A) the short-run Phillips curve shifts left
B) unemployment rises
C) the price level rises
D) output falls
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In his famous article published in an economics journal in 1958,A.W.Phillips
A) used data for the United States to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of the U.S.consumer price index and the U.S.unemployment rate.
B) used data for the United States to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of wages in the U.S.and the U.S.unemployment rate.
C) used data for the United Kingdom to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of the U.K.consumer price index and the U.K.unemployment rate.
D) used data for the United Kingdom to show a negative relationship between the rate of change of wages in the U.K.and the U.K.unemployment rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Samuelson and Solow argued that a combination of low unemployment and low inflation
A) was impossible given the historical data as summarized by the Phillips curve.
B) could be achieved with an "appropriate" fiscal policy.
C) could be achieved with an "appropriate" monetary policy.
D) could be achieved with an "appropriate" mix of monetary and fiscal policies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the short-run Phillips curve,inflation
A) and unemployment would fall if the policymakers decreased the money supply.
B) would fall and unemployment would rise if policymakers decreased the money supply.
C) and unemployment would fall if the policymakers increased the money supply.
D) would fall and unemployment would rise if policymakers increased the money supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Fed increases the growth rate of the money supply,in the long run which of the following is unchanged?
A) the unemployment rate and inflation
B) the unemployment rate but not inflation
C) inflation but not the unemployment rate
D) neither inflation nor the unemployment rate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Samuelson and Solow argued that when unemployment is high,
A) aggregate demand is high,which puts upward pressure on wages and prices.
B) aggregate demand is high,which puts downward pressure on wages and prices.
C) aggregate demand is low,which puts upward pressure on wages and prices.
D) aggregate demand is low,which puts downward pressure on wages and prices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the late 1970s,proponents of rational expectations argued that
A) the Fed should not attempt to aggressively fight inflation.
B) the sacrifice ratio was smaller than previously thought.
C) the short run was relatively long.
D) None of the above is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 22-2
Use the pair of diagrams below to answer the following questions.
 -Refer to Figure 22-2.If the economy starts at C and 1,then in the short run,an increase in taxes moves the economy to
-Refer to Figure 22-2.If the economy starts at C and 1,then in the short run,an increase in taxes moves the economy to
A) B and 2.
B) D and 3.
C) E and 2.
D) None of the above is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 22-8.The left-hand graph shows a short-run aggregate-supply (SRAS) curve and two aggregate-demand (AD) curves.On the right-hand diagram,"Inf Rate" means "Inflation Rate." 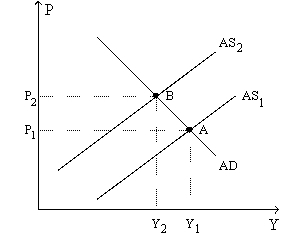
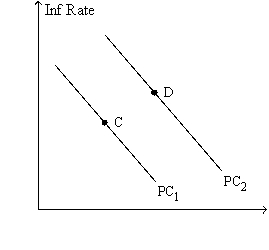 -Refer to Figure 22-8.The shift of the aggregate-supply curve from AS1 to AS2
-Refer to Figure 22-8.The shift of the aggregate-supply curve from AS1 to AS2
A) results in a more favorable trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) results in a more favorable trade-off between inflation and the growth rate of real GDP.
C) represents an adverse shock to aggregate supply.
D) represents a favorable shock to aggregate supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Unexpectedly high inflation reduces unemployment in the short run,but as inflation expectations adjust the unemployment rate returns to its natural rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A favorable supply shock will cause
A) unemployment to rise and the short-run Phillips curve to shift right.
B) unemployment to rise and the short-run Phillips curve to shift left.
C) unemployment to fall and the short-run Phillips curve to shift right.
D) unemployment to fall and the short-run Phillips curve to shift left.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Natural rate of unemployment - a *(ctual inflation - Expected inflation) =
A) Quantity of goods and services demanded.
B) Quantity of goods and services supplied.
C) Unemployment rate.
D) Previous year's inflation rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Federal Reserve decreases the rate at which it increases the money supply,then unemployment is higher in
A) the long run and the short run.
B) the long run but not the short run.
C) the short run but not the long run.
D) neither the short run nor the long run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The misery index is supposed to measure the
A) social cost of unemployment.
B) health of the economy.
C) lost output associated with a particular unemployment rate.
D) short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In responding to the Phillips curve hypothesis,Friedman argued that the Fed can peg the
A) unemployment rate.
B) inflation rate.
C) growth rate of real national income.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As aggregate demand shifts right along the aggregate supply curve,
A) inflation and unemployment are higher.
B) inflation is higher and unemployment is lower.
C) unemployment is higher and inflation is lower.
D) unemployment and inflation are lower.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a central bank increases the money supply in response to an adverse supply shock,then which of the following quantities moves closer to its pre-shock value as a result?
A) both the price level and output
B) the price level but not output
C) output but not the price level
D) neither output nor the price level
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The experience of the Volcker disinflation of the early 1980s
A) generally increased estimates of the sacrifice ratio.
B) generally decreased estimates of the sacrifice ratio.
C) clearly refuted the predictions of the proponents of rational expectations.
D) clearly refuted the predictions of the opponents of rational expectations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If unemployment is below its natural rate,what happens to move the economy to long-run equilibrium?
A) Inflation expectations rise which shifts the short-run Phillips curve to the right.
B) Inflation expectations rise which shifts the short-run Phillips curve to the left.
C) Inflation expectations fall which shifts the short-run Phillips curve to the right.
D) Inflation expectations fall which shifts the short-run Phillips curve to the left.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A favorable supply shock causes the price level to
A) rise.To counter this a central bank would increase the money supply.
B) rise.To counter this a central bank would decrease the money supply.
C) fall.To counter this a central bank would increase the money supply.
D) fall.To counter this a central bank would decrease the money supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 240 of 415
Related Exams