A) 6.39 atm
B) 11.4 atm
C) 0.211 atm
D) 2.84 atm
E) 1.59 atm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If equal amounts of helium and argon are placed in a porous balloon, the argon will escape faster.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the number of moles in 75.0 g of O2, and the pressure that it would exert at 80.0 C in a 5.00 L steel tank.
A) 4.69 mol, 6.18 atm
B) 4.69 mol, 27.2 atm
C) 2.34 mol, 13.6 atm
D) 2.34 mol, 3.09 atm
E) 9.38 mol, 27.2 atm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which characteristic does not describe an ideal gas?
A) negligible volume occupied by ideal gas molecules
B) no attractive forces between ideal gas molecules
C) obeys the equation PV = nRT
D) PV/RT = a constant
E) strong repulsions between molecules
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements related to kinetic-molecular theory of gases is correct for an ideal gas?
A) There are no attractive or repulsive forces between and among gas particles.
B) Gas particles move slowly in a chaotic pattern until they collide with something.
C) For a given amount of gas, the smaller the volume of the container, the fewer the collisions that occur with the container walls, since there is less surface area.
D) The density of a gas is somewhat lower than that of a liquid.
E) The more gas particles there are in a container, the more frequently they collide with one another, so the particles stick together, resulting in a lower pressure.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "Before" image in the figure shows the initial condition of a gas at a certain temperature in a container with a movable piston.Which of the images represents the condition of the gas when the temperature of the gas is increased, and the external pressure is held constant? 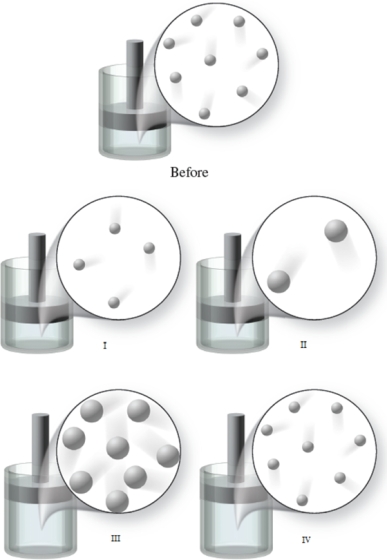
A) image I
B) image II
C) image III
D) image IV
E) None of the images
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The ideal gas law is a combination of several other gas laws which deal with fewer variables.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The two balloons shown in the figure each have the same volume, temperature, and pressure.Which of the following statements regarding the two balloons is correct? 
A) The CO2 balloon has fewer molecules than the O2 balloon.
B) The density of the O2 balloon is greater than the density of the CO2 balloon.
C) The mass of the O2 balloon is greater than the mass of the CO2 balloon.
D) The CO2 balloon is more buoyant than the O2 balloon.
E) None of these statements is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the number of moles and the mass of He gas present in a 2.00 L steel container if the pressure is 6.50 atm, and the temperature is 42.0 C.
A) 1.00 mol, 4.00 g
B) 0.503 mol, 2.01 g
C) 3.77 mol, 15.1 g
D) 4.99 x 104 mol, 1.25 x 104 g
E) 6.65 x 103 mol, 2.66 x 105 g
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following gases will have a density of 2.104 g/L at 303 K and 1.31 atm?
A) He
B) Ne
C) Ar
D) Kr
E) Xe
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the temperature of a gas at a constant pressure is increased, the volume will
A) become smaller because of fewer collisions with the sides of the container.
B) become larger because of fewer collisions with the sides of the container.
C) become smaller because of more collisions with the sides of the container.
D) become larger because of more collisions with the sides of the container.
E) stay the same because temperature has no effect on pressure.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sample of CO2 is collected over water at 23 C.If the total pressure of the sample is 734 torr, what is the partial pressure of the CO2? The vapor pressure of water at 23 C is 21.2 torr.
A) 734 torr
B) 755 torr
C) 713 torr
D) 34.6 torr
E) not enough information
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the molar mass of a gas that has a density of 1.428 g/L at STP.
A) 15.70 g/mol
B) 14.28 g/mol
C) 0.4460 g/mol
D) 32.01 g/mol
E) 0.7002 g/mol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the molar mass of a gas that has a density of 1.250 g/L at STP.
A) 11.42 g/mol
B) 12.50 g/mol
C) 28.02 g/mol
D) 0.05577 g/mol
E) 0.8000 g/mol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure shows two balloons.They are at the same temperature and pressure, and contain equal volumes of gas, but one is floating, and the other is not.The reason for this behavior is that: 
A) the balloon that is not floating has the molecules more closely spaced than the other.
B) the balloon that is not floating has a gas with a higher molar mass than that of air.
C) the balloon that is floating has molecules with more kinetic energy.
D) the balloon that is not floating has molecules that have slowed down, since it was filled before the floating balloon.
E) the balloon that is floating has a more dense gas than the one that is not floating, so it holds up the balloon better.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the number of moles in 75 g of O2, and the volume that it would occupy at STP.
A) 2.3 mol, 52 L
B) 2.3 mol, 0.10 L
C) 2.4 x 103 mol, 107 L
D) 2.4 x 103 mol, 5.4 x 104 L
E) 4.7 mol, 52 L
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which physical characteristic does not apply to a gas?
A) It can be compressed.
B) Its molecules are separated by large distances.
C) It occupies the total volume of its container.
D) It has a high density.
E) It can be formed by the evaporation of its liquid state.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rank the following substances in order of increasing average velocity, assuming they are all at the same temperature: N2, CH4, Ne, Kr
A) N2 < CH4 < Ne < Kr
B) CH4 < Ne < N2 < Kr
C) Kr < N2 < Ne < CH4
D) Ne < CH4 < N2 < Kr
E) Ne < Kr < N2 < CH4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Propane burns in air according to the equation: C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) What volume of O2 would be required if 8.00 L of propane burns, assuming that all of the gases are under the same conditions?
A) 8.00 L
B) 40.0 L
C) 20.0 L
D) 15.0 L
E) 1.60 L
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Convert 705 torr to atm.
A) 7.01 x 107 atm
B) 0.705 atm
C) 0.928 atm
D) 1.08 atm
E) 5.36 x 105 atm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 116
Related Exams