A) It matches HTTP traffic for use in a policy map.
B) It applies a service policy to all interfaces remarking HTTP traffic.
C) It creates an ACL named WEB that filters HTTP traffic.
D) It modifies the default policy map to allow all HTTP traffic through the router.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
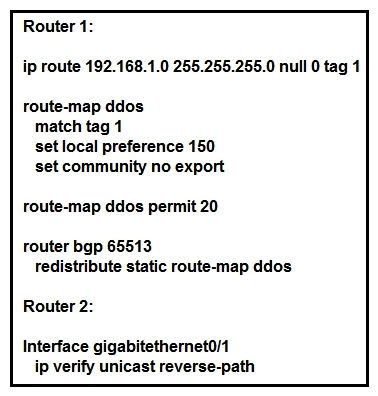 Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is preparing to implement data plane security configuration. Which statement about this configuration is true?
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is preparing to implement data plane security configuration. Which statement about this configuration is true?
A) Router 2 is the router receiving the DDoS attack.
B) Router 1 must be configured with uRPF for the RTBH implementation to be effective.
C) Router 1 is the trigger router in a RTBH implementation.
D) Router 2 must configure a route to null 0 for network 192.168.1.0/24 for the RTBH implementation to be complete.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
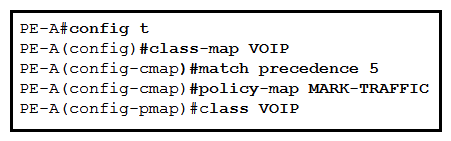 Refer to the exhibit. Which command is used to complete this configuration for QoS class-based marking?
Refer to the exhibit. Which command is used to complete this configuration for QoS class-based marking?
A) PE-A(config-pmap-c) #set dscp ef
B) PE-A(config-pmap-c) #priority
C) PE-A(config-pmap-c) #random-detect
D) PE-A(config-pmap-c) #fair-queue
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Refer to the exhibit. Which purpose of implementing NSF with this configuration is true?
Refer to the exhibit. Which purpose of implementing NSF with this configuration is true?
A) The router uses NSF to handle RP switchover while allowing neighbor relationships to remain up.
B) The router uses NSF to reduce neighbor-relationship downtime during RP switchover.
C) The router uses NSF to load balance traffic on a routed EtherChannel.
D) The router uses NSF to load balance traffic between two links, with the primary link alternating every 90 seconds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How can shared services in an MPLS Layer 3 VPN provide Internet access to the Customers of a central service provider?
A) Static routes on CE routers allow route leakage from a PE global routing table.
B) The CE router can establish a BGP peering to a PE router and use the PE device to reach the Internet.
C) The customer VRF uses route targets to import and export routes to and from a shared services VRF.
D) Route distinguishers are used to identify the routes that CEs can use to reach the Internet.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
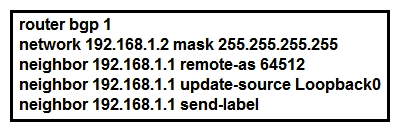 Refer to the exhibit. Which statement about the neighbor statements for 192.168.1.1 is true?
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement about the neighbor statements for 192.168.1.1 is true?
A) The router sends BGP labels for its prefixes to this peer.
B) The router must have TDP configured for the send-label command to operate.
C) The neighbor router receives at least four labels from this router.
D) The router sends only a label for the prefix for Loopback0.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are two factors to consider when implementing NSR High Availability on an MPLS PE router? (Choose two.)
A) It requires all PE-CE sessions to support NSR
B) It requires routing protocol extensions
C) It consumes more memory and CPU resources than NSF
D) It operates normally without NSR support on the PE peers
E) It cannot sync state information across redundant RPs
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
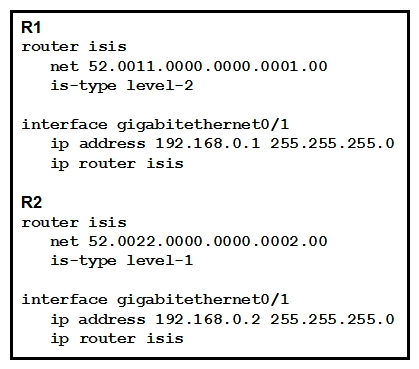 Refer to the exhibit. Which statement about the status of the neighbor relationship between R1 and R2 is true?
