A) Because the use of antibiotics lowers the effectiveness of the immune system, the student continually reinfected himself with the bacteria. The third time, the student happened to be reinfected with a resistant strain.
B) When the student stopped taking the drug, a small number of bacteria-those that were more drug resistant-still survived in his body. Those bacteria repopulated his throat and over time, drug-resistant alleles became more common.
C) The student must have eaten produce that had been genetically engineered with antibiotic-resistant genes. When he consumed them, the bacteria in the student's throat picked up these genes through horizontal gene transfer.
D) The antibiotic caused mutations in the bacterium. The more exposure to the antibiotic, the more mutations. Even one random mutation can confer antibiotic resistance.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Although they are protected in many countries, humans still hunt elephants for their ivory tusks. A mutation that results in tuskless elephants is increasing in frequency in some elephant populations as a result of the evolutionary mechanism of ____________________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A scientist is studying beak length in a species of hummingbird. The scientist establishes a population of birds with beaks ranging from very small to very long and allows the population to breed for 10 years. At the end of the experiment, she finds that the majority of birds in the population have very long beaks. This is an example of _____ selection.
A) disruptive
B) stabilizing
C) directional
D) sexual
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the total number of alleles present for any given gene in a population of 100 individuals?
A) 50
B) 100
C) 200
D) 400
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If p is the frequency of the W allele in a population, why do we equate the WW individuals with the p² portion of the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
A) The Hardy-Weinberg equation describes the frequencies of dominant alleles only.
B) The WW individuals have two copies of the allele represented by p.
C) The ww individuals are all killed by lethal recessive genes.
D) The frequency of p is always equal to the frequency of q.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A few members of a species establish themselves on a small island far from other populations of that species. They may experience a genetic bottleneck due to the ____________________ effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fisherman catches one trout from each of two ponds. Pond A contains 100 trout and pond B contains 1,000 trout. Which population is more affected by the fisherman?
A) Pond A; the fisherman has a greater likelihood of completely removing alleles from the gene pool by taking a fish from the smaller population.
B) Pond A; fewer fish are able to move into a small pond and find mates.
C) Pond B; the fisherman is more likely to catch a fish that is undergoing evolution in a bigger population.
D) Pond B; the process of evolution occurs more slowly in large populations and removing a fish speeds up the process.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A used car is shipped from Australia to the United States. Stowed away in the trunk of the car is a piece of wood infected with Australian termites. Once in the United States, the buyer of the car finds the rotting wood and dumps it on the side of the road. The termites survive and establish a colony on the side of the road, but do not mate with local termite populations. This is an example of
A) genetic drift.
B) mutation.
C) natural selection.
D) gene flow.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One factor that complicates the treatment of AIDS is the
A) low mutation rate of HIV.
B) high mutation rate of HIV.
C) random mating between viral particles.
D) nonrandom mating between viral particles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a step in the evolutionary process?
A) Mutation results in the formation of new alleles and sexual reproduction results in new combinations of alleles.
B) New genes are introduced into a population when members of that population mate with members of other species.
C) Genetic variation is inherited by the next generation of a population.
D) Genetic drift, gene flow, and or natural selection cause allele frequencies to change over time.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
If the genotype values predicted by the Hardy-Weinberg equation are greatly different from the values found in the real population, we can say that the population is ____________________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the figure below, the flying bird moves permanently into the population shown on land. As a result, the allele frequency of A in the population changes from 
A) 1 to 0.75.
B) 0 to 0.25.
C) 0 to 0.75.
D) 1 to 0.25.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Disruptive selection operates whenever
A) natural selection is disrupted by genetic drift.
B) there is a balanced gene pool.
C) only the smallest individuals survive.
D) both the recessive and the dominant homozygotes are more successful.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning evolution is false?
A) Natural selection requires variation in the population.
B) An individual that is better adapted than others in a population will always be more reproductively successful.
C) Genetic drift causes little evolutionary change in large populations.
D) Evolution involves a change of frequency of alleles in the gene pool.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Microevolution
A) does not alter the genotype frequencies of a population.
B) is caused by speciation.
C) occurs only in microorganisms.
D) is the smallest scale at which evolution occurs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a given population has 30 RR individuals, 10 Rr individuals, and 10 rr individuals, what is the genotype frequency of Rr?
A) 0.10
B) 0.20
C) 0.30
D) 0.50
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
In ____________________ selection, individuals with one extreme of an inherited phenotypic trait have an advantage over other individuals in the population.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Larger male elephant seals have more mates than smaller male elephant seals because they are better at defending their territory (and mates). This is an example of ____________________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Is the effect of an individual permanently leaving a population likely to have a greater genetic effect if the home population was large or if the home population was small?
A) Large, because this is an example of disruptive selection.
B) Large, because natural selection will cause a bottleneck to occur in the remaining individuals.
C) Small, because the loss of just a few individuals may greatly reduce the remaining genetic variation.
D) Small, because the remaining individuals will no longer be able to practice nonrandom mating.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The bell-shaped curve at the top of the figure below shows the distribution of a phenotype in a population at the start of an experiment. The three graphs (lettered A-C) beneath predict what the distribution will look like if a certain type of selection occurs. Which graph represents what the phenotypic distribution will look like if the population undergoes stabilizing selection? 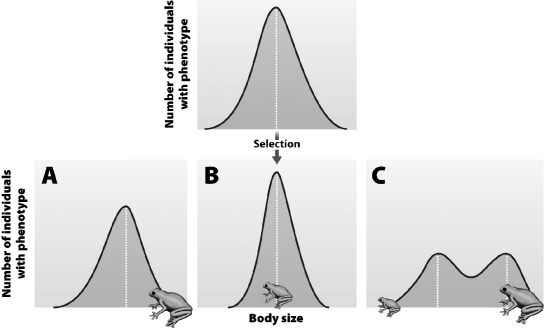
A) Graph A
B) Graph B
C) Graph C
D) These graphs all show natural selection, but none show stabilizing selection.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 80
Related Exams