A) 32 percent, and total expenditure will rise.
B) 50 percent, and total expenditure will rise.
C) 15 percent, and total expenditure will fall.
D) 15 percent, and total expenditure will rise.
E) 12 percent, and total expenditure will fall.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the quantity of lemonade demanded falls from 103 000 litres per week to 97 000 litresper week as a result of a 10 percent increase in its price. The price elasticity of demand forlemonade is therefore
A) 6.0.
B) 1.03.
C) 0.6.
D) 1.97.
E) impossible to compute unless we know the before and after prices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the quantity demanded of skipping ropes rises from 1250 to 1750 units when the price falls from $1.25 to $0.75 per unit. The price elasticity of demand for this product is
A) 2.
B) 2/3.
C) 1/3.
D) 3/2.
E) 1.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that as the price of some product increases from $4.00 to $5.00 per unit the quantitysupplied rises from 500 to 1000 units per month. The price elasticity of supply for this product is
A) 3.0.
B) 1.0.
C) 2.0.
D) 0.33.
E) 2.5.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements would you expect to be true about the demand elasticities for cornflakes and food?
A) Compared with food, cornflakes has a lower price elasticity of demand because it is specifically defined.
B) Food has a lower price elasticity of demand than cornflakes because it is more broadly defined.
C) Food has a higher price elasticity of demand because it is a necessity.
D) Because cornflakes is food, cornflakes would have the same price elasticity of demand as food.
E) Because cornflakes is food, but not all food is cornflakes, cornflakes would have a lower price elasticity of demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the current level of output of some good is 100 units. If market demand is inelastic at that quantity, total expenditure on this product would be higher if output was
A) kept constant.
B) maximized.
C) less than 100 units.
D) minimized.
E) greater than 100 units.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A value of infinity for the elasticity of supply of some product implies that
A) no product will be supplied at any price.
B) the supply curve is vertical.
C) supply is very unresponsive to price.
D) the supply curve is horizontal.
E) the product will be supplied at any price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following data for a hypothetical economy.  TABLE 4-4
-If demand is inelastic, an increase in price will cause total expenditure to
TABLE 4-4
-If demand is inelastic, an increase in price will cause total expenditure to
A) fall to zero.
B) remain constant.
C) decrease.
D) increase.
E) be negative.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the quantity of a good demanded rises from 90 units to 110 units when the price falls from $1.20 to 80 cents per unit. The price elasticity of demand for this product is
A) 1.0
B) 4.0
C) 0.5
D) 2.0
E) 1.5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If total expenditure on a product rises and falls directly with a product's price, then demand for this product has an elasticity of
A) zero.
B) greater than one.
C) less than one.
D) one.
E) direct proportions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following tends to be true of the income elasticity of demand for food?
A) At low levels of income, it tends to be fairly high; but as the level of income rises, it tends to fall.
B) It tends to be well above unity only at high levels of income.
C) It is usually zero, since we can only eat so much.
D) It tends to be well below unity only at low levels of income.
E) It tends to remain fairly constant at all levels of income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An upward-sloping straight-line supply curve through the origin has an elasticity of
A) zero.
B) infinity.
C) greater than one.
D) less than one.
E) one.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If Vicky's income increases by 8% and she increases her consumption of music downloads by 4%,then her income elasticity of demand for music downloads is
A) 2.0.
B) -0.5.
C) -2.0.
D) 4.0.
E) 0.5.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "economic incidence" of an excise tax illustrates
A) who is legally responsible for paying it to the government.
B) who bears the burden of the tax.
C) the legislative process it must pass through.
D) the political process for implementing a tax.
E) the economic costs of avoiding it.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Income elasticity of demand measures the extent to which
A) one household's income changes when there is a change in the income of another household.
B) the quantity demanded of a good changes when income changes.
C) the price of a good changes when there is a change in income.
D) quantity demanded changes when there is a change in price.
E) real household income changes when there is a change in the price of a good.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the price elasticity of demand is 1.4, a 10 percent increase in the price of the good results in
A) a 14 percent increase in the quantity demanded.
B) a 1.4 percent increase in the quantity demanded.
C) a 1.4 percent decrease in the quantity demanded.
D) a 14 percent decrease in the quantity demanded.
E) There is not enough information to answer this question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The price elasticity of demand for a product tends to be greater the
A) more close substitutes for it there are.
B) fewer close substitutes for it there are.
C) lower its price.
D) more broadly the product is defined.
E) shorter the time span being considered.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table below shows the demand schedule for museum admissions in a small city. 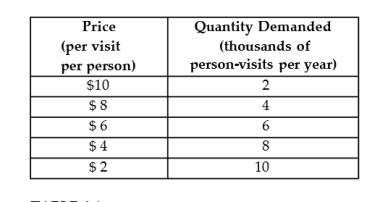 TABLE 4-1
-Refer to Table 4-1. Between the prices of $8 and $10, the elasticity of demand is
TABLE 4-1
-Refer to Table 4-1. Between the prices of $8 and $10, the elasticity of demand is
A) 1/3.
B) 3.
C) 2.
D) 2/3.
E) 1.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A vertical demand curve shows that the own-price elasticity of demand is
A) less than one.
B) unity.
C) zero.
D) not defined.
E) infinity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A perfectly horizontal demand curve shows that the own-price elasticity of demand is
A) unity.
B) less than one.
C) zero.
D) not defined.
E) infinite.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 94
Related Exams