A) Brachialis
B) Brachioradialis
C) Triceps brachii
D) Pronator teres
E) Flexor carpi ulnaris
F) Supinator
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following body structures is a medial soft tissue that should be palpated in order to assess an elbow injury?
A) The pronator teres
B) The radial collateral ligament
C) The annular ligament
D) The triceps
E) The ulnar nerve
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please check all of the injuries that can be caused by falling on an outstretch hand.
A) Cubital tunnel syndrome
B) Medial epicondylitis
C) Fracture of the elbow
D) Dislocation of the elbow
E) Volkmann's contracture
F) Pronator teres syndrome
G) Olecranon bursitis
Correct Answer

verified
C, D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following movements is the highlighted structure in the given figure of major importance? 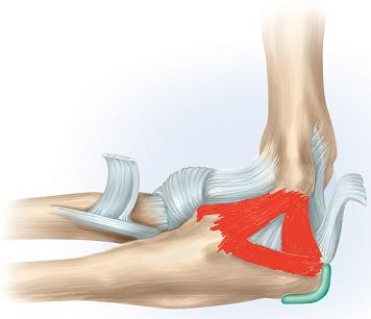
A) Forceful extension-pronation movement
B) Forceful extension-supination movement
C) Forceful extension movement
D) Forceful flexion-supination movement
E) Forceful flexion-pronation movement
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a patient suffers an elbow dislocation, what nerve(s) can be compromised?
A) Median
B) Ulnar
C) Musculocutaneous
D) Median and ulnar
E) Median, ulnar, and musculocutaneous
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What structure(s) reinforce the elbow capsule?
A) Brachialis muscle
B) Ulnar and radial collateral ligaments
C) Triceps brachii muscle
D) Anconeus muscle
E) Annular ligament
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is incorrectly listed as a factor that can lead to cubital tunnel syndrome?
A) Traction injury from a valgus force
B) Irregularities within the tunnel
C) Subluxation of the ulnar nerve because of a lax ligament
D) Progressive compression of the ligament on the nerve
E) Fracture of the olecranon
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the history section of an elbow assessment, what would be considered an inappropriate question to ask the patient?
A) Is the pain contributed to a sudden injury or overuse?
B) Is there any movement that makes the pain better or worse?
C) Do you have any cuts on your arm?
D) Is there a feeling of locking or catching?
E) What is your dominant arm/hand?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the context of the rehabilitation of the elbow, the initial stage of strength exercises should include
A) pronation and supination exercises.
B) manual resistance exercises.
C) isokinetic exercises.
D) subpainful submaximal isometric exercises.
E) neutral foot strike exercises.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A middle school tennis player comes to you complaining of sudden pain and locking in the elbow joint. They also have swelling, pain, and crepitation. What could be wrong with this athlete?
A) Elbow osteochondritis dissecans
B) Medial epicondylitis
C) Little League elbow
D) Cubital tunnel syndrome
E) Volkmann's contracture
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is another name for elbow osteochondritis dissecans?
A) Little League elbow
B) Golfers elbow
C) Tennis elbow
D) Panner's disease
E) Throwers elbow
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What artery is involved in a Volkmann's contracture?
A) Radial
B) Ulnar
C) Brachial
D) Axillary
E) Subclavian
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true of olecranon bursitis?
A) It can be managed by applying a cold compress for at least 15 minutes.
B) It is relieved by a program of conservative treatment primarily involving compression.
C) It invariably leads to serious health consequences such as the development of malignant tumors.
D) Cryotherapy is mostly unsuccessful in relieving or managing chronic olecranon bursitis.
E) It is invariably accompanied by extreme pain and heat.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What artery does the subclavian become?
A) Deep brachial
B) Ulnar recurrent
C) Brachial
D) Ulnar
E) Axillary
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following incorrectly describes Little League elbow?
A) An accelerated apophyseal growth region plus a delay in the medial epicondylar growth plate.
B) An avulsion of the lateral epicondyle
C) Osteochondrosis of the humeral capitulum
D) A nonunion stress fracture of the olecranon epiphysis
E) A traction apophysitis with a possible fragmentation of the medial epicondylar apophysis
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please check all of the types of sports where medial epicondylitis is common:
A) Javelin throw
B) Baseball
C) Swimming
D) Golf
E) Judo
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The humeroradial inferior glide demonstrated in this video is utilized to increase which of the following?
A) Elbow flexion
B) Elbow extension
C) Elbow pronation
D) Elbow flexion and extension
E) Elbow flexion, extension, and pronation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would be an inappropriate body structure to palpate during the palpation section of the elbow?
A) Anconeus muscle
B) Annular ligament
C) Wrist flexor muscle mass
D) Joint capsule
E) Radial head
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A softball catcher complains of loss of motor function of her fingers and sensory loss in her forearm. Her fingers are also beginning to form a contracture. She had an elbow dislocation 3 weeks ago. What is probably wrong with this athlete?
A) Brachial plexus injury
B) Volkmann's contracture
C) Carpal tunnel syndrome
D) Olecranon fracture
E) Rupture of the extensor muscles of the wrist
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please check all of the statements that are TRUE regarding the one-arm hop test.
A) There is a 3-minute break between the testing for each upper extremity
B) From a push-up position you hop with 1 arm onto a 10.2 cm step and back on to the floor
C) You perform 2 up-down repetitions
D) You check both the dominant and non-dominant side
E) You time how long it takes you to perfom the up-downs
F) The one-arm hop test may be useful as a basis for comparing performance of an injured contralateral upper extremity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 29
Related Exams