A) very cold environments
B) very hot environments
C) environments with a constant food source
D) environments with variable and limited food sources
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All types of muscle tissue have ________.
A) striated banding patterns seen under the microscope
B) cells that lengthen when appropriately stimulated
C) a response that can be consciously controlled
D) interactions between actin and myosin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The metabolic rate of an animal is most accurately determined by ________.
A) the amount of work done by an animal
B) the amount of food consumed during a meal
C) the amount of carbon dioxide produced by an animal in a given time.
D) the amount of energy used by an animal in a given time
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a cool environment, an ectotherm is more likely to survive an extended period of food deprivation than would an equally sized endotherm because the ectotherm ________.
A) maintains a higher basal metabolic rate
B) expends more energy per kilogram of body mass than does the endotherm
C) invests little energy in temperature regulation
D) has greater insulation on its body surface
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following animals most likely uses the largest percentage of its energy budget for homeostatic regulation?
A) a marine jelly (an invertebrate) living deep in the ocean
B) a snake in a tropical forest
C) a shark swimming in the open ocean
D) a bird living year-round in a desert
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would increase the rate of heat exchange between an animal and its environment?
A) feathers or fur
B) vasoconstriction
C) wind blowing across the body surface
D) blubber or fat layer
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some animals have no gills when young, but then develop gills that grow larger as the animal grows larger. What is the reason for this increase in gill size?
A) The young of these animals are much more active than the adult, which leads to a higher BMR (basal metabolic rate) and, therefore, a higher need for oxygen.
B) Relative to their volume, the young have more surface area across which they can transport all the oxygen they need.
C) The young have a higher BMR.
D) Relative to their surface area, the young have more body volume in which they can store oxygen for long periods of time.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) are born in freshwater environments and then migrate to the sea. Near the end of their lives, they return to the freshwater stream where they were born to spawn. In fresh water, water constantly diffuses into the body and ions are lost from the body. In salt water, body water diffuses out of the body and excess ions are gained from the water. A salmon's gills have special cells to pump salt in or out of the body to maintain homeostasis. In response to the salmon's moves between fresh water and salt water, some cells in the gills are produced and others are destroyed. These changes made in the cells of the gills during the lifetime of an individual salmon are an example of which of the following?
A) evolution
B) trade-off
C) acclimatization
D) adaptation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The body's automatic tendency to maintain a constant and optimal internal environment is termed as ________.
A) balanced equilibrium
B) physiological chance
C) homeostasis
D) static equilibrium
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The metabolic breakdown of specialized brown fat deposits in certain animals is substantially increased during ________.
A) acclimatization
B) torpor
C) nonshivering thermogenesis
D) shivering thermogenesis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Elephants can often be observed cooling off by spraying water over their bodies with their trunks. What type of heat exchange is occurring?
A) conduction
B) convection
C) radiation
D) evaporation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The use of brown fat to generate metabolic heat is mostly limited to small mammals. What is the basis of this adaptation?
A) Small mammals cannot grow enough fur to insulate their bodies.
B) Because of their large surface area to volume ratio, heat loss across the body surface is higher in small animals.
C) Small mammals do not have enough muscle to generate heat by shivering.
D) Large mammals have lost their brown fat through the course of their evolution.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The temperature-regulating center of vertebrate animals is located in the ________.
A) thyroid gland
B) hypothalamus
C) subcutaneous layer of the skin
D) liver
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hummingbirds are small birds that require a regular food supply. When hummingbirds are faced with a situation that decreases their food supply, such as a storm, which of the following adaptations would be most useful for the bird to survive such an unpredictable and short-term absence of food resources?
A) shivering
B) torpor
C) hibernation
D) burrowing into soil
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure to answer the following question.
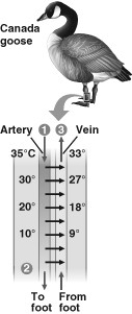 The countercurrent arrangement of blood vessels is an adaptation that allows the goose to ________.
The countercurrent arrangement of blood vessels is an adaptation that allows the goose to ________.
A) minimize heat exchange between the feet and water
B) generate heat using shivering thermogenesis
C) more effectively cool off in the summer
D) conserve heat in its core when the goose is swimming in cold water
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have a cube of modeling clay in your hands. Which of the following changes to the shape of this cube of clay will decrease its surface area relative to its volume?
A) Pinch the edges of the cube into small folds.
B) Flatten the cube into a pancake shape.
C) Round the clay up into a sphere.
D) Stretch the cube into a long, shoebox shape.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Much of the coordination of vertebrate body functions via chemical signals is accomplished by the ________.
A) respiratory system
B) endocrine system
C) integumentary system
D) excretory system
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most types of communication between cells utilize ________.
A) the exchange of cytosol between the cells
B) the movement of the cells
C) chemical or electrical signals
D) the exchange of DNA between the cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which principle of heat exchange is the most important explanation for why birds look larger in colder weather because they fluff their feathers?
A) Fluffing feathers results in less cooling by radiation because feathers emit less infrared radiation than other tissues do.
B) Fluffing decreases the amount of heat lost by conduction when the bird makes contact with cold objects in its environment.
C) Fluffing creates a pocket of air near the bird that acts as insulation.
D) Fluffing decreases the surface-area-to-volume ratio, thus decreasing the amount of heat lost to the environment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Independent of whether an organism is an endotherm or ectoderm, the least reliable indicator of an animal's metabolic rate is the amount of ________.
A) food eaten in one day
B) heat generated in one day
C) oxygen used in mitochondria in one day
D) water consumed in one day
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 68
Related Exams