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement about the status of the neighbor relationship between R1 and R2 is true?
A) The neighbor relationship is down because the two routers are configured with different area types.
B) The neighbor relationship is down because the two routers are in the same subnet.
C) The neighbor relationship is up because R2 is level 1 and Ievel 2 router.
D) The neighbor relationship is down because R2 is operating as a Level 1 router and the two routers are in different areas.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
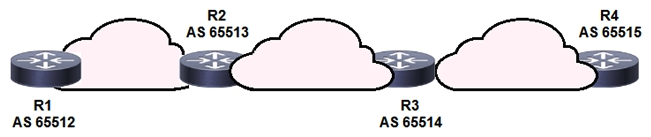 Refer to the exhibit. BGPsec is implemented on R1, R2, R3, and R4. BGP peering is established between neighboring autonomous systems. Which statement about implementation is true?
Refer to the exhibit. BGPsec is implemented on R1, R2, R3, and R4. BGP peering is established between neighboring autonomous systems. Which statement about implementation is true?
A) BGP updates from the iBGP peers are appended with a community of local-as.
B) BGP updates from the all BGP peers are appended with a community of no-export.
C) BGP updates from the eBGP peers are appended with an additional AS path value that is statically set by the domain administrator.
D) BGP updates from the eBGP peers are appended with a BGPsec attribute sequence that includes a public key hash and digital signature.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Refer to the exhibit. An engineer wants to authenticate the OSPF neighbor between PE-A and PE-B using MD5. Which command on PE-B successfully completes the configuration?
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer wants to authenticate the OSPF neighbor between PE-A and PE-B using MD5. Which command on PE-B successfully completes the configuration?
A) PE-B(config-if) #ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 44578611 PE-B(config-if) #ip ospf authentication null
B) PE-B(config-if) #ip ospf authentication key-chain 44578611
C) PE-B(config-if) #ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 44568611
D) PE-B(config-if) #ip ospf authentication message-digest
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which configuration enables BGP FlowSpec client function and installation of policies on all local interfaces?
A) flowspec address-family ipv4 local-install interface-all
B) install interface-all local
C) install interface-all
D) local-install all-interface
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Refer to the exhibit. What does this value mean when it is received in XML?
Refer to the exhibit. What does this value mean when it is received in XML?
A) It indicates a value assigned by a network administrator to tag a route.
B) It indicates a break in a sequence.
C) It means a data field is blank.
D) It shows the ending of the script.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the difference between SNMP and model-driven telemetry?
A) SNMP uses the YANG data modeling language.
B) Telemetry uses traps and inform messages to deliver data to a network administrator on a polling basis.
C) Telemetry allows for modeled network data to be pushed to the network administrator on an as-needed basis.
D) SNMP pushes network data to the network administrator whenever it is queried.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
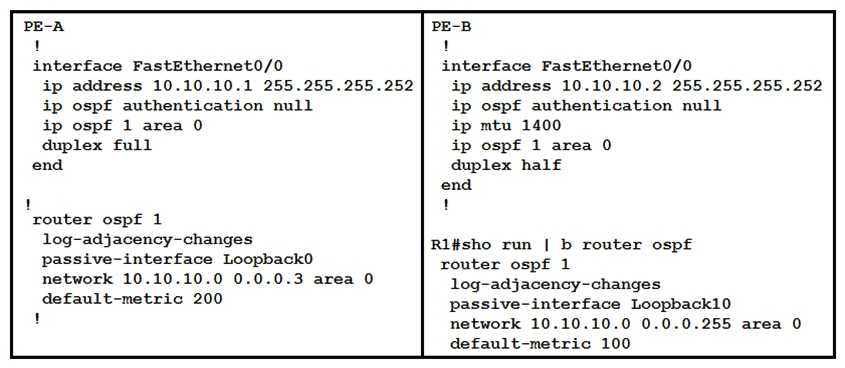 Refer to the exhibit. Which configuration prevents the OSPF neighbor from establishing?
