A) eight; $4
B) 12; $3
C) four; $6
D) three; $12
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A good that is excludable but nonrival in consumption is known as a _____ good.
A) public
B) club
C) private
D) proprietary
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the amount of a corrective tax that would resolve a negative externality problem?
A) The marginal social cost.
B) The total social cost.
C) The total external cost.
D) The marginal external cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Figure: Market 3) Use the graph to answer the question.
The graph shows the marginal social cost, demand, and supply curves in the toothpaste market. If market forces prevail, this market will produce and sell _____ tubes of toothpaste at a price of _____.
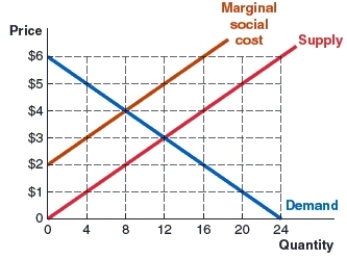
A) eight; $5
B) eight; $4
C) 12; $3
D) 12; $4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT an example of a corrective tax or subsidy used to address an externality problem?
A) A country charges a set fee to companies that manufacture in the country for every 100 gallons of a particular chemical that they release into the country's lakes and waterways.
B) The government sets a limit on the quantity of pollution companies can emit by issuing a set number of pollution permits that companies can trade.
C) An environmental protection organization publishes and publicizes an annual list of companies that have taken actions to protect the environment as well as a list of companies that it finds are damaging the environment.
D) A community distributes "I voted" stickers to everyone who votes in an election, hoping that seeing them on voters will encourage others to vote.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A negative externality is:
A) a side effect of an activity when the side effect harms bystanders.
B) a reduction in demand that occurs when agents outside a market influence market participants.
C) a change from a positive relationship between two variables to an inverse relationship.
D) an unintended consequence of an action that harms the decision maker.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What determines whether a corrective tax or quantity regulation is a better choice for controlling an externality?
A) It depends on whether the externality is positive or negative.
B) It depends on whether more is known about marginal external costs or about the socially optimal quantity.
C) It depends on how much damage is being done by the externality.
D) It depends on whether or not the rational rule can be applied.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An advantage of cap and trade is that:
A) pollution costs are more easily identifiable, making emission control easier.
B) some pollution controls are less costly than others.
C) the value that future generations place on pollution damages can be determined.
D) technological change is incentivized, making cleaning up easier and less costly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal private benefit plus the marginal external benefit equals the ____ benefit.
A) total public
B) total externality
C) marginal social
D) marginal public
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(Market 6) Use the graph to answer the question.
The graph shows the marginal social benefit, marginal private benefit, and marginal private curves in the taco market. The socially optimal quantity is _____, and the price is ______.
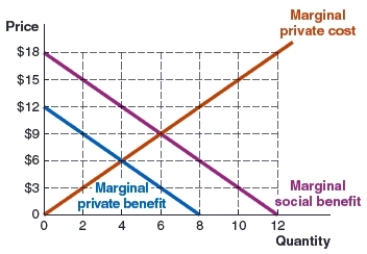
A) four; $12
B) nine; $6
C) four; $6
D) six; $9
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The outcome that is most efficient for society as a whole - including the interests of buyers, sellers, and bystanders - is the _____ outcome.
A) externally optimal
B) social benefit maximizing
C) public optimal
D) socially optimal
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the production of a good, pollution is emitted that affects people who are neither producers nor buyers of the good. The term for the impact of the pollution on these people is:
A) externality.
B) exploitation.
C) intrusion.
D) outside impact.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cost paid by the seller in producing one additional unit of output is known as the _____ cost.
A) marginal external
B) marginal private
C) external
D) marginal social
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Rational Rule for Society is that society should produce another unit of a good if:
A) the total social benefit exceeds the total social cost.
B) the marginal social benefit exceeds the marginal social cost.
C) the marginal private benefit exceeds the marginal private cost.
D) gains to the producer exceed losses to the producer.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the term for a quantity regulation that is implemented by allocating a fixed number of permits to producers, which can then be traded?
A) quota market
B) cap and trade
C) private bargaining
D) public goods
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Costs that arise from a market transaction but that are borne by people not involved in the transaction are called _____ costs.
A) outside
B) public
C) reversal
D) external
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pedro attends a university that provides antivirus software to all students, faculty, and staff for their personal computers as well as all university-owned computers. Why would the university pay for the protection of the personal computers of students, faculty, and staff?
A) Having this extra perk from being associated with the university makes it easier to attract high-quality students, faculty, and staff.
B) It reduces the cost of operations for the university because it can thereby buy software in bulk.
C) It reduces the number of viruses on university-owned computers by reducing the probability that viruses will spread through files transferred from personal computers to university-owned computers and systems.
D) Reducing the spread of viruses across campus promotes health among students and decreases absenteeism, which improve educational outcomes on campus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal social cost is:
A) the extra cost imposed on bystanders when an extra unit is produced and consumed.
B) the extra cost faced by a producer when an extra unit is produced and sold to a member of society.
C) the difference between the marginal external cost and the marginal private cost.
D) the sum of marginal private costs and marginal external costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of good is rival and excludable?
A) private goods
B) club goods
C) common resources
D) public goods
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sellers must cover _____ costs, but a market does not require them to cover _____ costs.
A) variable; fixed
B) average; fixed
C) marginal private; marginal external
D) marginal total; marginal private
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 201 - 220 of 241
Related Exams