A) two negative demand shocks.
B) a negative demand shock and a negative inflation shock.
C) two positive inflation shocks.
D) a negative demand shock and a positive inflation shock.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A negative demand shock will shift the ______ curve to the ______.
A) AD; left
B) AD; right
C) AS; left
D) AS; right
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the inflation rate increases, PAE ______, which in turn causes Y to ______ because of ______.
A) falls; fall; the income-expenditure multiplier
B) falls; rise; the income-expenditure multiplier
C) rises; rise; the wealth effect
D) rises; fall; the wealth effect
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a given inflation rate, if bright prospects for the future of the economy cause businesses to increase spending on new capital, then the ______ shifts _____.
A) aggregate demand curve; right
B) aggregate demand curve; left
C) aggregate supply curve; left
D) aggregate supply curve; right
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sudden change in the normal behavior of inflation, unrelated to the nation's output gap, is called:
A) short-run equilibrium.
B) long-run equilibrium.
C) an inflation shock.
D) inflation inertia.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Technological improvements:
A) decrease aggregate demand.
B) increase aggregate demand.
C) decrease aggregate supply.
D) increase aggregate supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Starting from potential output, if firms become less optimistic and decide to decrease their investment in new capital, then this will shift the ______ curve to the left and generate ______.
A) aggregate demand; a recessionary output gap
B) aggregate supply; a recessionary output gap
C) aggregate demand; an expansionary output gap
D) aggregate supply; an expansionary output gap
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Shifts in ______ can push the economy out of long-run equilibrium.
A) the AD curve only
B) the AS curve only
C) either the AD curve or the AS curve
D) the PAE line only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
High expected inflation leads to ____ increases in wages and costs and to ____ actual inflation.
A) large; high
B) large; low
C) small; low
D) small; high
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the economy is currently operating at potential output; an expansionary gap may be caused by each of the following except:
A) a positive demand shock.
B) a positive inflation shock.
C) an increase in government spending.
D) an increase in the inflation rate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The AD curve ______ because, holding all else constant, an increase in ______ causes C, IP and NX to fall.
A) slopes downward; real GDP
B) slopes downward; the inflation rate
C) slopes upward; real GDP
D) is horizontal; the inflation rate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graphically, short-run equilibrium occurs at the intersection of the aggregate demand curve and:
A) the aggregate supply curve and potential output.
B) the planned aggregate expenditure line.
C) the aggregate supply curve.
D) potential output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Due to menu costs, many firms in the economy will increase their output:
A) only after they raise the price at which they are willing to sell their output.
B) before raising the price at which they are willing to sell their output.
C) instead of raising the price at which they sell their output.
D) or raise the price at which they sell their output, but never both.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the economy is in short-run equilibrium, there will be ______ output gap.
A) no
B) only a recessionary
C) either a recessionary or an expansionary
D) only an expansionary
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure below.The current level of GDP in this economy is ______; the potential level of GDP is ______. 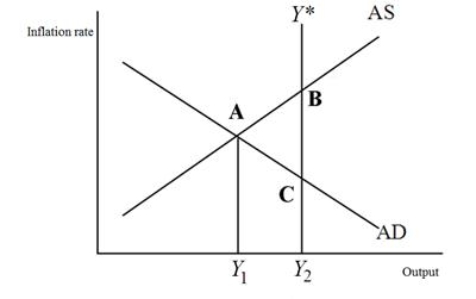
A) Y1; Y1
B) Y2; Y2
C) Y1; Y2
D) Y2; Y1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The self-correcting tendency of the economy means that falling inflation eventually eliminates:
A) expansionary gaps.
B) recessionary gaps.
C) exogenous spending.
D) unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When using the AD-AS model to understand business cycles, the question, "what are the fundamental causes of business cycles?" can be thought of as the question:
A) "what factors move the economy away from long-run equilibrium?"
B) "what factors move aggregate demand and aggregate supply in different directions?"
C) "what factors increase or decrease potential GDP?"
D) "what factors increase or decrease the expected rate of inflation?"
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Starting from long-run equilibrium, a large decrease in government purchases will result in a(n) ______gap in the short run and ____inflation and ____output in the long run.
A) expansionary; higher; potential
B) recessionary; lower; potential
C) expansionary; higher; higher
D) recessionary; higher; potential
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure below.Suppose the economy is initially in equilibrium with output Y2 and inflation rate of 3.An increase in military spending will: 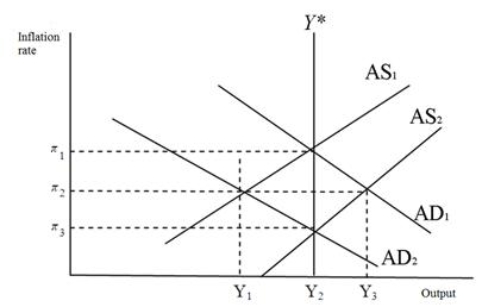
A) shift AD from AD2 to AD1.
B) shift AD from AD1 to AD2.
C) shift AS from AS2 to AS1.
D) shift AS from AS1 to AS2.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Changes in the expected rate of inflation will:
A) not shift the AS curve.
B) shift the AS curve leftward or rightward.
C) cause the AS curve to become vertical.
D) cause the AS curve to become downward-sloping.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 101
Related Exams