Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An unanticipated decrease in aggregate demand will cause an upward shift in the short-run Phillips curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 16-2
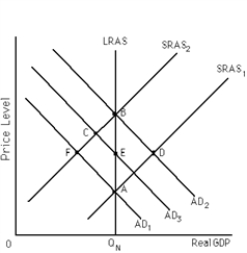 -Refer to Exhibit 16-2. Suppose the economy starts out at point A. Next, the public anticipates that the Fed will use expansionary monetary policy to shift the AD curve from AD1 to AD2. What happens, instead, is that the Fed does not raise aggregate demand as much as the public expects (bias upward) . Instead the Fed pushes the AD curve from AD1 to AD3. As a result, according to new classical theory in the short run the economy moves to point
-Refer to Exhibit 16-2. Suppose the economy starts out at point A. Next, the public anticipates that the Fed will use expansionary monetary policy to shift the AD curve from AD1 to AD2. What happens, instead, is that the Fed does not raise aggregate demand as much as the public expects (bias upward) . Instead the Fed pushes the AD curve from AD1 to AD3. As a result, according to new classical theory in the short run the economy moves to point
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Events of the 1970s and early 1980s showed that
A) the Phillips curve presents policymakers with a stable menu of choices.
B) cycles of unemployment and inflation rates appear to have gravitated around a 6 percent unemployment rate.
C) lower inflation rates are consistently accompanied by higher unemployment rates.
D) a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment may not always exist.
E) a and c
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to new classical economists, if a decrease in aggregate demand is correctly anticipated, the short-run aggregate supply curve will shift __________ at the same time the AD curve shifts _________ so that there will be no change in Real GDP.
A) rightward; rightward
B) leftward; leftward
C) leftward; rightward
D) rightward; leftward
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 16-2
 -Refer to Exhibit 16-2. Suppose the economy starts at point A. The AD curve shifts from AD1 to AD2 and the public perfectly anticipates this. Under new Keynesian macroeconomic assumptions, the most likely short-run equilibrium point will be
-Refer to Exhibit 16-2. Suppose the economy starts at point A. The AD curve shifts from AD1 to AD2 and the public perfectly anticipates this. Under new Keynesian macroeconomic assumptions, the most likely short-run equilibrium point will be
A) point B.
B) point E.
C) somewhere on the line between point D and point B.
D) somewhere on the line between point E and point B.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the original Phillips curve, the cost of reducing the unemployment rate in the short run is a
A) fall in Real GDP.
B) fall in nominal GDP.
C) lower rate of price inflation.
D) higher rate of wage inflation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The economy is in long-run equilibrium when there is an incorrectly anticipated increase in aggregate demand brought about by expansionary monetary policy. Specifically, aggregate demand increases by more than people anticipate (bias downward) . According to new classical theory, the price level will __________ and Real GDP will __________ in the short run. In the long run, the price level will be __________ than it was before aggregate demand increased.
A) rise; fall; higher
B) rise; rise; higher
C) fall; rise; lower
D) fall; rise; higher
E) rise; rise; lower
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Wages and prices are assumed to be completely inflexible in the new classical theory.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If expectations are formed rationally, wages and prices are completely flexible in both the short run and the long run, and policy is correctly anticipated, increases in aggregate demand will stimulate the economy to higher levels of Real GDP in
A) the short run or the long run.
B) neither the short run nor the long run.
C) the short run, but not in the long run.
D) the long run, but not in the short run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two key assumptions of new Keynesian theory include:
A) (1) people hold rational expectations, and (2) wages and prices are not completely flexible in the short run.
B) (1) people hold adaptive expectations, and (2) wages and prices are inflexible.
C) (1) people hold rational expectations, and (2) wages and prices are flexible.
D) (1) people hold neither adaptive nor rational expectations and (2) prices are inflexible.
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The economy was in long-run equilibrium when aggregate demand increased. At this point in time, the expected inflation has started to adjust to the new higher actual inflation rate. According to the (Friedman) natural rate theory, this means the unemployment rate in the economy must currently be
A) decreasing.
B) increasing.
C) higher than it was in long-run equilibrium.
D) equal to what it was in long-run equilibrium.
E) There is not enough information to answer the question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As the price level rises, real wage ____________and people choose to work ___________.
A) rises; more
B) rises; less
C) falls; more
D) falls; less
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In real business cycle theory, business cycle expansions begin as a result of changes in
A) GDP.
B) long-run aggregate supply.
C) aggregate demand.
D) consumption.
E) investment demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Samuelson and Solow, in their 1960 study of the Phillips curve as it applies to the U.S. experience, argued that there was a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. Later experience showed their analysis to be
A) entirely correct in every situation.
B) generally correct, but it could not explain stagflation.
C) wholly wrong in every situation.
D) in general agreement with rational expectations theory.
E) capable of explaining stagflation, but not other economic scenarios.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stagflation consists of
A) high inflation and low unemployment.
B) low inflation and high unemployment.
C) high inflation and high unemployment.
D) high unemployment and an economy in a deep recession.
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Samuelson-Solow version of the Phillips curve showed the relationship between unemployment rates and
A) Real GDP growth rates.
B) price inflation rates.
C) wage inflation rates.
D) imports.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that in a new classical model the public anticipates that policymakers will increase aggregate demand. However, aggregate demand increases by less than what the public anticipated. The result in the short run is that Real GDP ____________ and the price level ____________.
A) decreases; decreases
B) increases; increases
C) increases; decreases
D) decreases; increases
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 16-3
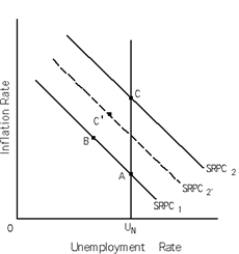 -Refer to Exhibit 16-3. The economy is at point A. As the result of an unexpected increase in aggregate demand, in the short run, the Friedman natural rate theory would predict
-Refer to Exhibit 16-3. The economy is at point A. As the result of an unexpected increase in aggregate demand, in the short run, the Friedman natural rate theory would predict
A) movement to point B.
B) movement to point C.
C) movement to point C'.
D) no movement from point A.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 16-8
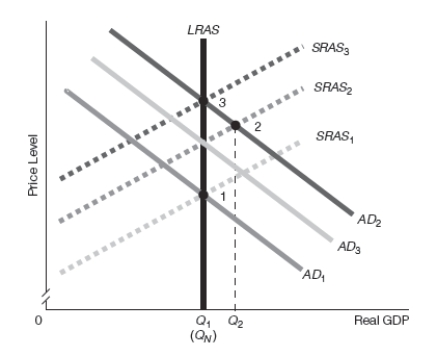 -Refer to Exhibit 16-8. Assume that the starting point is point 1. Suppose that the Fed implements expansionary monetary policy that raises aggregate demand. Which of the following best goes with the diagram shown?
-Refer to Exhibit 16-8. Assume that the starting point is point 1. Suppose that the Fed implements expansionary monetary policy that raises aggregate demand. Which of the following best goes with the diagram shown?
A) New classical theory with policy incorrectly anticipated, bias downward
B) New classical theory with policy incorrectly anticipated, bias upward
C) Real business cycle theory
D) New classical theory with policy unanticipated
E) Policy ineffectiveness proposition (PIP)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 150
Related Exams