Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following factors would be most likely to encourage investment and capital formation in a less-developed nation?
A) High and variable rates of inflation.
B) Tariffs and quotas that restrict international trade.
C) A legal system that provides for secure property rights and evenhanded enforcement of contracts.
D) High marginal tax rates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is infrastructure?
A) Schools.
B) Roads.
C) Public health and sanitation services.
D) All of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following helps low-income countries grow rapidly relative to high-income countries?
A) Low-income countries are in a better position to save a larger share of their income.
B) Low-income countries can employ technologies and practices that have been successful in high-income countries.
C) Low-income countries generally have legal systems that protect property rights and enforce contracts in a more evenhanded manner.
D) Low-income countries generally have more favorable weather conditions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A country with a high GDP per capita is classified as an industrially advanced country (IAC).
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an example of a country's infrastructure?
A) Transportation system.
B) Communications system.
C) Political system.
D) Educational system.
E) Energy system.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not hinder economic development?
A) Low birth rates.
B) Low GDP that limits saving and investment.
C) Lack of knowledge.
D) Lack of technology.
E) Lack of physical capital.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A country can develop without a large natural resource base.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a common characteristic of IACs?
A) Market-based economies.
B) Large stocks of technologically advanced capital.
C) Well-educated labor.
D) Low per capita energy consumption.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following represents a problem with using per capita GDP to compare standard of living between less-developed and industrially advanced countries?
A) GDP per capita does not take into account differences in population between countries.
B) GDP is particularly difficult to measure in industrially advanced countries because a much larger percentage of economic activity occurs outside of officially measured market activity than in less-developed countries.
C) GDP per capita will overstate the prevailing standard of living for the average person in countries with extreme levels of income inequality.
D) None of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In order for a country to develop a high per capita GDP, it must have a rich endowment of natural resources, particularly energy and mineral resources.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
According to the text, Singapore and Hong Kong are classified as industrially advanced countries (IACs).
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most likely to help the residents of a nation produce more goods and services and achieve higher income levels?
A) Higher tax rates.
B) A higher rate of investment.
C) A smaller trade sector.
D) Greater use of taxation to transfer income from the rich to the poor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In general, GDP per capita is highly correlated with alternative measures of quality of life.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a country's real GDP is growing at 5 percent and the population is also growing at 5 percent, its:
A) per capita real GDP grows at an increasing rate.
B) per capita real GDP grows at a constant rate.
C) population growth will eventually exceed real GDP.
D) per capita real GDP decreases at a constant rate.
E) per capita real GDP does not change.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
GDP per capita is a relatively good measurement of:
A) the distribution of income.
B) purchasing power.
C) household production.
D) the standard of living.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If population grows faster than GDP, then per capita GDP must fall.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 17-1 Nation of Padia 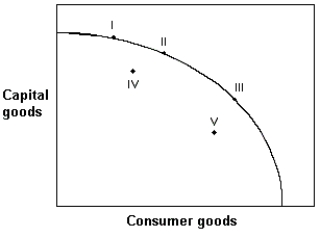 -Exhibit 17-1 shows the production possibility curve of the nation of Padia. Based only on this information, the point which would produce the highest rate of growth would be:
-Exhibit 17-1 shows the production possibility curve of the nation of Padia. Based only on this information, the point which would produce the highest rate of growth would be:
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy's population grows at 3 percent and real GDP grows at 2 percent, then:
A) per capita real GDP is declining.
B) the economy's standard of living is increasing.
C) per capita real GDP is negative.
D) per capita real GDP is growing.
E) the economy is experiencing unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) A less developed country (LDC) is a country with a low GDP per capita, low levels of capital, and uneducated workers.
B) The vicious circle of poverty exists because GDP must rise before people can save and invest.
C) LDCs are characterized by rapid population growth and low levels of investment in human capital.
D) All of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 117
Related Exams