A) They do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition when growing in culture.
B) When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle.
C) They are not subject to cell cycle controls.
D) B and C only
E) A, B, and C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If mammalian cells receive a go-ahead signal at the G₁ checkpoint, they will
A) move directly into telophase.
B) complete the cycle and divide.
C) exit the cycle and switch to a nondividing state.
D) show a drop in MPF concentration.
E) complete cytokinesis and form new cell walls.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Vinblastine is a standard chemotherapeutic drug used to treat cancer. Because it interferes with the assembly of microtubules, its effectiveness must be related to
A) disruption of mitotic spindle formation.
B) inhibition of regulatory protein phosphorylation.
C) suppression of cyclin production.
D) myosin denaturation and inhibition of cleavage furrow formation.
E) inhibition of DNA synthesis.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on Figure 12.3.
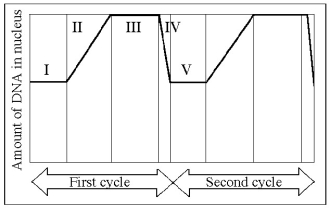 -Which number represents the point in the cell cycle during which the chromosomes are replicated?
-Which number represents the point in the cell cycle during which the chromosomes are replicated?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below.
The lettered circle in Figure 12.1 shows a diploid nucleus with four chromosomes. There are two pairs of homologous chromosomes, one long and the other short. One haploid set is symbolized as black and the other haploid set is gray. The chromosomes in the unlettered circle have not yet replicated. Choose the correct chromosomal conditions for the following stages.
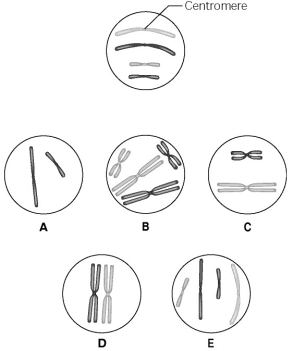 -Which term describes centromeres uncoupling, sister chromatids separating, and the two new chromosomes moving to opposite poles of the cell?
-Which term describes centromeres uncoupling, sister chromatids separating, and the two new chromosomes moving to opposite poles of the cell?
A) telophase
B) anaphase
C) prometaphase
D) metaphase
E) prophase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mutation results in a cell that no longer produces a normal protein kinase for the M phase checkpoint. Which of the following would likely be the immediate result of this mutation?
A) The cell would prematurely enter anaphase.
B) The cell would never leave metaphase.
C) The cell would never enter metaphase.
D) The cell would never enter prophase.
E) The cell would undergo normal mitosis, but fail to enter the next G₁ phase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. Those cells would have __________ picograms at the end of the S phase and __________ picograms at the end of G₂.
A) 8; 8
B) 8; 16
C) 16; 8
D) 16; 16
E) 12; 16
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order for anaphase to begin, which of the following must occur?
A) Chromatids must lose their kinetochores.
B) Cohesin must attach the sister chromatids to each other.
C) Cohesin must be cleaved enzymatically.
D) Kinetochores must attach to the metaphase plate.
E) Spindle microtubules must begin to depolymerize.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The drug cytochalasin B blocks the function of actin. Which of the following aspects of the cell cycle would be most disrupted by cytochalasin B?
A) spindle formation
B) spindle attachment to kinetochores
C) DNA synthesis
D) cell elongation during anaphase
E) cleavage furrow formation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An enzyme that attaches a phosphate group to another molecule is called a
A) phosphatase.
B) phosphorylase.
C) kinase.
D) cyclase.
E) ATPase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 12.2  -If there are 20 centromeres in a cell at anaphase, how many chromosomes are there in each daughter cell following cytokinesis?
-If there are 20 centromeres in a cell at anaphase, how many chromosomes are there in each daughter cell following cytokinesis?
A) 10
B) 20
C) 30
D) 40
E) 80
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNA is replicated at this time of the cell cycle:
A) G₀
B) G₁
C) S
D) G₂
E) M
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fibroblasts have receptors for this substance on their plasma membranes:
A) PDGF
B) MPF
C) protein kinase
D) cyclin
E) Cdk
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Movement of the chromosomes during anaphase would be most affected by a drug that
A) reduces cyclin concentrations.
B) increases cyclin concentrations.
C) prevents elongation of microtubules.
D) prevents shortening of microtubules.
E) prevents attachment of the microtubules to the kinetochore.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The centromere is a region in which
A) chromatids remain attached to one another until anaphase.
B) metaphase chromosomes become aligned at the metaphase plate.
C) chromosomes are grouped during telophase.
D) the nucleus is located prior to mitosis.
E) new spindle microtubules form at either end.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a protein maintained at constant levels throughout the cell cycle that requires cyclin to become catalytically active?
A) PDGF
B) MPF
C) protein kinase
D) cyclin
E) Cdk
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the data in Table 12.1 to answer the following questions. The data were obtained from a study of the length of time spent in each phase of the cell cycle by cells of three eukaryotic organisms designated beta, delta, and gamma. Table 12.1: Minutes Spent in Cell Cycle Phases -Of the following, the best conclusion concerning the difference between the S phases for beta and gamma is that
A) gamma contains more DNA than beta.
B) beta and gamma contain the same amount of DNA.
C) beta contains more RNA than gamma.
D) gamma contains 48 times more DNA and RNA than beta.
E) beta is a plant cell and gamma is an animal cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Besides the ability of some cancer cells to overproliferate, what else could logically result in a tumor?
A) metastasis
B) changes in the order of cell cycle stages
C) lack of appropriate cell death
D) inability to form spindles
E) inability of chromosomes to meet at the metaphase plate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The decline of MPF activity at the end of mitosis is due to
A) the destruction of the protein kinase Cdk.
B) decreased synthesis of cyclin.
C) the degradation of cyclin.
D) synthesis of DNA.
E) an increase in the cell's volume-to-genome ratio.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where do the microtubules of the spindle originate during mitosis in both plant and animal cells?
A) centromere
B) centrosome
C) centriole
D) chromatid
E) kinetochore
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 80
Related Exams