Refer to the exhibit. Which configuration prevents the OSPF neighbor from establishing?
A) default-metric
B) duplex
C) network statement
D) mtu
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Refer to the exhibit Which effect of this configuration is true?
Refer to the exhibit Which effect of this configuration is true?
A) R1 can support a peer that is configured for LDP SSO/NSF as the peer recovers from an outage.
B) R1can support a graceful restart operation on the peer, even if graceful restart is disabled on the peer.
C) R1 can failover to any peer.
D) R1 can failover only to a peer that is configured for LDF SSO/NSF.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Refer to the exhibit. Which statement describes this configuration?
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement describes this configuration?
A) Router 1 has a new data store to collect SNMP information, but configuration must still be done at the CLI only.
B) Router 1 can be remotely managed by the CLI using Telnet.
C) Router 1 has its running configuration locked so changes can be made only when the administrator issues a kill session.
D) Router 1 has a temporary data store where a copy of the running configuration can be manipulated and verified before committing the configuration.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
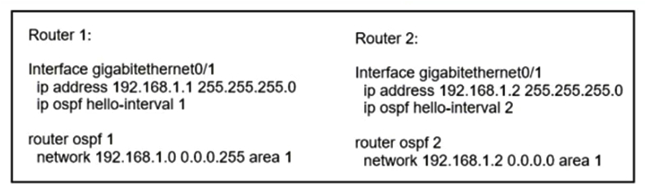 Refer to the exhibit. What reestablishes the OSPF neighbor relationship between Router 1 and Router 2?
Refer to the exhibit. What reestablishes the OSPF neighbor relationship between Router 1 and Router 2?
A) OSPF process IDs match
B) authentication is added to the configuration
C) correct wildcard mask is used on Router 2
D) hello intervals match
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Refer to the exhibit. What does the script configure?
Refer to the exhibit. What does the script configure?
A) a VLAN namespace
B) a physical domain
C) selectors for the in-band management
D) a static VLAN
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
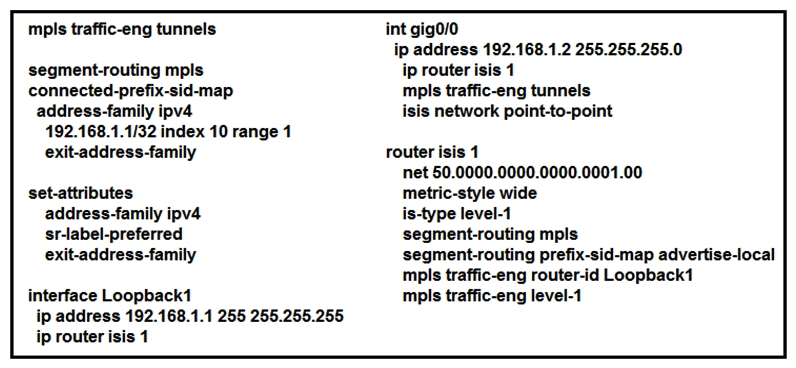 Refer to the exhibit. Which statement about this configuration is true?
Refer to the exhibit. Which statement about this configuration is true?
A) It requires a dynamic Cisco MPLS TE path to be configured for the tunnel to run.
B) It requires OSPF to also be running to have optimized Cisco MPLS TE tunnels.
C) It is the configuration for the head-end router of a Cisco MPLS TE tunnel with segment routing.
D) It requires an explicit Cisco MPLS TE path to be configured for the tunnel to run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is configuring router R1 for OSPFv3 as shown. Which additional configuration must be performed so that the three active interfaces on the router will advertise routes and participate in OSPF IPv6 processes?
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer is configuring router R1 for OSPFv3 as shown. Which additional configuration must be performed so that the three active interfaces on the router will advertise routes and participate in OSPF IPv6 processes?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 116
Related Exams