Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information for questions
Observation
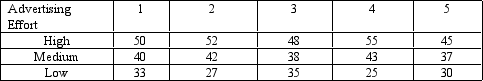 The numbers in each cell represent the sales level in thousands of
dollars.
-Which of the following statements is/are true? 1-MSS within rows) = MSS μ = 500 MSS between rows) = MSSr = 12.67 Total sum of squares = 1,152 2-MSSr = 500, MSS = 12.67, F = 37.5 3-The appropriate test statistic is F with 2 and 8 degrees of freedom 4-The appropriate test statistic is F with 2 and 12 degrees of freedom
The numbers in each cell represent the sales level in thousands of
dollars.
-Which of the following statements is/are true? 1-MSS within rows) = MSS μ = 500 MSS between rows) = MSSr = 12.67 Total sum of squares = 1,152 2-MSSr = 500, MSS = 12.67, F = 37.5 3-The appropriate test statistic is F with 2 and 8 degrees of freedom 4-The appropriate test statistic is F with 2 and 12 degrees of freedom
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 2 and 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information for questions
Observation
 The numbers in each cell represent the sales level in thousands of
dollars.
-Which of the following is/are true? 1-The appropriate null hypothesis would state, "Advertising levels have no effect on sales." 2-The appropriate null hypothesis would state, "There is an increase in the sales level due to an increase in the intensity of the advertising effort." 3-The appropriate statistic to test the null hypothesis would be 2 with 8 degrees of freedom.
The numbers in each cell represent the sales level in thousands of
dollars.
-Which of the following is/are true? 1-The appropriate null hypothesis would state, "Advertising levels have no effect on sales." 2-The appropriate null hypothesis would state, "There is an increase in the sales level due to an increase in the intensity of the advertising effort." 3-The appropriate statistic to test the null hypothesis would be 2 with 8 degrees of freedom.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 3
E) 2 and 3
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Type II error occurs when the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is false.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the p-value is less than or equal to 0.05, then it is valid to say that the sample evidence is significant at .05 level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the following 2 X 2 contingency table Q1 yes no yes 23 36 59 Q2 no 46 15 61 69 51 What would be the expected number of people that said yes to both the questions if your null hypothesis stated that you expected an equal number in all cells ?
A) 25
B) 30
C) 33.9
D) 40
E) not enough information given to test this hypothesis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information for questions
A subscription service stated that preferences for different
national magazines were independent of geographical location.A
survey was taken in which 300 respondents randomly chosen from three
areas were given a choice among three different magazines.Each
person expressed his or her favorite.The following results were
obtained:
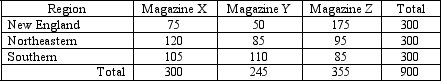 -The number of degrees of freedom is
-The number of degrees of freedom is
A) 4
B) 6
C) 7
D) 9
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the researcher, in making a statistical test, rejects a true hypothesis, the error is called
A) Type I error
B) Type II error
C) Type III error
D) no error is made
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Berkeley Supermarket buys its supplies of potatoes from two different farms, A and B.In a recent sampling test, it was found that the sample taken from Farm A had a mean weight of 10 ounces per potato, whereas the sample from Farm B had a mean weight of 10.3 ounces.In view of this test, is there a statistically discernible difference at the 95 percent confidence level) between the mean weights of the potatoes of the two farms?
A) Yes.
B) No, because the difference of 0.3 ounces is very small compared to the mean approximately 3 percent) .
C) The standard deviations of both samples must be known the sample sizes are irrelevant) before the above question can be answered.
D) Both the standard deviations and sample sizes must be known before the above question can be answered.
E) Even if both the standard deviations and sample sizes were known, the above question cannot be answered.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A major advantage of the Chi square statistic as a measurement of association between two questions is that it is independent of the sample size, making it easy to interpret in an absolute sense.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The manager of the marketing division of Acme Corporation forecasts an average monthly sales in 1978 of $65,000.In the first seven months of 1978, the average monthly sales were $63,200, with a standard deviation of $500.The management wishes to test the hypothesis Ho that "statistically" the manager was right Ho: = 65,000) against the alternative hypothesis that he was wrong in his forecast Ho: = 65,000) , using a two-tail test.Assuming normal distribution of monthly sales, which of the following statements is true?
