A) It is a mechanism for increasing the rate of translation.
B) It can allow the production of proteins of different sizes and functions from a single mRNA.
C) It can allow the production of similar proteins from different RNAs.
D) It increases the rate of transcription.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the central dogma, what is the intermediate molecule involved in the flow of information in a cell that should go in the blank? DNA → ________ → Proteins
A) mtDNA
B) rRNA
C) mRNA
D) tRNA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which component is not directly involved in translation?
A) GTP
B) DNA
C) tRNA
D) ribosomes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following molecules are required for the process of translation?
A) mRNA, tRNA, DNA, and rRNA
B) mRNA, DNA, and rRNA
C) mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA
D) mRNA, tRNA, and DNA
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Transcription in eukaryotes requires which of the following molecules in addition to RNA polymerase?
A) anticodons
B) ribosomes and tRNA
C) several transcription factors
D) aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In eukaryotic cells, transcription cannot begin until
A) the two DNA strands have completely separated and exposed the promoter.
B) several transcription factors have bound to the promoter.
C) the 5 caps are removed from the mRNA.
D) the DNA introns are removed from the template.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question.
A part of an mRNA molecule with the following sequence is being read by a ribosome: 5′-CCG-ACG-3′ (mRNA) . The following charged transfer RNA molecules (with their anticodons shown in the 3′ to 5′ direction) are available. Two of them can correctly match the mRNA so that a dipeptide can form.
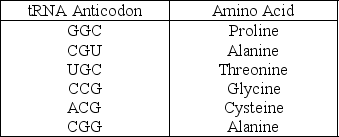 Which of the following anticodons in the first tRNA to bind will complement this mRNA?
Which of the following anticodons in the first tRNA to bind will complement this mRNA?
A) 3′-GGC-5′
B) 5′-GGC-3′
C) 5′-UGC-3′
D) 3′-UGC-5′
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
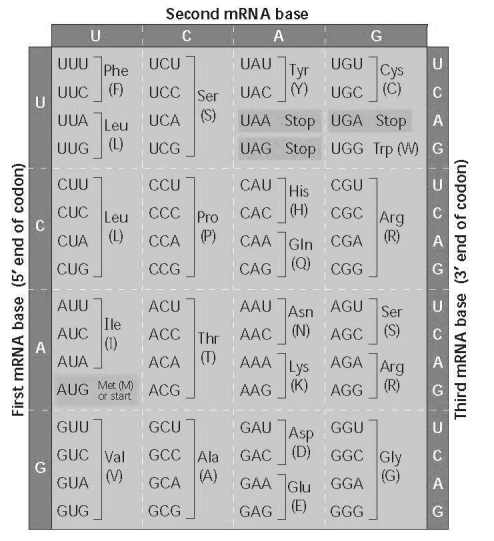 Using Figure 17.6, identify a 5′ → 3′ sequence of nucleotides in the DNA template strand for an mRNA coding for the polypeptide sequence Phe-Pro-Lys.
Using Figure 17.6, identify a 5′ → 3′ sequence of nucleotides in the DNA template strand for an mRNA coding for the polypeptide sequence Phe-Pro-Lys.
A) 5-UUUCCCAAA-3
B) 5-GAACCCCTT-3
C) 5-CTTCGGGAA-3
D) 5-AAACCCUUU-3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes the significance of the TATA box in the promoters of eukaryotes?
A) It is the recognition site for the binding of a specific transcription factor.
B) It sets the reading frame of the mRNA during translation.
C) It is the recognition site for ribosomal binding during translation.
D) It is the recognition site for ribosomal binding during transcription.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is the most current description of a gene?
A) a unit of heredity that causes formation of a phenotypic characteristic
B) a DNA subunit that codes for a single complete protein
C) a DNA sequence that is expressed to form a functional product: either RNA or polypeptide
D) a discrete unit of hereditary information that consists of a sequence of amino acids
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the function of the release factor during translation in eukaryotes?
A) It binds to the stop codon in the A site in place of a tRNA.
B) It releases the amino acid from its tRNA to allow the amino acid to form a peptide bond.
C) It supplies a source of energy for termination of translation.
D) It releases the ribosome from the ER to allow polypeptides into the cytosol.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Accuracy in the translation of mRNA into the primary structure of a polypeptide depends on specificity in the ________.
A) binding of ribosomes to mRNA
B) binding of the anticodon to small subunit of the ribosome
C) attachment of amino acids to rRNAs
D) binding of the anticodon to the codon and the attachment of amino acids to tRNAs
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most commonly occurring mutation in people with cystic fibrosis is a deletion of a single codon. What is the result of this type of mutation?
A) a base-pair substitution
B) a frameshift mutation
C) a polypeptide missing an amino acid
D) a nonsense mutation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of mutation, resulting in an error in the mRNA just after the AUG start of translation, is likely to have the most serious effect on the polypeptide product?
A) a deletion of a codon
B) a deletion of two nucleotides
C) a substitution of the third nucleotide in an ACC codon
D) a substitution of the first nucleotide of a GGG codon
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Post-translational modifications of proteins may include which of the following processes?
A) removal of introns
B) addition of a 5′ cap
C) addition of a poly-A tail
D) addition of carbohydrates to form a glycoprotein
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure to answer the question.
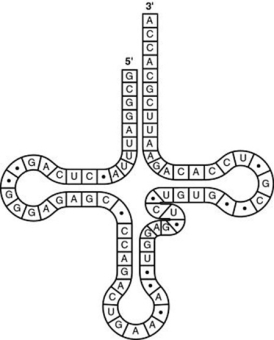 The figure represents tRNA that recognizes and binds a particular amino acid (in this instance, phenylalanine) . Which codon on the mRNA strand codes for this amino acid?
The figure represents tRNA that recognizes and binds a particular amino acid (in this instance, phenylalanine) . Which codon on the mRNA strand codes for this amino acid?
A) 5′-UGG-3′
B) 3′-GUG-5′
C) 5′-GUA-3′
D) 5′-UUC-3′
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes the effect a nonsense mutation would have on a gene?
A) It changes an amino acid in the encoded protein.
B) It has no effect on the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein.
C) It introduces a premature stop codon into the mRNA.
D) It alters the reading frame of the mRNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes a ribozyme?
A) It is a catalyst that uses RNA as a substrate.
B) It is an RNA with catalytic activity.
C) It is an enzyme that catalyzes the association between the large and small ribosomal subunits.
D) It is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA as part of the transcription process.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The anticodon of a particular tRNA molecule is
A) complementary to the corresponding mRNA codon.
B) complementary to the corresponding triplet in rRNA.
C) the part of tRNA that bonds to a specific amino acid.
D) catalytic, making the tRNA a ribozyme.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Codons are three-base sequences in mRNA that specify the addition of a single amino acid to the growing protein chain during translation. How do eukaryotic codons and prokaryotic codons compare?
A) Prokaryotic codons usually contain different bases than those of eukaryotes.
B) Prokaryotic codons usually specify different amino acids than those of eukaryotes.
C) The translation of codons is mediated by tRNAs in eukaryotes, but translation requires no intermediate molecules such as tRNAs in prokaryotes.
D) Codons are a nearly universal language among all organisms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 67
Related Exams