A) above the equilibrium price.
B) equal to the equilibrium price.
C) below the equilibrium price.
D) at any price on the supply curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the correct way to describe equilibrium in a market?
A) At equilibrium, demand equals supply.
B) At equilibrium, quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
C) At equilibrium, market forces are no longer at work.
D) Equilibrium is a tendency, a state of perpetual motion.
E) Equilibrium is the best combination of price and quantity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in price will decrease demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following are the equations for the supply and demand curves in the market for weezils: 
 where Qd is the quantity demanded, Qs is the quantity supplied, and P is the price per weezil in dollars.
-Refer to Exhibit 4-1.If the government imposes a price floor of $4 a weezil, how many weezils will be sold?
where Qd is the quantity demanded, Qs is the quantity supplied, and P is the price per weezil in dollars.
-Refer to Exhibit 4-1.If the government imposes a price floor of $4 a weezil, how many weezils will be sold?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 12
D) 14
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A supply curve slopes upward because quantity supplied is higher when price is higher.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Along a supply curve,
A) supply changes as price changes.
B) quantity supplied changes as price changes.
C) supply changes as technology changes.
D) quantity supplied changes as technology changes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
"Demand" is a series of quantities demanded, one for each person in the market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following suggests that the "laws" of supply and demand are being disobeyed?
A) Outside forces disturbing an equilibrium
B) Persistent shortages or surpluses
C) The market never moving from an equilibrium
D) "Other things" not always being equal
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following are the equations for the supply and demand curves in the market for weezils: 
 where Qd is the quantity demanded, Qs is the quantity supplied, and P is the price per weezil in dollars.
-Refer to Exhibit 4-1.According to the data given, when the market is in Equilibrium, how many weezils are sold?
where Qd is the quantity demanded, Qs is the quantity supplied, and P is the price per weezil in dollars.
-Refer to Exhibit 4-1.According to the data given, when the market is in Equilibrium, how many weezils are sold?
A) 3
B) 5
C) 11
D) 14
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a demand curve is constructed, each point that demand curve represents
A) the demand for the product.
B) the quantity demanded at that price.
C) the amount that people want to buy.
D) the amount people want to buy at different income levels.
E) All of these responses are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A surplus occurs when price is higher than the market equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mechanism of supply and demand is
A) a fundamental tool in both microeconomics and macroeconomics.
B) the only real "law" of economics.
C) a fundamental tool only in microeconomics.
D) a fundamental tool only in macroeconomics.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The U.S.government restricts the production of peanuts by limiting production licenses.By also prohibiting imports, the government maintains prices well above levels peanut farmers would obtain if supply were not restricted.This program has the same effect as a
A) price ceiling.
B) price floor.
C) opportunity cost.
D) shortage.
E) efficiency move.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A black market develops only when quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A severe freeze has damaged the Florida orange crop.The effect on the market for oranges will be a left shift of
A) demand, as consumers try to economize because of the shortage.
B) both the supply and demand curves.
C) the supply curve.
D) the supply curve and a right shift in the demand curve, and the outcome will be a higher price
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A common misperception about consumer demand is that
A) demand depends on many other variables.
B) price is a major determinant of quantity.
C) it is a fixed amount.
D) quantity cannot be determined in advance.
E) All of these responses are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in the price of gasoline shifts the demand for tires to the
A) left, because gasoline and tires are substitutes.
B) left, because gasoline and tires are normally used together.
C) right, because gasoline and tires are substitutes.
D) right, because gasoline and tires are normally used together.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
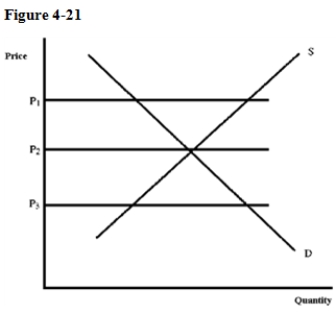 -A surplus will tend to occur at which price in Figure 4-21?
-A surplus will tend to occur at which price in Figure 4-21?
A) P1
B) P2
C) P3
D) There will be no surplus at the prices shown.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 4-23 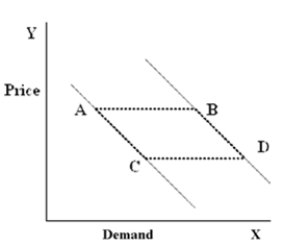 -In Figure 4-23, which of the following movements would be caused by a change in income?
-In Figure 4-23, which of the following movements would be caused by a change in income?
A) A to C
B) C to A
C) B to D
D) B to A
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Price controls date back to
A) World War II.
B) the U.S.Revolutionary War.
C) thousands of years, at least back to ancient Babylonia.
D) the 1970s.
E) the last 20 years.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 240 of 297
Related Exams