A) Ho is rejected at the 5 percent significance level but accepted at the 1 percent significance level.
B) Ho is accepted at both the 5 percent and 1 percent significance levels.
C) Ho is accepted at the 5 percent significance level but rejected at the 1 percent significance level.
D) Ho is rejected at both the 5 percent and 1 percent significance levels.
E) None of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The hypothesis test serves to quantify the reliability of research results, indicating the extent to which the data support the empirical findings.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information for questions
A subscription service stated that preferences for different
national magazines were independent of geographical location.A
survey was taken in which 300 respondents randomly chosen from three
areas were given a choice among three different magazines.Each
person expressed his or her favorite.The following results were
obtained:
 -If the null hypothesis were true, the best guess at the number of respondents who prefer magazine X in the Northeast is closest to
-If the null hypothesis were true, the best guess at the number of respondents who prefer magazine X in the Northeast is closest to
A) 75
B) 100
C) 125
D) 150
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A high value of b indicates that the test of hypothesis is working very well.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The limitation of chi square as an association measure is 1-it is hard to compare cross-tabulations with different sample sizes. 2-it doesn't indicate how the variables are related. 3-it is difficult to obtain a feel for its value since it has no upper bound..
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
E) 1 and 2 only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Two branches of a major multinational corporation conducted surveys to measure the association between income level low, mid, high) and need for a certain produce low, mid, high).The sample size in one survey was 100 and in the other, 200.The branches now wish to compare the two cross tabulations that were generated from the surveys.Given this information, the Chi square statistic would provide an easy-to-interpret method to compare the associations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The basic steps recommended in hypothesis testing, in the correct order, are
A) analyze data which support an alternative hypothesis or position, conceptualize a null hypothesis, raise the question of the
Probability that the empirical "evidence" supporting the original
Position could have been a statistical accident, calculate the p-value.
B) estimate a p-value, develop and analyze data, conceptualize a null hypothesis, cluster the data into two testable groups.
C) conceptualize a null hypothesis, raise the question of the probability that the empirical "evidence" supporting the original
Position could have been a statistical accident, develop and
Analyze data, calculate the p-value.
D) cluster the data into two or three groups, analyze the data, ![]() calculate the p-value, test the null hypothesis.
calculate the p-value, test the null hypothesis.
E) cluster the data into as many groups as needed, develop and analyze the data, raise the question of the probability that the
Empirical "evidence" supporting the original position could have
Been a statistical accident, calculate the p-value.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information for questions
A subscription service stated that preferences for different
national magazines were independent of geographical location.A
survey was taken in which 300 respondents randomly chosen from three
areas were given a choice among three different magazines.Each
person expressed his or her favorite.The following results were
obtained:
 -If the appropriate null hypothesis for a chi-square test were not rejected, the following would be implied: 1-Subscription for magazine X = subscription for magazine Y = subscription for magazine Z. 2-The probability of magazine preference unconditional on location) is equal to the probability of magazine preference conditional on location) . 3-Magazine preferences are uncorrelated with location.
-If the appropriate null hypothesis for a chi-square test were not rejected, the following would be implied: 1-Subscription for magazine X = subscription for magazine Y = subscription for magazine Z. 2-The probability of magazine preference unconditional on location) is equal to the probability of magazine preference conditional on location) . 3-Magazine preferences are uncorrelated with location.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 2 and 3
E) 1, 2, and 3
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An index that is calculated from sample data and whose value determines whether to accept or reject a null hypothesis is a
A) test statistic
B) critical value
C) significance level
D) decision rule
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Accepting a null hypothesis when it is false is called an)
A) type I error.
B) type II error.
C) hypothesis error.
D) power of the test.
E) significance level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 45
Related Exams