A) a decrease in the quantity of money
B) an increase in expected future income
C) an increase in factor prices
D) an increase in the quantity of capital
E) an increase in expected future profits
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
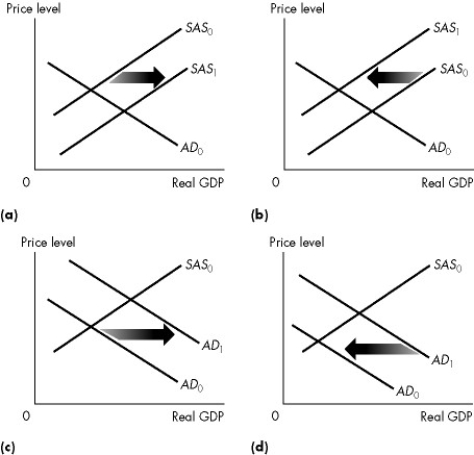 Figure 26.1.1
-Refer to Figure 26.1.1.Which graph illustrates what happens when factor prices decrease?
Figure 26.1.1
-Refer to Figure 26.1.1.Which graph illustrates what happens when factor prices decrease?
A) (a)
B) (b)
C) (c)
D) (d)
E) (a) and (b)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
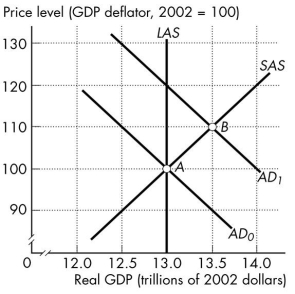 Figure 26.3.5
-Refer to Figure 26.3.5.If the aggregate demand curve is AD2,real GDP is
Figure 26.3.5
-Refer to Figure 26.3.5.If the aggregate demand curve is AD2,real GDP is
A) $13 trillion.
B) $13.5 trillion.
C) more than $13 trillion and less than $13.5 trillion.
D) less than $13 trillion.
E) 100
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the money wage rate falls,then
A) the AD curve shifts rightward.
B) firms hire less labour.
C) the LAS curve shifts rightward.
D) the SAS curve shifts rightward.
E) C and D.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
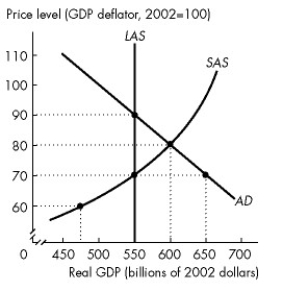 Figure 26.3.2
-Refer to Figure 26.3.2.As the economy of Mythlo automatically adjusts to long-run equilibrium,the
Figure 26.3.2
-Refer to Figure 26.3.2.As the economy of Mythlo automatically adjusts to long-run equilibrium,the
A) SAS curve shifts rightward.
B) AD curve shifts rightward.
C) SAS curve shifts leftward.
D) AD curve shifts leftward.
E) LAS curve shifts rightward.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 26.3.1
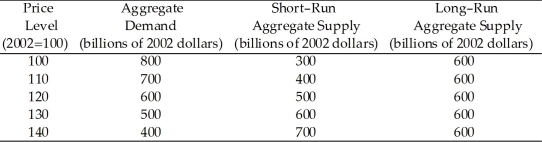 -Refer to Table 26.3.1.Consider the economy represented in the table.There is
-Refer to Table 26.3.1.Consider the economy represented in the table.There is
A) an inflationary gap equal to $100 billion.
B) an inflationary gap equal to $50 billion.
C) a recessionary gap equal to $50 billion.
D) a recessionary gap equal to $100 billion.
E) neither an inflationary nor a recessionary gap because the economy is at full employment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following question.
 Figure 26.3.4
-If real GDP is less than potential GDP,we would expect
Figure 26.3.4
-If real GDP is less than potential GDP,we would expect
A) the money wage rate to fall.
B) the money wage rate to rise.
C) potential GDP to increase.
D) potential GDP to decrease.
E) A and C.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An inflationary gap is the amount by which
A) potential GDP exceeds real GDP.
B) demand must increase to achieve full employment at a given price level.
C) supply must increase to achieve full employment at a given price level.
D) the price level must adjust to achieve full employment.
E) real GDP exceeds potential GDP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Everything else remaining the same,an increase in the expected inflation rate
A) shifts the aggregate demand curve rightward.
B) shifts the aggregate demand curve leftward.
C) shifts the short-run aggregate supply curve leftward.
D) shifts the long-run aggregate supply curve rightward.
E) creates a movement up along the aggregate demand curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Potential GDP is the level of real GDP at which
A) aggregate demand equals short-run aggregate supply.
B) there is full employment.
