A) implementing abatement technology.
B) patents.
C) property rights.
D) Pigovian taxes.
E) cap-and-trade.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal private benefit curve (MB) is a negatively-sloped straight line. If marginal external benefit decreases as output increases, the marginal social benefit curve is a negatively-sloped straight line
A) parallel to and above the MB curve.
B) parallel to and below the MB curve.
C) above the MB curve and steeper than the MB curve.
D) above the MB curve and flatter than the MB curve.
E) below the MB curve and flatter than the MB curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If positive externalities exist and production is left to the private market, then at the quantity produced,
A) MSC = MSB.
B) MSC < MSB.
C) MSC > MSB.
D) MSB = marginal external benefit.
E) MSB = 1/MSC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Coase theorem applies when transactions costs are
A) low and property rights exist.
B) low and property rights do not exist.
C) high and property rights exist.
D) high and property rights do not exist.
E) low and there are no externalities.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following question.
Table 16.2.3
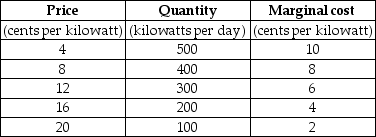 -Refer to Table 16.2.3. The first two columns of the table show the demand schedule for electricity from a coal burning utility; the second and third columns show the utility's cost of producing electricity. The marginal external cost of the pollution created is equal to the marginal cost.
Suppose the government levies a pollution tax such that the utility generates the efficient quantity of electricity. The pollution tax is ________ cents a kilowatt hour.
-Refer to Table 16.2.3. The first two columns of the table show the demand schedule for electricity from a coal burning utility; the second and third columns show the utility's cost of producing electricity. The marginal external cost of the pollution created is equal to the marginal cost.
Suppose the government levies a pollution tax such that the utility generates the efficient quantity of electricity. The pollution tax is ________ cents a kilowatt hour.
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
E) 10
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 16.3.1
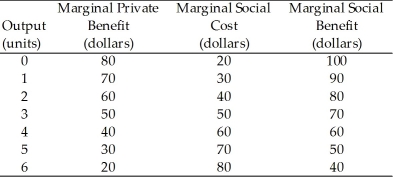 -Refer to Table 16.3.1. The table shows marginal private benefit and the marginal social benefit from the consumption of chemical fertilizer and the marginal social cost of the production of fertilizer. Choose the correct statement.
-Refer to Table 16.3.1. The table shows marginal private benefit and the marginal social benefit from the consumption of chemical fertilizer and the marginal social cost of the production of fertilizer. Choose the correct statement.
A) The marginal external benefit is $20 per unit.
B) The marginal external cost is $10 per unit.
C) There are no externalities associated with this market.
D) The marginal external benefit is $10 per unit.
E) There is not enough information provided to determine whether or not there are externalities.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A homeowner planting an attractive garden in front of his house creates ________. A bakery baking bread creates ________.
A) no externality; a positive production externality
B) a positive consumption externality; no externality
C) no externality; no externality
D) a positive consumption externality; a positive production externality
E) a positive production externality; no externality
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
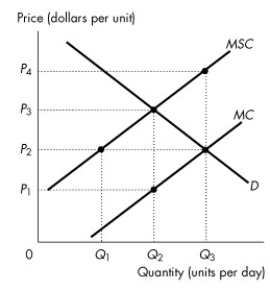 Figure 16.2.1
-Refer to Figure 16.2.1. The figure shows the marginal private cost curve, the marginal social cost curve and the market demand curve. If the market is unregulated, then the price is
Figure 16.2.1
-Refer to Figure 16.2.1. The figure shows the marginal private cost curve, the marginal social cost curve and the market demand curve. If the market is unregulated, then the price is
A) P₁.
B) P₄.
C) below P₁.
D) P₂.
E) P₃.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
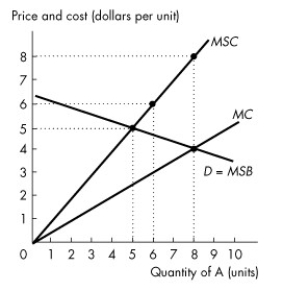 Figure 16.2.2
-Refer to Figure 16.2.2. This figure shows the demand curve, the marginal private cost curve and the marginal social cost curve of good A. Production of the 6th unit of output generates a marginal external
Figure 16.2.2
-Refer to Figure 16.2.2. This figure shows the demand curve, the marginal private cost curve and the marginal social cost curve of good A. Production of the 6th unit of output generates a marginal external
A) cost of $1.50.
B) cost of $3.
C) cost of $6.
D) benefit of $3.
E) benefit of $6.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most governments subsidize basic education because
A) there are external costs associated with well-educated citizens.
