A) hepatitis
B) liver cancer
C) pancreatic disease
D) prostate cancer
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following graph for the rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction. 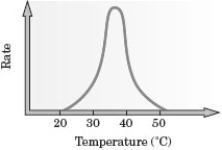 What is the approximate optimum temperature for carrying out this reaction?
What is the approximate optimum temperature for carrying out this reaction?
A) 20°C
B) 25°C
C) 35°C
D) 45°C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Identify the optimum pH for the activity of the enzyme lactase.
A) 2.0
B) 9.0
C) 10.0
D) 6.0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following two images depicting enzyme behavior. 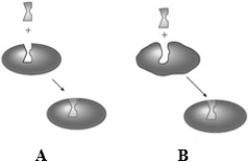 Which image provides a better explanation for the induced-fit model?
Which image provides a better explanation for the induced-fit model?
A) A only
B) B only
C) Both A and B
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of following statements is true of urease?
A) It catalyzes the degradation of uracil.
B) It catalyzes the synthesis of urea.
C) It catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea.
D) It catalyzes the hydrolysis of all amines.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lactate dehydrogenase belongs to which group of enzymes?
A) hydrolases
B) lyases
C) oxidoreductases
D) transferases
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which term refers to a species that can reversibly bind to an allosteric enzyme?
A) a zymogen
B) an isozyme
C) a cofactor
D) a regulator
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which type of inhibition is it possible to restore the maximum rate of enzyme activity by adding additional substrate?
A) cooperative inhibition
B) competitive inhibition
C) induced-fit inhibition
D) irreversible inhibition
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following enzymes is assayed to diagnose infectious hepatitis?
A) ALT
B) CPK
C) LDH
D) PHI
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which term is used for an enzyme regulation process where the formation of a product inhibits an earlier reaction in the sequence?
A) cooperative inhibition
B) competitive inhibition
C) feedback control
D) stereospecificity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aconitase belongs to which group of enzymes?
A) hydrolases
B) lyases
C) oxidoreductases
D) transferases
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true of enzymes?
A) All enzymes are fibrous proteins.
B) All enzymes are globular proteins.
C) The majority of enzymes are fibrous proteins.
D) The majority of enzymes are globular proteins.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following enzymes is assayed to diagnose liver or bone disease?
A) alkaline phosphatase
B) alkaline aminotransferase
C) acid phosphatase
D) lactate dehydrogenase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following reaction. 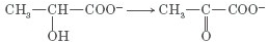 Which group of enzymes catalyzes this reaction?
Which group of enzymes catalyzes this reaction?
A) oxidoreductases
B) isomerases
C) transferases
D) ligases
E) hydrolases
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following terms refers to nonprotein parts of enzymes that are necessary for catalytic function?
A) apoenzyme
B) coenzyme
C) cofactor
D) substrate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following enzymes is an example of a lyase?
A) aconitase
B) acetylcholinesterase
C) aspartate transaminase
D) lactate dehydrogenase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true of trypsin?
A) It does not affect any peptide bond.
B) It hydrolyzes all peptide bonds.
C) It hydrolyzes peptide bonds only on the carboxyl side of leucine and phenylalanine residues.
D) It hydrolyzes peptide bonds only on the carboxyl side of arginine and lysine residues.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following changes gives a saturation curve for the rate of enzyme activity?
A) an increase in enzyme concentration
B) an increase in substrate concentration
C) an increase in temperature
D) an increase in pH
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which type of inhibition does an inhibitor bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site?
A) cooperative inhibition
B) competitive inhibition
C) noncompetitive inhibition
D) selective inhibition
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Examine the following graph. 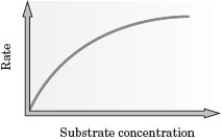 Which of the following explains why the "line" on the graph does not continue in a linear fashion?
Which of the following explains why the "line" on the graph does not continue in a linear fashion?
A) All of the added substrate is bound to the enzyme.
B) All of the enzyme active sites are occupied.
C) The amount of enzyme present is greater than needed by the substrate.
D) An inhibitor is present.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 62
Related Exams