A) only in the presence of oxygen.
B) by aerobic respiration only.
C) by fermentation or aerobic respiration.
D) only in the absence of oxygen.
E) by glycolysis only.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An enzyme, citrate synthase, in the Krebs cycle is inhibited by ATP. This is an example of all of the following EXCEPT
A) noncompetitive inhibition.
B) allosteric inhibition.
C) competitive inhibition.
D) feedback inhibition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.2 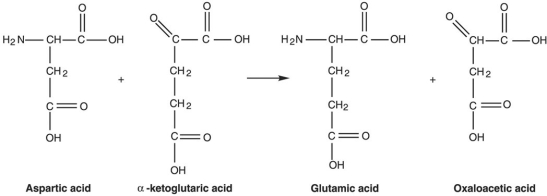 What type of reaction is in Figure 5.2?
What type of reaction is in Figure 5.2?
A) decarboxylation
B) dehydrogenation
C) oxidation
D) reduction
E) transamination
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Catabolic reactions are generally degradative and hydrolytic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.7 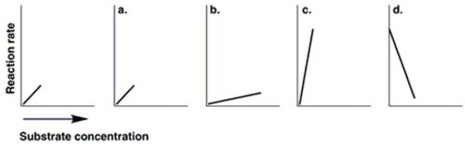 The graph at the left in Figure 5.7 shows the reaction rate for an enzyme at its optimum temperature. Which graph shows enzyme activity at a higher temperature?
The graph at the left in Figure 5.7 shows the reaction rate for an enzyme at its optimum temperature. Which graph shows enzyme activity at a higher temperature?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fatty acids are oxidized in
A) the Krebs cycle.
B) the Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
C) the pentose phosphate pathway.
D) the electron transport chain.
E) glycolysis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT necessary for respiration?
A) cytochromes
B) a source of electrons
C) quinones
D) flavoproteins
E) oxygen
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the best definition of oxidative phosphorylation?
A) A proton gradient allows hydrogen ions to flow back into the cells through transmembrane protein channels, releasing energy that is used to generate ATP.
B) Electrons are passed through a series of carriers to an organic compound.
C) Electrons are passed through a series of carriers to O₂.
D) ATP is directly transferred from a substrate to ADP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about substrate-level phosphorylation is FALSE?
A) It occurs in glycolysis.
B) It involves the direct transfer of a high-energy phosphate group from an intermediate metabolic compound to ADP.
C) No final electron acceptor is required.
D) It occurs to a lesser degree in the Krebs cycle than in glycolysis.
E) The oxidation of intermediate metabolic compounds releases energy that is used to generate ATP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.6 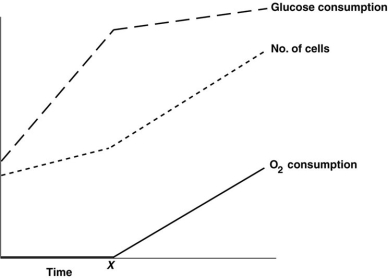 The rates of O₂ and glucose consumption by a bacterial culture are shown in Figure 5.6. Assume a bacterial culture was grown in a glucose medium without O₂. Then O₂ was added at the time marked X. The data indicate that
The rates of O₂ and glucose consumption by a bacterial culture are shown in Figure 5.6. Assume a bacterial culture was grown in a glucose medium without O₂. Then O₂ was added at the time marked X. The data indicate that
A) these bacteria cannot grow anaerobically.
B) these bacteria get more energy anaerobically.
C) aerobic metabolism is more efficient than fermentation.
D) these bacteria donʹt use O₂.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the best definition of fermentation?
A) the production of energy by oxidative-level phosphorylation
B) the complete catabolism of glucose to CO₂ and H₂O
C) the production of energy by both substrate and oxidative phosphorylation
D) the partial oxidation of glucose with organic molecules serving as electron acceptors
E) the partial reduction of glucose to pyruvic acid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.4 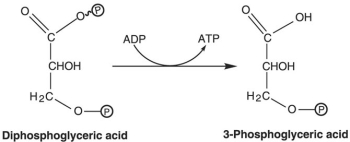 How is ATP generated in the reaction shown in Figure 5.4?
How is ATP generated in the reaction shown in Figure 5.4?
A) glycolysis
B) oxidative phosphorylation
C) photophosphorylation
D) fermentation
E) substrate-level phosphorylation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about anaerobic respiration is FALSE?
A) It requires cytochromes.
B) The complete Krebʹs cycle is utilized.
C) It yields lower amounts of ATP when compared to aerobic respiration.
D) It involves the reduction of an organic final electron acceptor.
E) It generates ATP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In green and purple bacteria, electrons to reduce CO₂ can come from
A) chlorophyll.
B) H2S.
C) CO₂.
D) C6H12O6.
E) H₂O.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding metabolism is FALSE?
A) ATP is formed in catabolic reactions.
B) Heat may be released in both anabolic and catabolic reactions.
C) ADP is formed in anabolic reactions.
D) Anabolic reactions are degradative.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.5 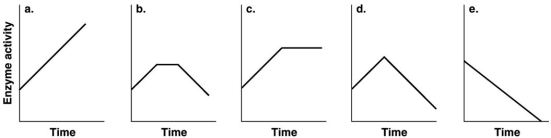 Which of the graphs in Figure 5.5 best illustrates the activity of an enzyme that is saturated with substrate?
Which of the graphs in Figure 5.5 best illustrates the activity of an enzyme that is saturated with substrate?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 5.8
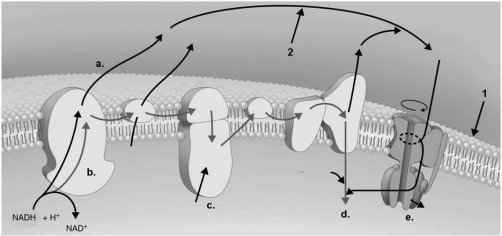 -In Figure 5.8, where is ATP produced?
-In Figure 5.8, where is ATP produced?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 57 of 57
Related Exams