A) are examples of neoplasms
B) contain cells tightly controlled by the cell cycle
C) contain nondividing cells
D) are caused by the normal expression of homeotic genes
E) are localized in one part of the body
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cells able to divide and form some types of cells in an organism are called:
A) pluripotent stem cells
B) terminally differentiated cells
C) germ line cells
D) morphogenic cells
E) developmental cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Hox gene clusters in mouse are very similar to those identified in Drosophila .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gap genes of Drosophila embryos:
A) organize the embryo into broad regions and influence the activity of pair-rule genes.
B) are missing from the chromosomes of mutant flies.
C) are genes that have moved to gaps on other chromosome during meiosis.
D) cause gaps in the cell cycle.
E) cause the death of embryos before they hatch.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some Drosophila developmental genes result in the loss of alternate segments in the larva when mutated. These genes are called:
A) embryonic segment genes
B) larval segmentation genes
C) segment polarity genes
D) pair-rule genes
E) gap genes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
____ promote cancer development, while ____ prevent cancer development.
A) Oncogenes; tumor suppressor genes
B) Tumor suppressor genes; homeobox genes
C) Tumor suppressor genes; oncogenes
D) Oncogenes; homeobox genes
E) Homeobox genes; proto-oncogenes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Totipotent nuclei are capable of:
A) controlling the expression of other genes in the nucleus
B) directing normal development of an organism
C) causing cells to lose the ability to differentiate
D) undergoing unlimited nuclear divisions
E) stopping the cell cycle at will
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a goal of human therapeutic cloning?
A) to transfer cells from an unrelated individual into a patient needing a transplant
B) to create pluripotent cells for medical research only
C) to make a new individual, who is genetically identical to a patient needing a transplant
D) to create pluripotent stem cells using a patient's nucleus
E) to extract ES cells from an embryo
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Adult stem cells are found only in adults.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Matching
Match the developmental process with the organism best suited for its study.
Correct Answer
Multiple Choice
The first cloned mammal, Dolly:
A) was stillborn
B) developed arthritis and a virus-induced lung cancer at a relatively young age
C) lived a short period of time before suffering advanced aging effects
D) lived to a normal age for sheep
E) lived longer than normal sheep
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The results of the experiment outlined in the accompanying figure clearly demonstrate:
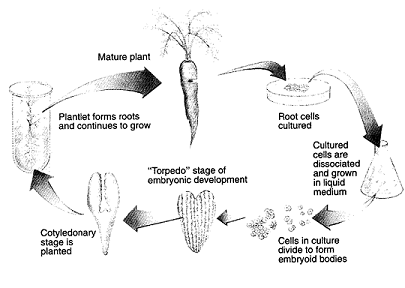
A) gene amplification
B) founder cell development pattern
C) mosaic development
D) apoptosis
E) totipotency
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 17-4
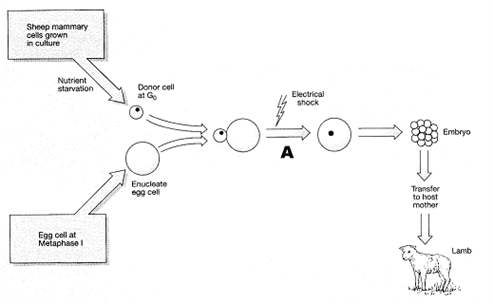 In the accompanying figure, the purpose of electrical shock at the stage of the process labeled as A is to:
In the accompanying figure, the purpose of electrical shock at the stage of the process labeled as A is to:
A) kill the egg cell nucleus
B) initiate fusion of the two cells
C) stimulate cell division
D) induce mutations
E) initiate apoptosis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Instances in which cells die shortly after they are produced in development illustrate:
A) morphogenesis
B) mosaic development
C) apoptosis
D) non-specific differentiation
E) caspases
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the process known as ____, the fate of a cell is influenced by interactions with neighboring cells.
A) determination
B) induction
C) apoptosis
D) differentiation
E) tumor suppression
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
____ are known as master genes of development, and may hold clues to the field of evolutionary developmental biology known as Evo Devo.
A) Nuclear equivalent genes
B) Stem cell genes
C) Prokaryotic transcription factors
D) Segmentation genes
E) Homeobox genes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Maternal effect genes form ____ gradients in the developing egg.
A) maternal Hox protein
B) segment
C) polarity gene
D) morphogen
E) maternal growth factor
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Matching
Match the developmental process with the organism best suited for its study.
Correct Answer
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is characteristic of mosaic development?
A) The cells of the adult are very different from each other.
B) The fate of adult cells is predetermined in embryonic founder cells.
C) Adult cells are richly interspersed with proteins.
D) Embryonic cells have a wide range of possible developmental patterns.
E) Embryos have a wide range of morphologies, but all look identical as adults.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Drosophila melanogaster is a suitable research subject for developmental genetics studies because:
A) the fly is large enough for many surgical procedures.
B) many developmental control genes observed in the fly are also present in humans.
C) flies are not subject to genetic mutations.
D) while flies are small and easy to house, they require specialized and expensive dietary requirements.
E) the control of fly development is unique and unrelated to human development.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 90
Related Exams