B) the marginal social benefit from education is greater than the marginal private benefit.
C) of the existence of private schools.
D) the marginal social cost of education is greater than the marginal private cost.
E) otherwise too many students will receive educations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
CoolU has solved its smoking problem by allocating each student 5 smoking permits a day, and allowing trading. This is an example of
A) cap-and-trade.
B) emission charges.
C) the Coase theorem.
D) a pollution tax.
E) a voucher.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One way to solve negative externality problems is
A) to organize a limited boycott of the products.
B) subsidize the externalities.
C) eliminate transactions costs when property rights are not legally established.
D) issue pollution permits to polluting firms and establish a system of cap-and-trade.
E) establish and enforce patents and copyrights.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Producing paper creates pollution. There is no externality in the consumption of paper. The efficient quantity of paper produced occurs when the
A) marginal social benefit from paper is equal to zero.
B) marginal social cost of the pollution from making paper is equal to zero.
C) marginal private cost of the pollution from making paper is equal to zero.
D) marginal private cost of paper equals the marginal private benefit from paper.
E) marginal social benefit from paper is equal to the marginal social cost of paper.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Smoking tobacco creates a ________ externality.
A) negative consumption
B) negative production
C) positive consumption
D) positive production
E) marginal
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 16.2.1
-Refer to Figure 16.2.1. The figure shows the marginal private cost curve, the marginal social cost curve and the market demand curve. To promote an efficient allocation of resources, the government could impose a constant per unit tax equal to
Figure 16.2.1
-Refer to Figure 16.2.1. The figure shows the marginal private cost curve, the marginal social cost curve and the market demand curve. To promote an efficient allocation of resources, the government could impose a constant per unit tax equal to
A) zero.
B) P₁.
C) P₃ - P₁.
D) P₄ - P₁.
E) P₃ - P₂.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
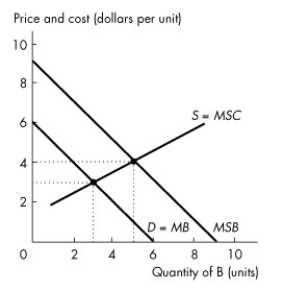 Figure 16.3.2
-In Figure 16.3.2. The figure shows the market for good B. Which of the following government policies creates an efficient outcome?
Figure 16.3.2
-In Figure 16.3.2. The figure shows the market for good B. Which of the following government policies creates an efficient outcome?
A) Tax the production of B by $3 per unit.
B) Tax the production of B by $4 per unit.
C) Provide vouchers for consumption of B of $1 per unit.
D) Provide vouchers for consumption of B of $3 per unit.
E) Provide vouchers for consumption of B of $4 per unit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
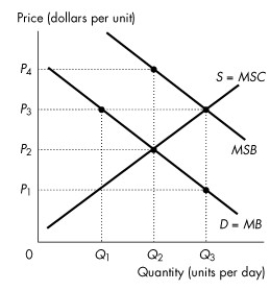 Figure 16.3.1
-Refer to Figure 16.3.1. The figure shows the marginal private benefit curve, the marginal social benefit curve, and the market supply curve. If production is left to the private market, then
Figure 16.3.1
-Refer to Figure 16.3.1. The figure shows the marginal private benefit curve, the marginal social benefit curve, and the market supply curve. If production is left to the private market, then
A) the quantity produced is less than the efficient quantity.
B) the quantity produced is greater than the efficient quantity.
C) price is greater than marginal social benefit quantity.
D) the marginal cost curve is horizontal.
E) the quantity produced is zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal private cost curve (MC) is a positively-sloped straight line starting at the origin. If marginal external cost increases as output increases, then the marginal social cost curve is a positively-sloped straight line
A) parallel to and above the MC curve.
B) parallel to and below the MC curve.
C) starting at the origin, above the MC curve, and with a slope greater than the MC curve.
D) starting at the origin, below the MC curve, and with a slope less than the MC curve.
E) starting above the origin, with a slope less than the MC curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 16.3.2
-Refer to Figure 16.3.2. The figure shows the market for good B. How many units of good B are produced and consumed in an unregulated market?
Figure 16.3.2
-Refer to Figure 16.3.2. The figure shows the market for good B. How many units of good B are produced and consumed in an unregulated market?
A) 0 units
B) 3 units
C) 5 units
D) 6 units
E) 9 units
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the absence of government intervention, a profit-maximizing firm producing a good with an external cost will produce a quantity at which
A) price is greater than marginal private cost.
B) price is less than marginal revenue.
C) price is less than marginal private cost.
D) price equals marginal private cost.
E) marginal revenue equals marginal social cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 116
Related Exams