A) inhabit aquatic environments.
B) develop an endoskeleton.
C) move quickly and precisely.
D) undergo complete metamorphosis.
E) have young disperse from sessile adults.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 32.4 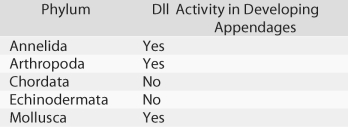 -Dll is a gene known to direct limb development in the fruit fly.Researchers studying this gene have found that it is also expressed in developing appendages in animals from many other phyla as well,supporting the hypothesis that all animal appendages may be homologous.However,suppose researchers looking at Dll activity had instead found the results shown in Figure 32.4. What would these results suggest?
-Dll is a gene known to direct limb development in the fruit fly.Researchers studying this gene have found that it is also expressed in developing appendages in animals from many other phyla as well,supporting the hypothesis that all animal appendages may be homologous.However,suppose researchers looking at Dll activity had instead found the results shown in Figure 32.4. What would these results suggest?
A) Dll is not actually involved in appendage development.
B) Appendages evolved separately in protostomes and deuterostomes.
C) Appendages coevolved with segmentation.
D) All animal appendages are homologous.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following groups of terms best describes the acoelomorpha?
A) diploblastic;bilaterally symmetric;complex digestive tracts;mobile
B) triploblastic;radially symmetric;simple digestive tracts;mobile
C) triploblastic;bilaterally symmetric;simple digestive tracts;mobile
D) triploblastic;radially symmetric;simple digestive tracts;immobile
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Comb jellies may not be the most familiar animal to you,but they are critical in the food chain because they make up a significant portion of the planktonic biomass.Their feeding strategy is predatory and involves adhesives or mucous on their tentacles or other body parts.What feeding tactic do these animals use?
A) suspension feeder
B) fluid feeder
C) deposit feeder
D) food-mass feeder
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 32.1  -From the information provided in the figure above,how would you classify the feeding strategy of organism C?
-From the information provided in the figure above,how would you classify the feeding strategy of organism C?
A) suspension feeding
B) predation
C) parasitism
D) A and B
E) B and C
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The embryo doesn't grow larger during the stage known as cleavage.What is going on in the embryo during this process?
A) Cleavage is just the stage at which cells begin to differentiate;that is,endodermal cells start to look different from ectodermal and mesodermal cells.
B) The cells are dividing at this stage,but all the cytoplasm is being split between resulting cells without the formation of new cytoplasm.
C) Cleavage is the formation of the gastropore that is used to differentiate protostomes and deuterostomes.
D) Cleavage is the process by which the polarity of the cell is established;that is,the anterior is distinguished from the posterior.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following feeding tactics is consistent with this list of features: two-part stomach capable of breaking down tough food particles;simple mouthparts;the ability to burrow through,and consume,indigestible fecal material to get to hidden food?
A) suspension feeder
B) fluid feeder
C) deposit feeder
D) food-mass feeder
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To reproduce,many plants produce seeds-structures containing embryonic offspring along with nutrients inside a tough case.These offspring develop after being released by the parent plant.To which animal reproductive strategy is seed production most comparable?
A) oviparous reproduction
B) ovoviviparous reproduction
C) viviparous reproduction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The text describes four ways,or tactics,of feeding.Which of the following is NOT one of those ways?
A) suspension feeding
B) food-mass feeding
C) herbivory feeding
D) deposit feeding
E) fluid feeding
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are true about choanoflagellates EXCEPT
A) they are suspension feeders.
B) they are sessile as adults.
C) they live in aquatic habitats.
D) they are animals.
E) they reproduce asexually.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following characteristics is not true of animals?
A) They typically have more haploid cells than diploid cells.
B) They have an extracellular matrix.
C) They are the only group on the tree of life with muscle and nervous tissue.
D) They have a cell wall.
E) All of the above are true of animals.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following combinations of embryonic features is common in the deuterostomes?