C) there is a recessionary gap.
D) there is over-full employment.
E) prices are sure to rise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
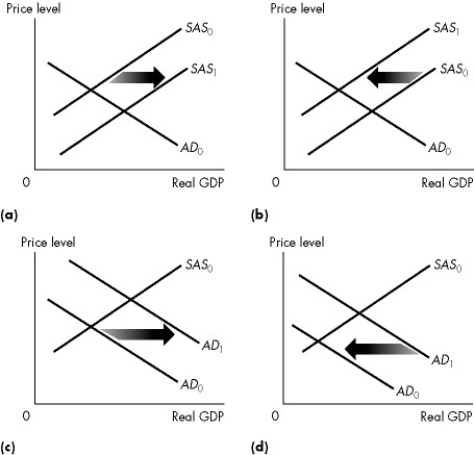 Figure 26.2.1
-Refer to Figure 26.2.1.Which graph illustrates what happens when expected future income increases?
Figure 26.2.1
-Refer to Figure 26.2.1.Which graph illustrates what happens when expected future income increases?
A) (a)
B) (b)
C) (c)
D) (d)
E) None of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 26.3.3
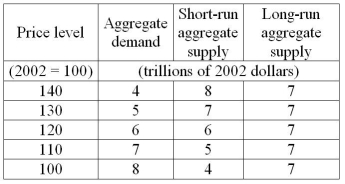 -Refer to Table 26.3.3.When the economy is at its short-run macroeconomic equilibrium,
-Refer to Table 26.3.3.When the economy is at its short-run macroeconomic equilibrium,
A) the unemployment rate is below its natural rate.
B) the unemployment rate is above its natural rate.
C) the money wage rate will rise.
D) the long-run aggregate supply curve will shift eventually shift leftward to return to full employment.
E) potential GDP will eventually increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 26.3.2
-Refer to Figure 26.3.2.Consider statements (1) and (2) and select the correct answer. (1) The actual unemployment rate exceeds the natural unemployment rate in the short run.
(2) SAS automatically shifts rightward as the economy adjusts to long-run equilibrium.
Figure 26.3.2
-Refer to Figure 26.3.2.Consider statements (1) and (2) and select the correct answer. (1) The actual unemployment rate exceeds the natural unemployment rate in the short run.
(2) SAS automatically shifts rightward as the economy adjusts to long-run equilibrium.
A) (1) is true; (2) is false.
B) (2) is true; (1) is false.
C) (1) and (2) are false.
D) (1) and (2) are true.
E) (1) is false; (2) is true if the LAS curve shifts rightward at the same time.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Complete the following sentence.Potential GDP
A) increases as the price level rises.
B) is the level of real GDP when unemployment is zero.
C) increases as the quantity of money in the economy increases.
D) does not vary with the price level.
E) never changes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Everything else remaining the same,an increase in the interest rate increases saving and
A) increases aggregate demand through the international substitution effect.
B) decreases aggregate demand through the international substitution effect.
C) increases aggregate demand through the intertemporal substitution effect.
D) decreases aggregate demand through the intertemporal substitution effect.
E) increases aggregate demand through the wealth effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 26.3.2
-Refer to Figure 26.3.2.If the economy of Mythlo automatically adjusts to long-run equilibrium,then
Figure 26.3.2
-Refer to Figure 26.3.2.If the economy of Mythlo automatically adjusts to long-run equilibrium,then
A) the price level rises to 90.
B) real GDP is $600 billion.
C) the actual unemployment rate exceeds the natural unemployment rate.
D) potential GDP decreases.
E) the SAS curve shifts rightward.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A ________ macroeconomist believes that the economy is self-regulating and always at full employment. A ________ macroeconomist believes the economy requires active help from fiscal policy and monetary policy to maintain full employment.
A) Keynesian; new Keynesian
B) classical; monetarist
C) classical; Keynesian
D) new classical; monetarist
E) monetarist; classical
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The quantity of real GDP demanded does not depend on decisions made by
A) foreigners.
B) households.
C) suppliers.
D) governments.
E) firms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If real GDP is greater than potential GDP,the economy is
A) not in short-run equilibrium.
B) in a recessionary equilibrium.
C) in an above full-employment equilibrium.
D) in a below full-employment equilibrium.
E) in long-run equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A vertical long-run aggregate supply curve indicates that
A) an increase in the price level will not expand an economy's output in the long run.
B) output rates greater than the long-run output rate are unattainable.
C) an increase in the price level will permit the economy to achieve a higher level of output.
D) an increase in the price level will increase technological change and economic growth.
E) the long-run aggregate supply curve never shifts.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 124
Related Exams