A) The marginal propensity to save is 0.2.
B) Savings are not the only source of leakage.
C) The spending multiplier is 5.
D) The spending multiplier is more than 5.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an economy is operating on the classical range on the short-run aggregate supply curve, a decrease in _____ will NOT lead to a decrease in equilibrium price.
A) money supply
B) income taxes
C) discretionary government spending
D) exports to foreign countries
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use Figure: Macroeconomic Equilibrium. This figure shows four different macroeconomic equilibria for an economy. Which of the following can shift the macroeconomic equilibrium from point A to point B?
Figure: Macroeconomic Equilibrium
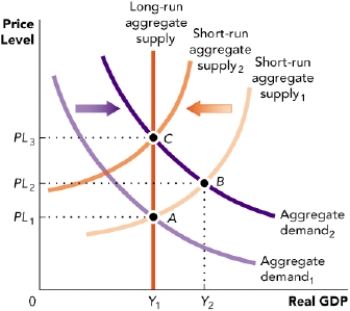
A) The money supply increases.
B) The income tax rate increases.
C) Input prices increase.
D) Business taxes increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The short-run aggregate supply curve is perfectly inelastic in the classical range because:
A) large amounts of unused labor and other inputs can be obtained at no additional cost.
B) nominal wages are sticky, so firms can supply additional output at higher price.
C) input and output prices change at the same rate, so there is no incentive to produce extra output.
D) a higher price leads to lower demand, so there is no incentive to produce extra output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following will increase aggregate supply, thereby shifting the curve right?
A) Nominal wages increase as a result of a decreased labor supply.
B) The productivity of workers increases as a result of technological improvements.
C) A new government policy increases business taxes.
D) The price of oil, which is a major input into most production activities, increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If short-run output is greater than potential output, then:
A) the unemployment rate in the economy is zero.
B) frictional unemployment is less than its natural rate.
C) frictional unemployment is greater than its natural rate.
D) structural unemployment is greater than frictional unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an economy that has no leakages except savings, the government injects $200 of new spending into the economy, and the total spending in the economy increases by $1,000. The spending multiplier in the economy is _____, and the marginal propensity to consume is:
A) 0.8; 0.2.
B) 5; 0.8.
C) 0.2; 0.8.
D) 0.8; 5.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If short-run output is less than the potential output, then:
A) the unemployment rate in the economy is zero.
B) frictional unemployment is less than its natural rate.
C) frictional unemployment is greater than its natural rate.
D) structural unemployment is greater than frictional unemployment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the short-run macroeconomic equilibrium occurs in the upward-sloping range of the short-run aggregate supply curve, then an increase in government spending will lead to:
A) an increase in output.
B) a decrease in output.
C) no change in price.
D) a decrease in price.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The total investment spending in an economy decreases as a result of an increase in the interest rate, which is driven by an increase in the overall price level. This will be represented as a:
A) rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
B) leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve.
C) movement along the aggregate demand curve.
D) leftward shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the interest rate effect, a higher price level implies a _____ demand for money, which leads to a _____ interest rate and a lower planned investment spending.
A) higher; higher
B) higher; lower
C) lower; higher
D) lower; lower
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long-run aggregate supply curve is:
A) horizontal.
B) upward sloping.
C) downward sloping.
D) vertical.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aggregate demand includes the demand for all goods and services in an economy EXCEPT the goods and service that are:
A) purchased by the government.
B) purchased by firms.
C) exported to other countries.
D) imported from other countries.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the marginal propensity to save for an economy is 0.2, then the marginal propensity to consume for the economy is:
A) 0.5.
B) 0.6.
C) 0.7.
D) 0.8.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic growth is depicted by a:
A) rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve.
B) rightward shift in the upward-sloping range of the short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) downward shift in the Keynesian range of the short-run aggregate supply curve.
D) rightward shift in the long-run aggregate supply curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following can lead to a rightward shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve?
A) The money supply increases.
B) Discretionary government spending increases.
C) The labor force increases.
D) Consumer expectations about future income increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the short-run output is more than the potential output, then in the long run, the nominal wage will _____ and output will:
A) fall; fall.
B) rise; fall.
C) fall; rise.
D) rise; rise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use Figure: Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curve. The figure shows two long-run aggregate supply curves for an economy. Which of the following CANNOT lead to a shift from long-run aggregate supply curve 1 to long-run aggregate supply curve 2?
Figure: Long-Run Aggregate Supply Curve

A) The labor force increases.
B) The money supply increases.
C) The educational attainment of the population improves.
D) Technology improves.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following would constitute a positive supply shock?
A) The supply of money in the economy increases.
B) Discretionary government spending increases.
C) The price of oil decreases as a result of conflict or war.
D) The federal income tax decreases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The short-run aggregate supply curve is:
A) upward sloping in the classical range.
B) downward sloping in the Keynesian range.
C) vertical in the Keynesian range.
D) vertical in the classical range.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 105
Related Exams