A) no change; no change; no change
B) an increase; an increase; an increase
C) a decrease; an increase; an increase
D) an increase; a decrease; a decrease
E) a decrease; a decrease; a decrease
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The slope of a country's production possibility frontier is equal to ________ and the optimal production point is located where the slope is equal to ________.Assume that output of good Y is measured on the vertical axis,output of good X is measured on the horizontal axis,MPL is the marginal product of labor with a subscript indicating which good,P is the price of a good,and w is the wage rate.
A) -MPLY/MPLX; -PX/PY
B) -PX/PY; -MPLY/MPLX;
C) -PX/w; -PY/w
D) -MPLY/w; -MPLF/w
E) -MPLX/MPLY; -PX/PY
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the specific factors model,which of the following will increase the quantity of labor used in cloth production?
A) an increase in the price of cloth relative to that of food
B) an increase in the price of food relative to that of cloth
C) a decrease in the price of labor
D) an equal percentage decrease in the price of food and cloth
E) an equal percentage increase in the price of food and cloth
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
U) S.imports of sugar are limited by an import quota that,according to a study updated in 2013,imposed a total cost on American consumers close to $________,or an average cost of ________ per year for every man,woman,and child in the country.
A) $3 billion; $10
B) $105 million; $3
C) $2 billion; $110
D) $3 billion; $2,000
E) $370 million; $2,000
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effect of trade on specialized employees of exporting industries will be ________ jobs and ________ pay because they are relatively ________.
A) more; higher; immobile
B) fewer; lower; immobile
C) fewer; lower; mobile
D) more; lower; immobile
E) more; higher; mobile
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the four-quadrant diagram of the specific factors model,the graph in the upper right quadrant is a country's
A) labor allocation constraint.
B) production possibility frontier.
C) production function for food.
D) production function for cloth.
E) labor supply curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
U) S.imports of sugar are limited by an import quota that,according to a study updated in 2013,imposed annual costs on American consumers of
A) $2,000,000.
B) $1,500,000.
C) $1,000,000,000.
D) $200,000.
E) $370,000.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The slope of a country's production possibility frontier with cloth measured on the horizontal and food measured on the vertical axis in the Ricardian model is equal to ________ and it ________ as more cloth is produced.
A) -MPLF/MPLC; is constant
B) -MPLF/MPLC; becomes steeper
C) -MPLF/MPLC; becomes flatter
D) -MPLC/MPLF; becomes steeper
E) -MPLC/MPLF; is constant
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the four-quadrant diagram of the specific factors model,the graph in the upper right quadrant is a country's
A) production possibility frontier.
B) labor allocation constraint.
C) production function for food.
D) production function for cloth.
E) labor supply curve.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effect of trade on income distribution
A) can be significant in the sort run.
B) is positive for all segments of an economy.
C) is insignificant in the short run.
D) implies that there are no real gains from trade.
E) refutes the model of comparative advantage.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The degree of a factor's specificity is directly related to
A) the amount of time required to redeploy the factor to a different industry.
B) the cost of the factor as a proportion of the long-run total cost of production.
C) the mobility of the factor, with more mobile factors having more specificity.
D) technology differences between two countries, with a more advanced technology resulting in more factor specificity.
E) factor quality, with higher quality factors having a higher level of specificity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the two-country model of international labor mobility
A) the effect of migration is to cause real wages in the two countries to converge.
B) the effect of migration is to cause real wages in the two countries to diverge.
C) labor has only limited international mobility.
D) the long-run equilibrium global real wage is equal to the lesser of the pre-migration wages in the two countries.
E) the long-run equilibrium global real wage is equal to the greater of the pre-migration wages in the two countries.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effect of trade on specialized employees of import-competing industries will be ________ jobs and ________ pay because they are relatively ________.
A) fewer; lower; immobile
B) fewer; lower; mobile
C) more; lower; immobile
D) more; higher; mobile
E) more; higher; immobile
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the specific factors model,a country's production function is ________ because of ________.
A) a straight line; diminishing marginal returns
B) a curved line; diminishing marginal returns
C) a straight line; constant marginal returns
D) a curved line; constant marginal returns
E) a curved line; a limited supply of labor
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
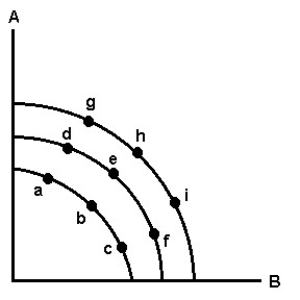 -Refer to the production possibility graph above.Assume that the economy is in equilibrium at point e.If the labor supply increases due to immigration,the new equilibrium is most likely to be
-Refer to the production possibility graph above.Assume that the economy is in equilibrium at point e.If the labor supply increases due to immigration,the new equilibrium is most likely to be
A) point h.
B) point f.
C) point d.
D) point e.
E) point b.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Immigration into the U.S.over the past century has caused the percentage of immigrants in the U.S.population to
A) fall steadily until the 1970s and increase thereafter.
B) remain relatively constant over the time period.
C) fall steadily over the entire century.
D) rise steadily over the entire century.
E) rise steadily until the 1970s and fall thereafter.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the specific factors model,a 5% increase in the price of food accompanied by a 1% increase in the price of cloth will cause ________ in the welfare of labor,________ in the welfare of the fixed factor in the production of food,and ________ in the welfare of the fixed factor in the production of cloth.
A) an ambiguous change; an increase; a decrease
B) an ambiguous change; a decrease; an increase
C) an ambiguous change; an ambiguous change; an ambiguous change
D) a decrease; an ambiguous change; an ambiguous change
E) an increase; a decrease; an increase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the specific factor model,the effect of an increase in the productivity of labor in the production of cloth will cause a(an) ________ in the quantity of labor used to produce cloth,a(an) ________ in the quantity of labor used to produce food and a(an) ________ in the wage rate.
A) increase; decrease; increase
B) decrease; increase; increase
C) increase; decrease; decrease
D) decrease; increase; no change
E) increase; increase; no change
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the four-quadrant diagram of the specific factors model,the graph in the lower right quadrant is a country's
A) production function for cloth.
B) production possibility frontier.
C) labor allocation constraint.
D) production function for food.
E) labor supply curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The specific factors model assumes that there are ________ goods and ________ factor(s) of production.
A) two; three
B) two; two
C) two; one
D) three; two
E) four; three
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 70
Related Exams