A) increase inflation without reducing unemployment.
B) increase unemployment while exerting little impact on inflation.
C) decrease unemployment while exerting little impact on inflation.
D) fail to exert a significant impact on either unemployment or inflation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under the rational expectations hypothesis,which of the following is the most likely effect of a shift to a more expansionary monetary policy?
A) In the short run,the real rate of output will be unaffected,but in the long run,it will increase.
B) In the short run,the real rate of output will increase,but in the long run,it will be unchanged.
C) There will be a permanent increase in the real rate of output,but the inflation rate will also be a little higher.
D) In the short run,the impact on the real rate of output is uncertain;in the long run,it will remain unchanged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the theory of rational expectations,errors in predicting inflation will
A) be biased upward more often than not.
B) be purely random.
C) tend to be biased downward when inflation is rising,and tend to be biased upward when inflation is falling.
D) tend to be biased upward when inflation is rising,and tend to be biased downward when inflation is falling.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If monetary and fiscal policy are going to promote economic stability,they must _________ during a recession,and _________ during an economic boom.(Fill in the blank)
A) add stimulus;apply restraint
B) apply restraint;add stimulus
C) add stimulus;add stimulus
D) apply restraint;apply restraint
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Between 1983 and 2007,the U.S.economy was in recession ___________ share of the time,compared to ___________ share of the time during 1910-1959.(Fill in the blank)
A) 6 percent;33 percent
B) 20 percent;10 percent
C) 33 percent;12 percent
D) 15 percent;50 percent
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most important for the achievement of long-term prosperity and strong economic growth?
A) expansionary monetary policy
B) expansionary fiscal policy
C) price stability
D) a balanced federal budget
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under the adaptive expectations hypothesis,which of the following is the most likely long-run effect of a move to a more expansionary monetary policy?
A) higher prices and no change in real output
B) higher prices and expansion in real output
C) no change in prices but an expansion in real output
D) no change in either prices or real output
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
(I) In the 1960s and 1970s,most economists believed that there was a permanent trade-off between inflation and unemployment. (II) Today,most economists believe there is no permanent trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
A) Both I and II are true.
B) Both I and II are false.
C) I is true;II is false.
D) I is false;II is true.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following factors substantially reduces the effectiveness of discretionary changes in tax rates or government expenditures as a stabilization tool?
A) Even though computer models have enhanced our forecasting ability,policy makers at the Federal Reserve have been reluctant to utilize information supplied by the models.
B) When fiscal policy is altered,the Fed generally shifts monetary policy in a manner that offsets the impact of the fiscal action.
C) Changes in government expenditures and taxes are always offset by equal changes in private spending.
D) Since it takes time for fiscal policy to work and since the future is difficult to forecast,it is difficult to time fiscal policy changes correctly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to choose the correct answer.
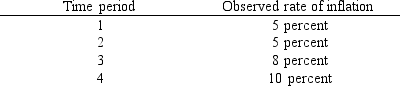 According to the adaptive expectations hypothesis,at the beginning of period 3,decision makers would expect inflation during period 3 to be
According to the adaptive expectations hypothesis,at the beginning of period 3,decision makers would expect inflation during period 3 to be
A) 2.5 percent.
B) 5 percent.
C) 7.5 percent.
D) 8 percent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the Modern Expectational Phillips curve diagram below to answer the following question(s) .
Figure 15-4
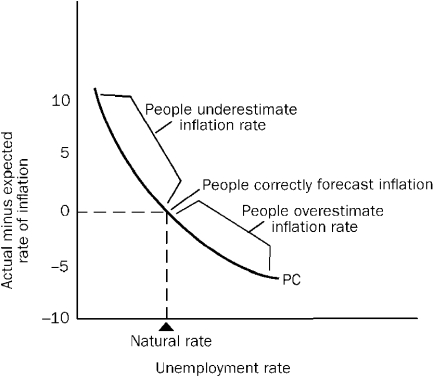 -Refer to Figure 15-4.According to the modern expectational Phillips curve,actual unemployment will generally fall below the natural rate of unemployment if
-Refer to Figure 15-4.According to the modern expectational Phillips curve,actual unemployment will generally fall below the natural rate of unemployment if
A) inflation falls to zero.
