A) a shape similar to that of the land surface lying above it
B) a shape that is opposite of the shape of the surface of the land lying above it
C) an exact shape of the surface of the land lying above it
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The part of the subsurface where most of the pore spaces are filled with air is the:
A) unsaturated zone
B) saturated zone
C) aquifer
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following rocks has the highest porosity?
A) a fine-grained shale
B) lightly cemented sandstone
C) a coarsely crystalline granite
D) a metamorphic schist or gneiss
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A spring is a place where water flows naturally from rock:
A) onto the land surface
B) into a cave
C) farther underground
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these four numbered features on the surface or in a cave are formed by the precipitation of calcium carbonate, due to the evaporation of water? 
A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 4
D) 1 and 3
E) 1 and 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following materials probably has the highest permeability?
A) highly fractured granite
B) compacted clays with moderate porosity
C) highly porous volcanic rock with holes that are isolated from one another
D) granite with sparse fractures that are filled with insoluble material
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency establishes drinking water standards to:
A) determine how much water each state can use on a yearly basis
B) set a safe limit on the concentration of select contaminants in groundwater
C) control the bottled drinking water industry
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This map shows elevations of the water table beneath an area. Which way does the upper level of groundwater flow? Generally toward the: 
A) south
B) north
C) northeast
D) northwest
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about porosity is NOT valid?
A) the amount of water that can be stored depends on the porosity
B) porosity partly depends on size and shape of grains and clasts
C) better sorted sediments have more porosity than unsorted ones
D) fractures may be the only real porosity in some igneous rocks
E) all of these are valid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following settings contains the least amount of water?
A) oceans
B) lakes
C) groundwater
D) ice caps and glaciers
E) atmosphere
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Approximately how fast does groundwater move beneath the surface of the Earth?
A) a few centimeters per day
B) a few meters per day
C) a few kilometers per day
D) a few kilometers per hour
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about the water table?
A) the shape of the water table does not mimic topography
B) the water table generally is highest in elevation beneath lakes
C) the water table can slope in opposite directions beneath a hill
D) all of these
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A large body of permeable, saturated material through which groundwater can flow well enough to yield sufficient water to wells and springs is an) :
A) aquifer
B) groundwater divide
C) hydraulic gradient
D) aquitard
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What sedimentary rock is composed primarily of calcium carbonate?
A) limestone
B) sandstone
C) shale
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a common setting for a spring?
A) the water table intersects the surface
B) a permeable rock overlies a less permeable one
C) sedimentary rocks overlie crystalline rocks along an unconformity
D) all of these
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is occurring in the Snake River Plain of southern Idaho?
A) water from rivers soaks into the ground, causing the rivers to disappear be lost)
B) a large amount of water flows underground
C) huge springs result where groundwater flows onto the surface
D) all of these are occurring
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT true about groundwater flow?
A) in some igneous groundwater reservoirs, flow is determined by the orientation of fractures
B) excess pumping from wells can cause subsidence and reduction of porosity
C) a decrease in the gradient slope of the water table) increases the velocity
D) water moves from areas where the water table is highest to areas where it is lowest
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a valid statement with relevance to groundwater?
A) In most sediments, adjacent grains fit tightly together.
B) Fractures are the main way groundwater moves through some rocks, such as granite.
C) Most groundwater occurs in caves and underground lakes.
D) None of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The term for groundwater that is confined and rises in a well because it is under pressure is:
A) artesian
B) groundwater divide
C) hydraulic gradient
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where on this cross section would groundwater most likely flow out to the surface? 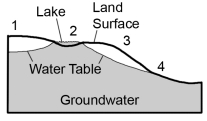
A) 1, 2, and 3
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 4
D) 2 only
E) 4 only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 142
Related Exams