A) a lepton.
B) a meson.
C) a baryon.
D) a gauge boson.
E) hadrons.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron with an energy of 20 GeV (3.20 × 10-9 J) moving in the +x direction collides head on with a stationary proton. After the collision, the electron travels in the -x direction. What is the momentum of the electron after the collision? Note that this is an ultrarelativistic collision so that the energy of the moving masses can be approximated by the expression E ≈ pc. The mass of a proton is 1.67 × 10-27 kg and that of an electron is 9.11 × 10-31kg.
A) 2.5 × 10-19 kg∙m/s
B) 5.0 × 10-19 kg∙m/s
C) 1.1 × 10-17 kg∙m/s
D) 2.2 × 10-17 kg∙m/s
E) 2.7 × 10-22 kg∙m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The greater the width of a resonance,
A) the greater the rest energy of the resonance.
B) the greater the lifetime of the resonance.
C) the lower the rest energy of the resonance.
D) the shorter the lifetime of the resonance.
E) None of the above answers are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The competition between the electrostatic force between the protons in a nucleus and the strong nuclear force determines whether a nucleus is stable.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the particle groups listed below includes two other groups on the list. Which group is it?
A) leptons
B) hadrons
C) mesons
D) bosons.
E) baryons
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One reason a photon could not create an odd number of electrons and positrons is that such a process would
A) not conserve charge.
B) not conserve energy.
C) require photon energies that are not attainable.
D) result in the creation of mass.
E) result in the destruction of mass.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a positronium atom (electron + positron) decays, it emits two photons. What are the energies of the photons?
A) 0.511 MeV and 1.022 MeV
B) 0.225 MeV and 1.022 MeV
C) 0.225 MeV and 0.285 MeV
D) 0.256 MeV and 0.256 MeV
E) 0.511 MeV and 0.511 MeV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Particles that do not interact via the strong force but do interact via the weak nuclear force (and presumably by the much weaker gravitation force) are called
A) gauge bosons.
B) leptons.
C) baryons.
D) mesons.
E) hadrons.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Is the following decay allowed? Σ+ → p + π+
A) Yes.
B) No, because charge is not conserved.
C) No, because mass is created.
D) No, because lepton number is not conserved.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The proton composition by quarks is
A) u ![]() d.
d.
B) uud.
C) udd.
D) u ![]()
![]() .
.
E) u ![]() d.
d.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Is the following decay permissible? Σ+ → Λ° + π+
A) Yes.
B) No, because charge is not conserved.
C) No, because mass is created.
D) No, because lepton number is not conserved.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The neutrino has
A) enormous rest mass, positive charge, and spin quantum number 1/2.
B) enormous rest mass, no charge, and spin quantum number 1.
C) negligible rest mass, negative charge, and spin quantum number 1.
D) negligible rest mass, no charge, and spin quantum number 1/2.
E) none of the given answers
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Large Hadron Collider is expected to produce protons with kinetic energy 7 TeV. What is the speed of these protons?
A) less than 0.9000 c
B) 0.9500 c
C) 0.9990 c
D) greater than 0.9999 c
E) 0.9000 c
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An electron undergoes a collision with a proton. In the center of mass system, the energy of the electron is 4000 MeV. What is the energy of the electron in the lab system, where the proton is at rest before the collision?
A) 34 GeV
B) 37 GeV
C) 40 GeV
D) 43 GeV
E) 46 GeV
F) 52 GeV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A neutron is an example of
A) a lepton.
B) a meson.
C) a baryon.
D) a gauge boson.
E) none of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If electrons are accelerated from rest in a 30 MeV tandem Van de Graaff Accelerator, what is their final kinetic energy?
A) 15 MeV
B) 20 MeV
C) 30 MeV
D) 40 MeV
E) 60 MeV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A deuteron has the same charge as a proton but approximately twice the proton mass. Suppose deuterons are being accelerated in a cyclotron in an orbit of radius 75 cm at a frequency of 8.0 MHz. What magnetic field is needed?
A) 0.011 T
B) 0.11 T
C) 1.1 T
D) 11 T
E) 111 T
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A photon is an example of
A) a lepton.
B) a meson.
C) a baryon.
D) a gauge boson.
E) hadrons.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A proton is an example of
A) a lepton.
B) a meson.
C) a baryon.
D) a gauge boson.
E) none of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction p + e- → 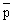 + e+ is not possible because
+ e+ is not possible because
A) the baryon number is not conserved.
B) the lepton number is not conserved.
C) the angular momentum cannot conserved.
D) the charge is not conserved.
E) The statement is untrue; the reaction is possible.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 66
Related Exams