregate supply.
D) increase in aggregate supply.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that a presidential candidate who promised large personal income tax cuts is elected. Which outcome is MOST likely?
A) a decrease in short-run aggregate supply
B) a decrease in aggregate demand
C) an increase in short-run aggregate supply
D) an increase in aggregate demand
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Aggregate Supply 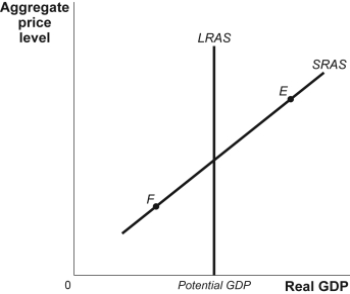 -(Figure: Aggregate Supply) Refer to Figure: Aggregate Supply. At point F, potential output is _____ than actual output and unemployment is _____.
-(Figure: Aggregate Supply) Refer to Figure: Aggregate Supply. At point F, potential output is _____ than actual output and unemployment is _____.
A) less; high
B) less; low
C) higher; high
D) higher; low
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate demand curve is negatively sloped in part because of the impact of:
A) the wealth effect on consumption.
B) the interest rate effect on government spending.
C) the stickiness of nominal wages and salaries.
D) the flexibility of nominal wages and salaries.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Potential output:
A) is the level of output that the economy would produce if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible.
B) varies with the price level.
C) depends on the level of consumer confidence.
D) is greater in periods of expansion than in recessions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When short-run aggregate supply increases, it means that the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right, showing that producers are willing to produce more at each price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest rate effect leads to a downward-sloping aggregate demand curve because a higher price level causes consumption to _____ and investment to _____.
A) decrease; decrease
B) decrease; increase
C) increase; decrease
D) increase; increase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The aggregate demand curve is negatively sloped because of the:
A) substitution effect of an aggregate price level change.
B) wealth effect of an aggregate price level change.
C) elasticity effect of an aggregate price level change.
D) fiscal policy effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run, changes in the aggregate price level will be accompanied by _____ proportional changes in input prices.
A) less than
B) more than
C) equal
D) opposite
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An inflationary gap will be eliminated because there is _____ pressure on wages, shifting the _____.
A) downward; long-run aggregate supply curve to the right
B) downward; long-run aggregate supply curve to the left
C) downward; aggregate demand curve to the left
D) upward; short-run aggregate supply curve to the left
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Policy Alternatives 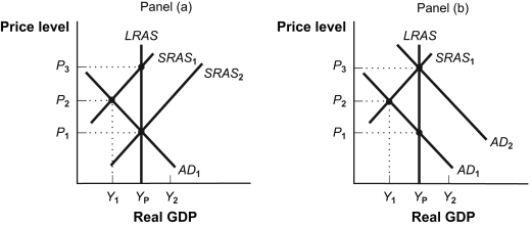 -(Figure: Policy Alternatives) Refer to Figure: Policy Alternatives. If the economy is in equilibrium at Y1 in panel (a) and the government decides to intervene, it will MOST likely:
-(Figure: Policy Alternatives) Refer to Figure: Policy Alternatives. If the economy is in equilibrium at Y1 in panel (a) and the government decides to intervene, it will MOST likely:
A) increase taxes.
B) decrease the money supply.
C) increase its spending.
D) decrease its spending.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A change in _____ has the MOST direct effect on aggregate demand.
A) taxes
B) interest rates
C) the money supply
D) government spending
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An economic policy maker would rank a _____ shock as the MOST preferred type.
A) positive demand
B) negative demand
C) positive supply
D) negative supply
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 308
Related Exams