B) inflation exceeds what was anticipated by decision makers.
C) inflation is less than anticipated by decision makers.
D) people fully anticipate the inflationary side effects of expansionary macroeconomic policies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The modern view of the Phillips curve indicates that in the long run there
A) is no trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
B) is a definite trade-off between unemployment and inflation.
C) will be a trade-off if the rational expectations hypothesis is correct.
D) may be a long-run trade-off between unemployment and inflation,but there is no such trade-off in the short run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that during the last several years,the annual rate of inflation was 4 percent and the annual growth rate of the money supply was 5 percent.During the last 12 months,however,the monetary authorities have increased the money supply at a 12 percent annual rate.The expected inflation rate for the next period will be
A) higher than 4 percent under the rational expectations hypothesis.
B) 4 percent under the adaptive expectations hypothesis.
C) higher than 4 percent under both the adaptive and rational expectations hypotheses.
D) both a and b.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 15-3
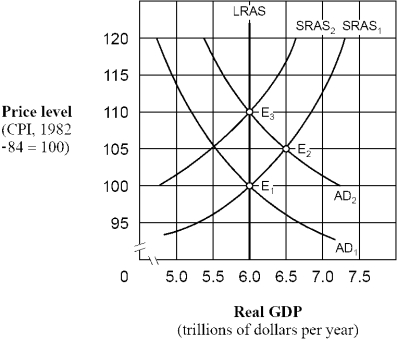 -As shown in Figure 15-3,if people behave according to rational expectations theory,an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD₁ to AD₂ will cause the price level to move
-As shown in Figure 15-3,if people behave according to rational expectations theory,an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD₁ to AD₂ will cause the price level to move
A) directly from 100 to 105 and then remain at 105.
B) directly from 100 to 110 and then remain at 110.
C) from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move back to 100.
D) from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move to 110.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the adaptive expectations hypothesis,people will
A) anticipate that what has happened in the immediate past will continue.
B) systematically overestimate inflation when inflation is increasing.
C) use all available information,including information on the expected impact of economic policy,when they formulate expectations about economic events.
D) systematically underestimate inflation when inflation is declining.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the index of leading indicators and other forecasting devices suggested that the economy is moving into an inflationary boom,activists' economic policy would call for
A) a decrease in money supply growth and a tax increase.
B) an increase in money supply growth and a shift toward a budget deficit.
C) an increase in money supply growth and a tax decrease.
D) a continuation of the policies already in place.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When there is an abrupt reduction in the rate of inflation,
A) the actual rate of unemployment will tend to fall below the natural rate.
B) the actual rate of unemployment will tend to rise above the natural rate.
C) the actual and natural rate of unemployment will generally be equal.
D) the natural rate of unemployment will tend to rise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following contributed to the weak recovery from the 2008-2009 recession?
A) constant policy changes that generated uncertainty and undermined private investment
B) the restrictive monetary policy followed by the Fed
C) the tax increases instituted by a Congress intent on balancing the budget
D) the inability of the federal government to borrow because of the sharply higher interest rates
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The proponents of adaptive expectations believe that
A) there will be a substantial time lag before people anticipate the effects of a shift to a more expansionary macro-policy.
B) macro-policies that stimulate demand and place upward pressure on the general level of prices will temporarily increase output and employment.
C) discretionary changes in macro-policy can be made in a manner that will reduce the economic ups and downs of a market economy.
D) all of the above are true.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most economists believe that
A) a monetary policy that achieves price stability will reduce uncertainty and provide the framework for strong economic growth.
B) demand stimulus policies will reduce the long-term average rate of unemployment.
C) expansionary monetary policy,if persistently followed,will reduce nominal interest rates.
D) inflation is primarily the result of large budget deficits and other elements of expansionary fiscal policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 177
Related Exams