A) raise taxes to move to AD1.
B) cut taxes to move to AD3.
C) cut spending to move to AD3.
D) not change its policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the U.S. economy, the effect on federal tax revenues and spending of an increase in the unemployment rate is to:
A) cut tax revenues and raise expenditures.
B) cut expenditures and raise tax revenues.
C) raise both tax revenues and expenditures.
D) cut both expenditures and tax revenues.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Programs that automatically increase government spending (relative to revenue) during a recession and automatically decrease government spending (relative to revenue) during an economic boom are called:
A) discretionary fiscal policy.
B) supply-side programs.
C) automatic stabilizers.
D) tax credits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the marginal propensity to consume (MPC)is 0.80, the value of the spending multiplier is 2.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To combat a recession, Keynesian fiscal policy recommends:
A) an increase in taxes.
B) an increase in government spending.
C) an increase in taxes and a decrease in government purchases to balance the budget.
D) a reduction in both taxes and government spending.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal propensity to save (MPS) is computed as the change in:
A) savings divided by the change in saving.
B) savings divided by the change in income.
C) saving divided by the change in GDP.
D) None of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the economy enters a recession, automatic stabilizers create:
A) higher taxes.
B) more discretionary spending.
C) budget deficits.
D) budget surpluses.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal propensity to consume is:
A) the change in income divided by the change in consumption.
B) consumption spending divided by income.
C) income divided by consumption spending.
D) the change in consumption divided by the change in income.
E) the change in consumption divided by income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Laffer curve is representative of which of the following schools?
A) Supply-side school.
B) Rational expectations school.
C) Keynesians.
D) Neo-Keynesians.
E) Classical school.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the marginal propensity to save (MPS) is 0.50, the value of the spending multiplier is:
A) 1.
B) 2.
C) 4.
D) 9.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is inflationary for government to increase spending if:
A) it also cuts taxes.
B) the aggregate supply curve is flat.
C) the economy is at full employment.
D) equilibrium real GDP is well below full employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fiscal policy is concerned with:
A) encouraging businesses to invest.
B) regulation of net exports.
C) changes in government spending and\or tax revenues.
D) expanding and contracting the money supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Structures in the economy increase aggregate demand when the economy is in recession and decrease aggregate demand when the economy is inflationary are known as:
A) tax transfers.
B) inventory investment.
C) accelerators.
D) depreciation.
E) automatic stabilizers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If no fiscal policy changes are made, suppose the current aggregate demand curve will increase horizontally (shift rightward) by $1,000 billion and cause inflation. If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.90, federal policymakers could follow Keynesian economics and restrain inflation by decreasing:
A) government spending by $100 billion.
B) taxes by $100 billion.
C) taxes by $1,000 billion.
D) government spending by $1,000 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 11-6 Aggregate demand and supply model 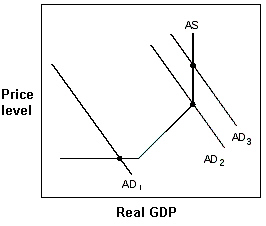 In Exhibit 11-6, if the aggregate demand curve is at AD3, the government should:
In Exhibit 11-6, if the aggregate demand curve is at AD3, the government should:
A) raise taxes to move to AD1.
B) cut taxes to move to AD2.
C) cut taxes to move to AD1.
D) cut spending to move to AD2.
E) not change its behavior.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The formula to compute the spending multiplier is:
A) 1 \ (MPC + MPS) .
B) 1 \ (1 - MPC) .
C) 1 \ (1 - MPS) .
D) 1 \ (C + I) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The spending multiplier is:
A) 1 \ (1 - MPC) .
B) 1 - MPC.
C) MPC.
D) MPC \ (1 - MPC) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an economy dips into recession, automatic stabilizers will:
A) enlarge the budget deficit (or reduce the surplus) .
B) reduce the budget deficit (or increase the surplus) .
C) ensure that the budget remains in balance.
D) expand the supply of money and, thereby, stimulate aggregate demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true ?
A) Fiscal policy is the manipulation of the nation's money supply to influence the nation's output, employment and price level.
B) Discretionary fiscal policy is the deliberate use of changes in government spending and taxes to stabilize the economy.
C) The tax multiplier is the change in aggregate demand resulting from an initial change in government spending.
D) A budget deficit exists when government tax revenues exceed government spending.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Equal increases in government spending and taxes will:
A) cancel each other out so that the equilibrium level of real GDP will remain unchanged.
B) lead to an equal decrease in the equilibrium level of real GDP.
C) lead to an equal increase in the equilibrium level of real GDP.
D) lead to an increase in the equilibrium level of real GDP real GDP that is larger than the initial change in government spending and taxes.
E) lead to an increase in the equilibrium level of output that is smaller than the initial change in government spending and taxes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 223
Related Exams