A) ![]() .
.
B) ![]() .
.
C) ![]() .
.
D) π.
E) 120π.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A disk (radius = 8.0 cm) that rotates about a fixed axis starts from rest and accelerates at a constant rate to an angular velocity of 4.0 rad/s in 2.0 s. What is the magnitude of the total linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the disk at the instant when the angular velocity of the disk is 1.5 rad/s?
A) 24 cm/s2
B) 16 cm/s2
C) 18 cm/s2
D) 34 cm/s2
E) 44 cm/s2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A small sphere attached to a light rigid rod rotates about an axis perpendicular to and fixed to the other end of the rod. Relative to the positive direction of the axis of rotation, the angular positions of the sphere are negative, its angular velocity is negative, and its angular acceleration is negative. The sphere is
A) rotating clockwise and slowing down.
B) rotating counterclockwise and slowing down.
C) rotating clockwise and speeding up.
D) rotating counterclockwise and speeding up.
E) first rotating counterclockwise and then clockwise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Four identical particles (mass of each = 0.24 kg) are placed at the vertices of a rectangle (2.0 m × 3.0 m) and held in those positions by four light rods which form the sides of the rectangle. What is the moment of inertia of this rigid body about an axis that passes through the center of mass of the body and is parallel to the shorter sides of the rectangle?
A) 2.4 kg⋅m2
B) 2.2 kg⋅m2
C) 1.9 kg⋅m2
D) 2.7 kg⋅m2
E) 8.6 kg⋅m2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two particles (m1 = 0.20 kg, m2 = 0.30 kg) are positioned at the ends of a 2.0-m long rod of negligible mass. What is the moment of inertia of this rigid body about an axis perpendicular to the rod and through the center of mass?
A) 0.48 kg⋅m2
B) 0.50 kg⋅m2
C) 1.2 kg⋅m2
D) 0.80 kg⋅m2
E) 0.70 kg⋅m2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A uniform sphere of radius R and mass M rotates freely about a horizontal axis that is tangent to an equatorial plane of the sphere, as shown below. The moment of inertia of the sphere about this axis is 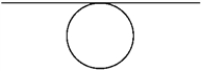
A) ![]() .
.
B) ![]() .
.
C) ![]() .
.
D) ![]() .
.
E) ![]() .
.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The graph below shows a plot of angular acceleration in rad/s2 versus time from t = 0 s to t = 8 s. The change in angular velocity, Δω, during this 8-second period is 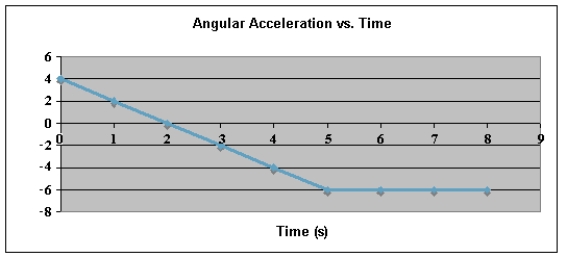
A) ![]() , CW.
, CW.
B) ![]() , CCW.
, CCW.
C) ![]() , CW.
, CW.
D) ![]() , CCW.
, CCW.
E) ![]() , CW.
, CW.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A uniform cylinder of radius R, mass M, and length L rotates freely about a horizontal axis parallel and tangent to the cylinder, as shown below. The moment of inertia of the cylinder about this axis is 
A) ![]() .
.
B) ![]() .
.
C) MR2.
D) ![]() .
.
E) ![]() .
.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A nonuniform 2.0-kg rod is 2.0 m long. The rod is mounted to rotate freely about a horizontal axis perpendicular to the rod that passes through one end of the rod. The moment of inertia of the rod about this axis is 4.0 kg⋅m2. The center of mass of the rod is 1.2 m from the axis. If the rod is released from rest in the horizontal position, what is its angular speed as it swings through the vertical position?
A) 3.4 rad/s
B) 4.4 rad/s
C) 4.3 rad/s
D) 5.8 rad/s
E) 6.8 rad/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two forces of magnitude 50 N, as shown in the figure below, act on a cylinder of radius 4 m and mass 6.25 kg. The cylinder, which is initially at rest, sits on a frictionless surface. After 1 second, the velocity and angular velocity of the cylinder in m/s and rad/s are respectively 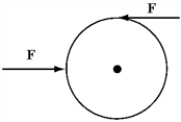
A) v = 0; ω = 0.
B) v = 0; ω = 4.
C) v = 0; ω = 8.
D) v = 8; ω = 8.
