Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a barrier to entry in an industry?
A) economies of scale
B) profit maximization
C) strategic pricing
D) government licensing
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question on the basis of the accompanying table, which shows the demand schedule facing a nondiscriminating monopolist. 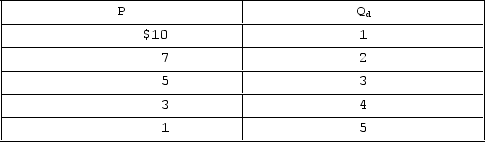 Assume that this monopolist faces zero production costs. The profit-maximizing monopolist will set a price of
Assume that this monopolist faces zero production costs. The profit-maximizing monopolist will set a price of
A) $10.
B) $1.
C) $7.
D) $5.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
For a monopolist, maximum profits will occur when the gap between average revenue (or price)and average cost is biggest.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a precondition for price discrimination?
A) The commodity involved must be a durable good.
B) The good or service cannot be profitably resold by original buyers.
C) The seller must be able to segment the market, that is, to distinguish buyers with different elasticities of demand.
D) The seller must possess some degree of monopoly power.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
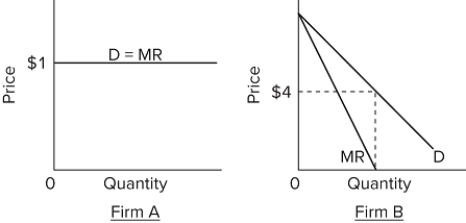 Refer to the diagrams. The demand for Firm B's product is
Refer to the diagrams. The demand for Firm B's product is
A) perfectly elastic over all ranges of output.
B) perfectly inelastic over all ranges of output.
C) elastic for prices above $4 and inelastic for prices below $4.
D) inelastic for prices above $4 and elastic for prices below $4.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
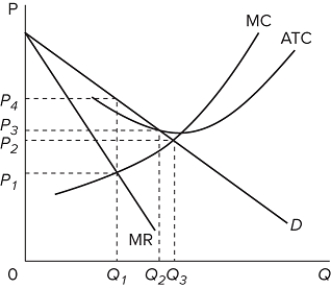 Refer to the graph for a pure monopoly. A profit-maximizing monopolist would set what price and quantity levels in the short run?
Refer to the graph for a pure monopoly. A profit-maximizing monopolist would set what price and quantity levels in the short run?
A) P₁ and Q₁
B) P₂ and Q₃
C) P₃ and Q₂
D) P₄ and Q₁
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic profit in the long run is
A) possible for both a pure monopoly and a pure competitor.
B) possible for a pure monopoly but not for a pure competitor.
C) impossible for both a pure monopolist and a pure competitor.
D) only possible when barriers to entry are nonexistent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolistic firm has a sales schedule such that it can sell 10 prefabricated garages per week at $10,000 each, but if it restricts its output to 9 per week it can sell these at $11,000 each. The marginal revenue of the 10th unit of sales per week is
A) $-1,000.
B) $9,000.
C) $1,000.
D) $10,000.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand curve faced by a pure monopolist
A) may be either more or less elastic than that faced by a single purely competitive firm.
B) is less elastic than that faced by a single purely competitive firm.
C) has the same elasticity as that faced by a single purely competitive firm.
D) is more elastic than that faced by a single purely competitive firm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal revenue curve for a monopolist
A) is a straight, upsloping curve.
B) rises at first, reaches a maximum, and then declines.
C) becomes negative when output increases beyond some particular level.
D) is a straight line, parallel to the horizontal axis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
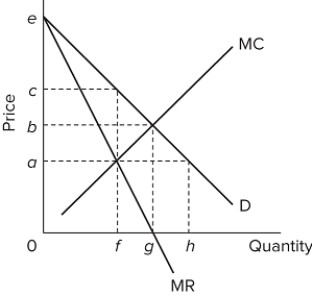 Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be
A) e.
B) c.
C) b.
D) a.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is a major criticism of a monopoly as a source of allocative inefficiency?
A) A monopolist fails to expand output to the level where the consumers' valuation of an additional unit is just equal to its opportunity cost.
B) A monopolist has no incentive to produce efficiently, because even the inefficient monopolist can be assured of economic profits.
C) A monopolist will always earn profits, and that means that prices are too high.
D) A monopolist has an unfair advantage because it can purchase labor at a lower price than competitive firms can.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The problem with adopting a fair-return pricing policy for a natural monopoly is that
A) economic profits will be positive.
B) economic profits will be negative.
C) it is not productively efficient.
D) it is not allocatively efficient.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the meaning of the phrase "dilemma of regulation"?
A) Natural monopolies achieve economies of scale but charge high prices when there is no government regulation; government regulation reduces prices but results in diseconomies of scale.
B) Natural monopolies are profitable, but only if the government permits price discrimination; government regulation to restrict price discrimination reduces monopoly prices, but the regulation also reduces monopoly output.
C) The fair-return price achieves allocative efficiency but may produce economic losses; the socially optimal price yields a normal profit but may not be allocatively efficient.
D) The socially optimal price achieves allocative efficiency but may produce economic losses; the fair-return price yields a normal profit but may not be allocatively efficient.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best approximates a pure monopoly?
A) a gas station in a large city
B) the Kansas City wheat market
C) the only grocery store in a small isolated town
D) the soft drink market
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
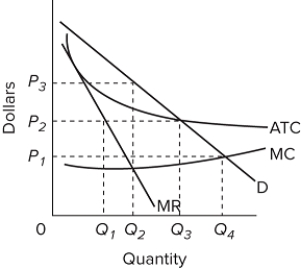 Refer to the diagram for a natural monopolist. If a regulatory commission set a maximum price of P₂, the monopolist would
Refer to the diagram for a natural monopolist. If a regulatory commission set a maximum price of P₂, the monopolist would
A) produce output Q₁ and realize an economic profit.
B) produce output Q₃ and realize an economic profit.
C) close down in the short run.
D) produce output Q₃ and realize a normal profit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The supply curve for a monopolist is
A) perfectly elastic.
B) upsloping.
C) that portion of the marginal cost curve lying above minimum average variable cost.
D) nonexistent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
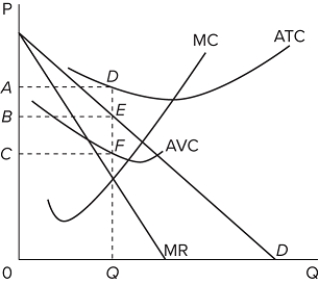 Refer to the graph for a monopolist in short-run equilibrium. This monopolist has total cost equal to area
Refer to the graph for a monopolist in short-run equilibrium. This monopolist has total cost equal to area
A) CADF.
B) 0ADQ.
C) ADFC.
D) 0 CFQ.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The supply curve of a pure monopolist
A) is that portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above average variable cost.
B) is the same as that of a purely competitive industry.
C) is its average variable cost curve.
D) does not exist because prices are not "given" to a monopolist.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 381 - 400 of 407
Related Exams