A) 1, 2, 3, and 4
B) 1, 2, 5, and 6
C) 3, 4, 7, and 8
D) 5, 6, 7, and 8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fruit fly population has a gene with two alleles, A1 and A2. Tests show that 70% of the gametes produced in the population contain the A1 allele. If the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, what proportion of the flies carry both A1 and A2?
A) 0.7
B) 0.49
C) 0.42
D) 0.21
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A population of dark-eyed junco birds became established near the California coastline, many miles from the junco's normal habitat in the mixed-coniferous temperate forests in the mountains. Juncos have white outer tail feathers that the males display during aggressive interactions and during courtship displays. Males with more white in their tail are more likely to win aggressive interactions, and females prefer to mate with males with more white in their tails. Population sizes in the coastal areas have been reasonably large, and there are significant differences between the coastal and the mountain habitats. The coastal habitat is more open (making birds more visible) and has a lower junco density (decreasing intraspecific competition) than the mountain forests. Given this information, which of the following evolutionary mechanisms is the most likely cause of the difference between the coastal and mountain populations?
A) natural selection
B) genetic drift
C) gene flow
D) mutation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The value of the Hardy-Weinberg equation is that it allows scientists to perform which of the following assessments?
A) to detect whether an evolutionary force is acting on a population
B) to provide proof that natural selection is acting
C) to predict the percentage of people in a population that is homozygous for the recessive allele that causes a genetic disease
D) to measure the effects of gene flow among populations
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following situations would genetic drift most likely cause evolution?
A) The size of the gene pool increases because a smaller group establishes a new population.
B) Chance events cause allele frequencies to fluctuate unpredictably.
C) A sudden change in the environment drastically increases the population size.
D) The population has inherited traits better suited to a different environment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Researchers studying a small milkweed population note that some plants produce a toxin and other plants do not. They identify the gene responsible for toxin production. One allele (T1) codes for an enzyme that makes the toxin, and another allele (T2) codes for a nonfunctional enzyme that cannot produce the toxin. Heterozygotes produce an intermediate amount of toxin. The researchers measured the abundance of each of the three possible genotypes and compared those numbers to the expected numbers if the population were in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Those numbers are shown in the chart.
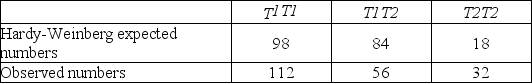 Based on these data, which answer correctly identifies whether the population is likely in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
Based on these data, which answer correctly identifies whether the population is likely in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A) Yes, the population appears to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
B) No, there are more heterozygotes than expected.
C) No, there are more homozygotes than expected.
D) More information is needed to answer this question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A researcher has maintained a small population of fruit flies in the laboratory by transferring the flies to a new culture bottle after each generation. After several generations, the viability of the flies decreased greatly. Recognizing that small population size is likely to be linked to decreased viability, which of the following approaches would be the best way to reverse this trend of decreased viability?
A) cross the flies with flies from another lab
B) reduce the number of flies that are transferred at each generation
C) transfer only the largest flies
D) change the temperature at which the flies are reared
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the nucleotide variability of a locus equals 0%, what is the gene variability and number of alleles at that locus?
A) gene variability = 0%; number of alleles = 0
B) gene variability = 0%; number of alleles = 1
C) gene variability = 0%; number of alleles = 2
D) gene variability > 0%; number of alleles = 2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A large population of laboratory animals has been allowed to breed randomly for a number of generations. After several generations, 25% of the animals display a recessive trait (A2A2) , the same percent as at the beginning of the breeding program. The rest of the animals show the dominant phenotype, with heterozygotes indistinguishable from the homozygous dominants. What proportion of the population is most likely heterozygous (A1A2) for this trait?
A) 0.05
B) 0.25
C) 0.50
D) 0.75
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the best definition of evolution on the smallest scale?
A) descent with modification
B) change in allele frequencies in a population over time
C) survival of the fittest
D) inheritance of acquired characters
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about genetic variation is accurate?
A) Genetic variation is created by the direct action of natural selection.
B) Genetic variation arises in response to changes in the environment.
C) Genetic variation must be present in a population before natural selection can act upon the population.
D) Genetic variation tends to be reduced when diploid organisms produce gametes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Restriction enzymes in bacteria protect the bacteria from successful attack by bacteriophages, whose genomes can be degraded by the restriction enzymes. The bacterial genomes are not vulnerable to these restriction enzymes because bacterial DNA is methylated. This situation selects for bacteriophages whose genomes are also methylated. As new strains of resistant bacteriophages become more prevalent, they in turn select for bacteria whose genomes are not methylated and whose restriction enzymes instead degrade methylated DNA. Which of the following factors is most likely to cause the changes?
A) frequency-dependent selection
B) evolutionary imbalance
C) heterozygote advantage
D) neutral variation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a species deviates from a 50:50 sex ratio (male to female) , the members of the minority sex often receive a greater proportion of care and resources from parents than do the offspring of the majority sex. Which of the following processes most likely causes this pattern?
A) sexual selection
B) balancing selection
C) stabilizing selection
D) frequency-dependent selection
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best explains the need for the "2" in the 2pq term in the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
A) The population is diploid.
B) Heterozygotes can come about in two ways.
C) The population is doubling in number.
D) Heterozygotes have two alleles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Over time, humans have steadily increased their movements across the continents of the Earth. Which of the following results has most likely been derived from these movements?
A) increased nonrandom mating
B) increased geographic isolation
C) increased genetic drift
D) increased gene flow
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a Hardy-Weinberg population with two alleles A1 and A2 that are in equilibrium, the frequency of allele A2 is 0.2. What is the frequency of individuals that are heterozygous for this allele?
A) 0.02
B) 0.04
C) 0.16
D) 0.32
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following conditions would most likely cause allele frequencies to change by chance?
A) large population
B) small populations
C) mutation
D) gene flow
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In 1986, a nuclear power accident in Chernobyl, USSR (now Ukraine) , led to high radiation levels for miles surrounding the plant. The high levels of radiation caused elevated mutation rates in the surviving organisms, and evolutionary biologists have been studying rodent populations in the Chernobyl area ever since. Which of the following events most likely occurred in the rodent populations following the accident?
A) Mutation caused major changes in rodent physiology over time.
B) Mutation led to increased genetic variation.
C) Mutation caused genetic drift and decreased fitness.
D) Mutation caused the fixation of new alleles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is accurate with regard to a population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
A) Allele frequencies should not change from one generation to the next.
B) Natural selection, gene flow, and genetic drift are acting equally to change allele frequencies.
C) Two alleles are present in equal proportions.
D) Individuals within the population are evolving.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Imagine a small herbaceous flowering plant whose conservation status is "endangered." Which of the following possible experiments would best test if a lack of genetic variability was partially responsible for low population numbers?
A) compare flower production rates in plants from populations that occur in dry versus moist conditions
B) compare flower production rates in small versus large plants
C) compare seed production rates in plants that are hand-pollinated with pollen from nearby individuals versus individuals 10 kilometers away
D) compare seed production rates in small versus large plants
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 65
Related Exams