A) the economy is in long-run equilibrium.
B) the economy is in long-run equilibrium
C) an expansionary fiscal policy may be warranted.
D) an expansionary fiscal policy may be warranted
E) a contractionary fiscal policy may be warranted.
F) a contractionary fiscal policy may be warranted
G) the economy is in a recessionary gap
H) the economy is in a recessionary gap.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Figure: Fiscal Policy I) Use Figure: Fiscal Policy I. Suppose that this economy is in equilibrium at E2. If there is an increase in taxes, _____ will shift to the _____, causing a(n) _____ in the price level and a(n) _____ in real GDP.

A) AD2; left; increase; decrease
B) AD2; left; increase; decrease.
C) AD2; left; decrease; decrease
D) AD2; left; decrease; decrease.
E) AD1; right; increase; increase
F) AD1; right; increase; increase.
G) AD1; right; decrease; increase
H) AD1; right; decrease; increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Net government debt is:
A) total public debt, adjusted for inflation.
B) the debt that the government owes to individuals, businesses, and other governments both here and abroad.
C) the debt that the government owes to foreigners, both in the United States and abroad.
D) the accumulation of all the deficits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Figure: Fiscal Policy Choices) Use Figure: Fiscal Policy Choices. In panel (a) , if the economy is at output level Y1, there is:
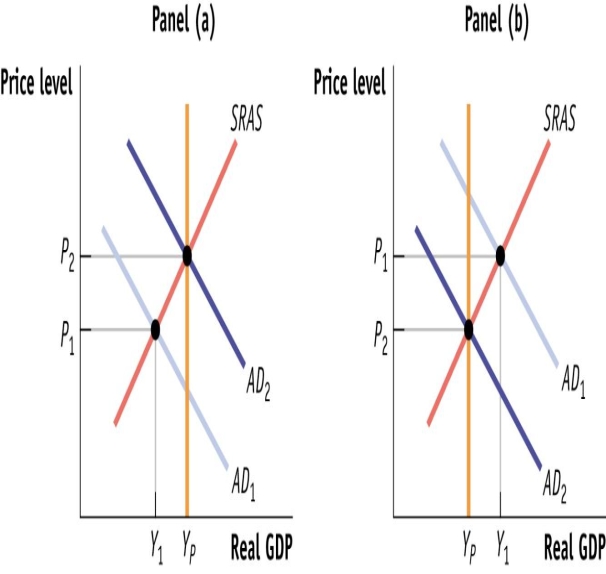
A) an inflationary gap.
B) an inflationary gap
C) a recessionary gap.
D) a recessionary gap
E) equilibrium at full employment.
F) equilibrium at full employment
G) no output gap.
H) no output gap
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If aggregate output lies above potential output, then an appropriate fiscal policy would be to _____, which will shift the AD curve to the _____.
A) decrease government purchases; right
B) decrease government purchases; right.
C) increase government purchases; left.
D) increase government purchases; left
E) decrease government purchases; left.
F) decrease government purchases; left
G) raise tax rates; right.
H) raise tax rates; right
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an item costs $95 in California and the sales tax is 7.25%, you will pay a total of $_____ at the register.
A) $101.89
B) $88.11
C) $7.25
D) $6.89
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The standard deduction for a single person is $12,200. Based on this table, if your total income is $47,000, what is the amount of tax you will pay on your taxable income?
A) $4,176
B) $3,012
C) $10,340
D) $3,982
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the economy is in an inflationary gap. To move aggregate output closer to potential output, the BEST fiscal policy option is to:
A) lower tax rates.
B) lower tax rates
C) decrease government purchases.
D) decrease government purchases
E) increase the investment tax credit.
F) increase the investment tax credit
G) lower the real interest rate.
H) lower the real interest rate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal tax rate is the:
A) tax on social security.
B) amount of your income that you pay taxes on.
C) amount of tax rebates that you receive at the end of the year.
D) tax rate you pay if you earn another dollar.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Why does discretionary fiscal policy experience time lags?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Figure: Short-Run Equilibrium) Use Figure: Short-Run Equilibrium. Given the scenario depicted in the diagram, an appropriate fiscal policy action would be:
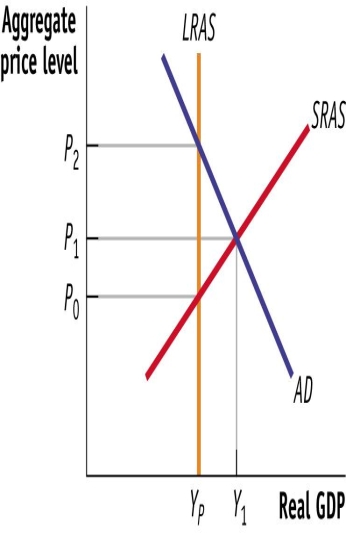
A) a decrease in transfer payments
B) a decrease in transfer payments.
C) an increase in government purchases
D) an increase in government purchases.
E) a decrease in tax rates.
F) a decrease in tax rates
G) an increase in transfer payments
H) an increase in transfer payments.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
_____ is an automatic stabilizer.
A) An infrastructure bill
B) An infrastructure bill.
C) Military spending
D) Military spending.
E) A fiscal stimulus.
F) A fiscal stimulus
G) Medicaid.
H) Medicaid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In late 2001, Argentina defaulted on more than $90 billion worth of its external debt. This is an example of:
A) a debt crisis.
B) net capital inflow.
C) crowding out.
D) discretionary spending.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the province of Ontario, consumers pay harmonized sales tax (HST) of 13%. If an item costs $179 in Ontario, you will pay a total of $_____ at the register.
A) $13
B) $202.27
C) $23.27
D) $155.73
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Medicare provides health care to:
A) people who earn $250,000 a year or more.
B) people over the age of 65.
C) foreign visitors to the United States.
D) high-income people who already have health care coverage through their workplaces.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Discuss three reasons why tax expenditures primarily benefit the wealthy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Payroll taxes are 6.2%, and Medicare taxes are 2.9%. Your employer owes you $850. How much will your work cost your employer?
A) $927.35
B) $77.35
C) $52.70
D) $24.65
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Why is fiscal policy very important at the zero lower bound?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Figure: Short-Run Equilibrium) Use Figure: Short-Run Equilibrium. The diagram indicates a short-run inflationary gap. The size of the inflationary gap is:
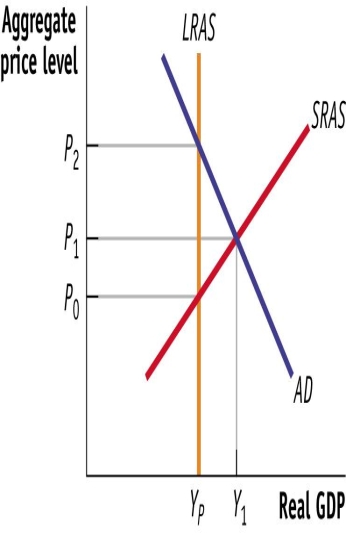
A) P2 - P1
B) P2 - P1.
C) Y1 - YP.
D) Y1 - YP
E) P2 - P0.
F) P2 - P0
G) P1 - P0.
H) P1 - P0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In your current job, you earn $41,000. You take the standard deduction of $12,200. You have an offer of a new job working for a different employer. Your salary would go up by $6,500. Given your current taxable income, what is your marginal tax rate?
A) 22%
B) 12%
C) 10%
D) 24%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 178
Related Exams