A) consumption schedule will shift upward.
B) aggregate demand curve will shift outward.
C) effect on equilibrium GDP will be the same as a cut in taxes.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Productivity increases, brought about by increased education and training, may shift the aggregate supply curve outward.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
____ is the income actually available to the consumers that determines aggregate demand.
A) Nominal income
B) Net domestic product
C) Income corrected for depreciation
D) Disposable income
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major complication with fiscal policy to control aggregate demand is the
A) inability to agree on macroeconomic goals.
B) accuracy of modern forecasting models.
C) inability to change aggregate demand with fiscal tools.
D) constantly changing investment and net exports because of other events.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 11-1
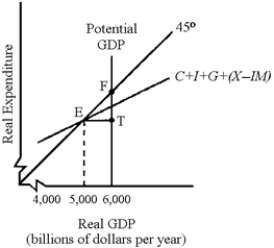 -In Figure 11-1, the economy is experiencing a(n)
-In Figure 11-1, the economy is experiencing a(n)
A) inflationary gap equal to EF.
B) inflationary gap equal to ET.
C) recessionary gap equal to ET.
D) recessionary gap equal to FT.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An active stabilization policy designed to limit the size of government would
A) raise G to eliminate a recessionary gap and lower taxes to eliminate an inflationary gap.
B) raise G to eliminate a recessionary gap and raise taxes to eliminate an inflationary gap.
C) reduce taxes to eliminate a recessionary gap and raise G to eliminate an inflationary gap.
D) reduce taxes to eliminate a recessionary gap and reduce G to eliminate an inflationary gap.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are a member of Congress in 2007-2009 when the economy is in a recessionary gap.If your goal is to achieve full employment, you should vote for
A) decreased government purchases, increased taxes, and a cut in transfer payments.
B) a balanced federal budget.
C) increased government purchases, decreased taxes, and an increase in transfer payments.
D) increased government purchases and transfer payments, and an equal increase in taxes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The main idea behind supply-side tax cuts is that
A) tax cuts increase spending, which increases aggregate supply.
B) some tax cuts can increase aggregate supply.
C) people like lower taxes and will spend more if they get them.
D) it is easier to shift aggregate supply than aggregate demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tax cuts associated with supply-side economics often lead to increased
A) federal budget surpluses.
B) federal budget deficits.
C) foreign trade surpluses.
D) government spending.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an effort to balance the federal budget, an increase in Social Security taxes is passed.What is the most likely effect of this on equilibrium GDP?
A) GDP will increase.
B) GDP will decrease.
C) GDP will not change but prices will rise.
D) GDP will not change but employment will increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Government transfer payments
A) are subtracted from national income to obtain disposable income.
B) can be considered as negative taxes.
C) intervene between national product and disposable income in the same way as taxes.
D) are counted the same as taxes in computing national income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the multiplier for a change in government spending compare to the multiplier for a change in taxes?
A) It is smaller.
B) It is the same.
C) It is larger.
D) It cannot be calculated.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Capital gains tax cuts inevitably benefit
A) low-income workers.
B) retired persons.
C) workers in large cities.
D) high-income stock owners.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ronald Reagan's presidency could be characterized as a period of
A) passive monetary policy.
B) passive fiscal policy.
C) active fiscal policy.
D) active regulatory policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For liberals, the United States has a(n)
A) public sector that is too large.
B) private sector that is too small.
C) economy that is too heavily regulated.
D) public sector that is too small.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the MPC in the United States was high, it would increase the value of the multiplier.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does a tax cut affect the expenditure schedule?
A) It causes movement to the left along the schedule.
B) It causes the schedule to shift upward.
C) It causes movement to the right along the schedule.
D) It causes the schedule to shift downward.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most tax payments increase as GDP increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A "conservative" would most likely argue in favor of
A) tax increases when fiscal stimulus is necessary, and spending cuts when fiscal restraint is necessary.
B) tax cuts when fiscal restraint is necessary, and spending cuts when fiscal stimulus is necessary.
C) tax cuts when fiscal stimulus is necessary, and spending cuts when fiscal restraint is necessary.
D) spending increases when fiscal expansion is necessary, and tax increases when fiscal stimulus is necessary.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Keynesian theory, a decrease in government expenditures would be a proper fiscal policy during
A) an inflationary gap.
B) a recessionary gap.
C) a natural disaster.
D) none of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 207
Related Exams