A) spiral cleavage and the gastrulation pore (or gastropore) becomes the anus
B) radial cleavage and the gastropore becomes the mouth
C) absence of cleavage and gastropore becomes the anus
D) spiral cleavage and the absence of gastropore formation
E) radial cleavage and the gastropore becomes the anus
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Parasitism is one of the most successful life strategies ever to evolve.Which of the following is consistent with this finding?
A) Parasites almost always predigest their hosts' tissues and,therefore,spend less energy and require fewer structural adaptations.
B) Parasites,unlike predators,feed on almost all the tissues of their host.
C) Parasites do not generally kill their hosts,thus they can feed on the same host throughout the host's normal life span and do not have competition from decomposers.
D) Parasites generally kill their host and can feed for a very long time because they are much smaller than their host.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following objects most closely resembles the pattern of the tube-within-a-tube body plan?
A) a bowling ball (with finger holes drilled)
B) a pipe with a straw inside
C) a cup with a straw in it
D) a soda can with the tab removed
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are healthy corals brightly colored?
A) Corals secrete colorful pigments to warn predators that they are poisonous.
B) Corals secrete colorful pigments to attract mates.
C) Corals host symbionts with colorful photosynthetic pigments.
D) Corals build their skeletons from colorful minerals.
E) Corals secrete colorful pigments to protect themselves from UV light.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 32.2 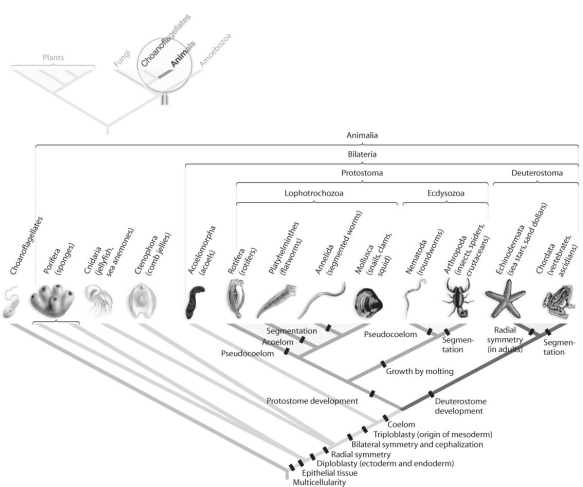 -Which morphological trait evolved more than once in animals,according to the phylogeny based on DNA sequence data found in Figure 32.2 above?
-Which morphological trait evolved more than once in animals,according to the phylogeny based on DNA sequence data found in Figure 32.2 above?
A) coelom
B) bilateral symmetry
C) segmentation
D) tissue
E) protostome development
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose you came across a novel organism you suspected belonged to one of the following animal phyla: Porifera,Cnidaria,Ctenophora,or Acoelomorpha.Which of the following characteristics would not be helpful in placing the organism into the correct phylum?
A) the organism's feeding strategy
B) the organism's habitat
C) whether the organism has a coelom
D) whether the organism has a gut
E) whether adults are sessile or motile
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While looking at some seawater through your microscope,you spot the egg of an unknown animal.Which of the following tests could you not use to determine whether the developing organism is a protostome or a deuterostome?
A) See whether the ectoderm forms the mature animal's skin/exoskeleton or nervous system
B) See whether the animal exhibits spiral cleavage or radial cleavage during early development.
C) See whether the coelom is formed from a split in the mesoderm or from mesodermal pockets pinched off the gut.
D) See whether the pore formed during gastrulation becomes the mature animal's mouth or its anus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Due to its unusual habitat (inside the digestive tracts of other animals) ,the tapeworm lacks
A) a head
B) a mouth
C) a digestive tract
D) B and C
E) A,B,and C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose all of the suspension feeders were removed from a lake.What would you expect to happen after a brief period of time?
A) The water would become clearer.
B) The water would become murkier.
C) The water would remain the same.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 42
Related Exams