E) v = 16; ω = 8.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows a graph of angular velocity versus time for a woman bicycling around a circular track. 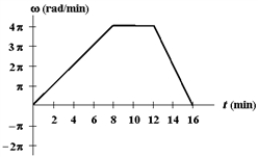 Use this exhibit to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Exhibit 10-1. What is her angular displacement (in rad) in the first 8 minutes?
Use this exhibit to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Exhibit 10-1. What is her angular displacement (in rad) in the first 8 minutes?
A) 0
B) π
C) 4π
D) 8π
E) 16π
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A small sphere attached to a light rigid rod rotates about an axis perpendicular to and fixed to the other end of the rod. Relative to the positive direction of the axis of rotation, the angular positions of the sphere are positive, its angular velocity is positive, and its angular acceleration is negative. The sphere is
A) rotating clockwise and slowing down.
B) rotating counterclockwise and slowing down.
C) rotating clockwise and speeding up.
D) rotating counterclockwise and speeding up.
E) first rotating clockwise and then counterclockwise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following diagrams shows the greatest magnitude net torque with a zero net force? All the rods, of length 2r, rotate about an axis that is perpendicular to the rod and fixed in the center of the rod. All the forces are of magnitude F or 2F and all distances from the axis are r or r/2.
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 10-2
The figure below shows a graph of angular velocity versus time for a man bicycling around a circular track. 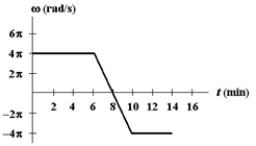 Use this exhibit to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Exhibit 10-2. What is his average angular acceleration, in rad/s2, in the period from t = 6 min to t = 8 min?
Use this exhibit to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Exhibit 10-2. What is his average angular acceleration, in rad/s2, in the period from t = 6 min to t = 8 min?
A) 0
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the sum of the external forces and the sum of the external torques on a body are both zero, we can conclude that
A) the body is moving at constant velocity but is not rotating.
B) the body is rotating at constant angular velocity but has no linear velocity.
C) the body has neither linear nor angular velocity.
D) the body may have constant linear or angular velocity, but not both simultaneously.
E) the body may have constant linear or constant angular velocity, or both simultaneously.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A wheel rotates about a fixed axis with a constant angular acceleration of 4.0 rad/s2. The diameter of the wheel is 40 cm. What is the linear speed of a point on the rim of this wheel at an instant when that point has a total linear acceleration with a magnitude of 1.2 m/s2?
A) 39 cm/s
B) 42 cm/s
C) 45 cm/s
D) 35 cm/s
E) 53 cm/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Particles (mass of each = 0.20 kg) are placed at the 40-cm and 100-cm marks of a meter stick of negligible mass. This rigid body is free to rotate about a frictionless pivot at the 0-cm end. The body is released from rest in the horizontal position. What is the initial angular acceleration of the body?
A) 12 rad/s2
B) 5.9 rad/s2
C) 8.4 rad/s2
D) 5.4 rad/s2
E) 17 rad/s2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three particles, each of which has a mass of 80 g, are positioned at the vertices of an equilateral triangle with sides of length 60 cm. The particles are connected by rods of negligible mass. What is the moment of inertia of this rigid body about an axis that is parallel to one side of the triangle and passes through the respective midpoints of the other two sides?
A) 0.018 kg⋅m2
B) 0.020 kg⋅m2
C) 0.016 kg⋅m2
D) 0.022 kg⋅m2
E) 0.032 kg⋅m2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mass m = 4.0 kg is connected, as shown, by a light cord to a mass M = 6.0 kg, which slides on a smooth horizontal surface. The pulley rotates about a frictionless axle and has a radius R = 0.12 m and a moment of inertia I = 0.090 kg⋅m2. The cord does not slip on the pulley. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of m? 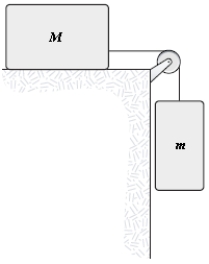
A) 2.4 m/s2
B) 2.8 m/s2
C) 3.2 m/s2
D) 4.2 m/s2
E) 1.7 m/s2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A uniform rod of length (L = 2.0 m) and mass (M = 1.5 kg) is pivoted about a horizontal frictionless pin through one end. The rod is released from rest at an angle of 30° below the horizontal. What is the angular speed of the rod when it passes through the vertical position? (The moment of inertia of the rod about the pin is 2.0 kg⋅m2.)
A) 3.5 rad/s
B) 2.7 rad/s
C) 3.1 rad/s
D) 2.3 rad/s
E) 1.6 rad/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 82
Related Exams